The difference between a switch and a router
Switches and routers are two common devices in computer networks, used to realize information transmission between local area networks (LAN) and wide area networks (WAN). Although they both play the role of network connectivity and data transmission, switches and routers have some significant differences in functionality and applications.
First of all, a switch is a multi-port device, mainly used to connect and manage various devices in the local network. It identifies different devices by using MAC addresses (Media Access Control Address) and forwards packets to the correct port based on the destination address. Switches enable fast and efficient data transmission within local area networks, providing high bandwidth and low latency performance. They maintain communication between devices by establishing a virtual connection table that is updated and maintained within the switch so that packets can be quickly forwarded to the target device.
In contrast, a router is a device used to connect different networks. It uses IP addresses (Internet Protocol addresses) to identify devices in different networks and forwards packets to the correct network based on the destination IP address. Routers are mainly responsible for selecting the best path between different networks to transmit data to achieve interconnection between different networks. It uses routing tables to maintain network topology and path information, and performs dynamic routing selection based on network protocols (such as OSPF and BGP). The router's feature set also includes Network Address Translation (NAT), security policies, firewalls, and more.
In addition to functional differences, switches and routers also work differently. The switch works at the data link layer and mainly relies on the physical address (MAC address) to forward data packets. It does not check the content of the IP message, but only forwards the packet to the correct port based on the destination MAC address. The router works at the network layer and needs to check the header and destination IP address of the IP packet, and select the best path for data forwarding based on the routing table. Routers can segment and isolate networks and provide more advanced and flexible network management functions.
In addition, switches and routers also have differences in application scenarios. Switches are mainly used to connect devices and quickly transmit large amounts of data within local area networks, such as offices, data centers, etc. Routers are mainly used to connect different networks to achieve Internet access and interconnection, such as home networks, enterprise networks, etc. In the networks of large enterprises or Internet service providers, switches and routers are usually used together to realize connections and data flow at different network levels.
To summarize, although switches and routers are both used to implement network connections and data transmission, they have many differences in functions, working principles, and application scenarios. Switches are mainly used for device connection and fast data transmission within the LAN, while routers are used to connect different networks and realize network interconnection. Understanding the differences between switches and routers can help us better understand network architecture and device selection to meet the requirements of different network needs.
The above is the detailed content of The difference between a switch and a router. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 How to forward WeChat voice messages How to forward WeChat voice messages
Feb 22, 2024 pm 05:30 PM
How to forward WeChat voice messages How to forward WeChat voice messages
Feb 22, 2024 pm 05:30 PM
Just convert your voice into notes and send them to others. Tutorial Applicable Model: iPhone13 System: iOS15.5 Version: WeChat 8.0.7 Analysis 1 First add the voice message to the collection, and then open the voice on the collection page. 2 Click the three dots in the upper right corner of the voice interface. 3 Then click Save as Notes in the list below. 4Finally, click Send to Friends on the note interface. Supplement: How to convert WeChat voice to text 1. First, long press the voice you want to convert on the WeChat chat interface. 2 Then click Convert to text in the pop-up window. 3Finally, the voice is converted into text. Summary/Notes WeChat voice messages cannot be forwarded directly and need to be converted into notes first.
 Complete Guide to Win11 Gamepad Connection
Jan 02, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Complete Guide to Win11 Gamepad Connection
Jan 02, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
After updating to the latest win11 system, many users are not sure how to connect the controller to play games. For this reason, we have brought you a detailed tutorial on connecting the win11 controller today. If you haven't completed the connection yet, let's take a look at how to operate it. . How to connect the controller in win11: 1. Click Start below and then enter Windows Settings to open the "Control Panel". 2. After entering, you can find "View devices and printers" to enter. 3. At this point you can see the information about the controller device and just make the connection. 4. After the connection is successful, a √ appears, and the connection is completed.
 How to forward WeChat voice? How to forward WeChat voice
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:00 AM
How to forward WeChat voice? How to forward WeChat voice
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:00 AM
WeChat, as a feature-rich social software, supports a variety of communication methods, including text, voice and video. Among them, voice messages provide users with a convenient way to communicate. However, WeChat does not natively support forwarding voice messages directly. But it can be achieved through other methods. There are many ways to forward WeChat voice. The following two common methods are provided: such as favorite forwarding or screen recording forwarding. How to forward WeChat voice? Method of forwarding WeChat voice The first method is to forward as a favorite. 1. Press and hold the WeChat voice message that needs to be forwarded until a multi-select menu appears. 2. Check the voice messages that need to be forwarded, and then click the [Collect] button at the bottom of the screen. 3. Enter the WeChat [Me] page, click the [Collect] option, and find the voice message you just collected. 4. Click Voice Cancel
 win7 printer cannot connect error code 0x0000011b
Dec 26, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
win7 printer cannot connect error code 0x0000011b
Dec 26, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
Many times we need to use a computer to connect to the printer for various printing operations, but sometimes some users will encounter the problem that win7 cannot connect to the printer 0x0000011b. The following is the specific solution. win7 cannot connect to the printer 0x0000011b1. Shortcut key "win+r", enter "regedit" 2. Find the following path "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Print" 3. Right-click to create a new value "DWORD (32-bit) value (D) and Set the value to 0. Name the new project "RpcAuthnLevelPri
 How to check network connection details and status on Windows 11
Sep 11, 2023 pm 02:17 PM
How to check network connection details and status on Windows 11
Sep 11, 2023 pm 02:17 PM
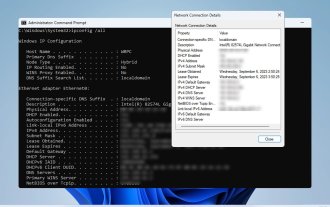
In order to make sure your network connection is working properly or to fix the problem, sometimes you need to check the network connection details on Windows 11. By doing this, you can view a variety of information including your IP address, MAC address, link speed, driver version, and more, and in this guide, we'll show you how to do that. How to find network connection details on Windows 11? 1. Use the "Settings" app and press the + key to open Windows Settings. WindowsI Next, navigate to Network & Internet in the left pane and select your network type. In our case, this is Ethernet. If you are using a wireless network, select a Wi-Fi network instead. At the bottom of the screen you should see
 How to connect keep body fat scale
Mar 07, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
How to connect keep body fat scale
Mar 07, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
How to connect the keep body fat scale? Keep has a specially designed body fat scale, but most users do not know how to connect the keep body fat scale. Next is the graphic tutorial on the connection method of the keep body fat scale that the editor brings to users. , interested users come and take a look! How to connect the keep body fat scale 1. First open the keep software, go to the main page, click [My] in the lower right corner, and select [Smart Hardware]; 2. Then on the My Smart Devices page, click the [Add Device] button in the middle; 3 , then select the device you want to add interface, select [Smart Body Fat/Weight Scale]; 4. Then on the device model selection page, click the [keep body fat scale] option; 5. Finally, in the interface shown below, finally [Add Now] at the bottom
 How to solve limited network connection in Windows 10
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:20 PM
How to solve limited network connection in Windows 10
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:20 PM
Solutions to Restricted Network Connections in Win10 With the rapid development of technology, the Internet has become an indispensable part of people's lives. However, sometimes we may encounter some problems when connecting to the Internet on computers using the Windows 10 operating system, one of which is restricted connections. In this case, we cannot access web pages, download files, or use network functions normally. So, is there any way to solve this problem? This article will introduce you to several common solutions. 1. Check the network connection settings. First, I
 How to fast forward on Weibo_Tutorial on fast forwarding on Weibo
Mar 30, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
How to fast forward on Weibo_Tutorial on fast forwarding on Weibo
Mar 30, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
1. First, enter Weibo on your mobile phone and click on the recommendation option. 2. Then select Weibo and click the share icon. 3. Then click on the fast forward option. 4. Finally, you can check that Weibo fast forwarding was sent successfully.




