 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 In-depth analysis of maven packaging plug-ins: understand common plug-in functions and usage methods
In-depth analysis of maven packaging plug-ins: understand common plug-in functions and usage methods
In-depth analysis of maven packaging plug-ins: understand common plug-in functions and usage methods

In the software development process, using Maven as a project build tool is a common practice. Maven provides a wealth of plug-ins to help developers simplify the process of project construction and management, of which packaging plug-ins are an important part. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of Maven's packaged plug-ins, understand the functions and usage of common plug-ins, and combine them with specific code examples to help developers better understand and apply these plug-ins.
1. Introduction to Maven packaging plug-in
Maven's packaging plug-in is a tool used to compile and package projects into different types of release packages or deployment packages. Common packaging plug-ins include maven-compiler-plugin, maven-resources-plugin, maven-war-plugin, maven-jar-pluginwait. Next we will conduct an in-depth analysis of these common plug-ins.
2. maven-compiler-plugin
maven-compiler-plugin is one of the most basic plug-ins in Maven, used to compile project source code. By configuring this plug-in, you can specify the compiler version, source code directory, object code directory, etc. The following is a sample configuration of maven-compiler-plugin:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>In the above configuration, we specified that the versions of both the source code and the target code are 1.8. Developers can flexibly configure these parameters according to project needs.
3. maven-resources-plugin
maven-resources-plugin is used to process project resource files, such as src/main/resources The resource files in the directory are copied to the output directory. This is useful during the packaging process to ensure that resource files are correctly included in the release package. The following is an example configuration of maven-resources-plugin:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<configuration>
<outputDirectory>${project.build.directory}/custom-resources</outputDirectory>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>In the above configuration, we output the resource files to ${project.build.directory}/custom -resources directory.
4. maven-war-plugin
maven-war-plugin is used to package projects into WAR packages, usually used for web application projects. This plug-in can configure Web resource directories, Web XML files, dependent libraries, etc. The following is a sample configuration of maven-war-plugin:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3</version>
<configuration>
<warSourceDirectory>src/main/webapp</warSourceDirectory>
<webXml>src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml</webXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>In the above configuration, we specified the location of the Web resource directory and the Web XML file.
5. maven-jar-plugin
maven-jar-plugin is used to package projects into JAR packages, usually used to package Java application projects. This plug-in can configure the entry class, dependent libraries, etc. of the JAR package. The following is an example configuration of maven-jar-plugin:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<configuration>
<archive>
<manifest>
<mainClass>com.example.Main</mainClass>
</manifest>
</archive>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build> In the above configuration, we specified the entry class of the JAR package as com.example.Main.
Conclusion
Through the in-depth analysis of this article, readers should understand the functions and usage of common packaging plug-ins in Maven, and master some specific configuration examples. In actual project development, flexible use of these plug-ins can help developers build and manage projects more efficiently. Hope this article is helpful to readers.
The above is the detailed content of In-depth analysis of maven packaging plug-ins: understand common plug-in functions and usage methods. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 PyCharm Beginner's Guide: Comprehensive understanding of plug-in installation!
Feb 25, 2024 pm 11:57 PM
PyCharm Beginner's Guide: Comprehensive understanding of plug-in installation!
Feb 25, 2024 pm 11:57 PM
PyCharm is a powerful and popular Python integrated development environment (IDE) that provides a wealth of functions and tools so that developers can write code more efficiently. The plug-in mechanism of PyCharm is a powerful tool for extending its functions. By installing different plug-ins, various functions and customized features can be added to PyCharm. Therefore, it is crucial for newbies to PyCharm to understand and be proficient in installing plug-ins. This article will give you a detailed introduction to the complete installation of PyCharm plug-in.
 What is the Chrome plug-in extension installation directory?
Mar 08, 2024 am 08:55 AM
What is the Chrome plug-in extension installation directory?
Mar 08, 2024 am 08:55 AM
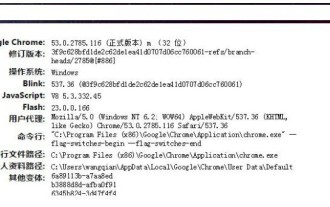
What is the Chrome plug-in extension installation directory? Under normal circumstances, the default installation directory of Chrome plug-in extensions is as follows: 1. The default installation directory location of chrome plug-ins in windowsxp: C:\DocumentsandSettings\username\LocalSettings\ApplicationData\Google\Chrome\UserData\Default\Extensions2. chrome in windows7 The default installation directory location of the plug-in: C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User
 Share three solutions to why Edge browser does not support this plug-in
Mar 13, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
Share three solutions to why Edge browser does not support this plug-in
Mar 13, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
When users use the Edge browser, they may add some plug-ins to meet more of their needs. But when adding a plug-in, it shows that this plug-in is not supported. How to solve this problem? Today, the editor will share with you three solutions. Come and try it. Method 1: Try using another browser. Method 2: The Flash Player on the browser may be out of date or missing, causing the plug-in to be unsupported. You can download the latest version from the official website. Method 3: Press the "Ctrl+Shift+Delete" keys at the same time. Click "Clear Data" and reopen the browser.
 Java Maven build tool advancement: optimizing compilation speed and dependency management
Apr 17, 2024 pm 06:42 PM
Java Maven build tool advancement: optimizing compilation speed and dependency management
Apr 17, 2024 pm 06:42 PM
Optimize Maven build tools: Optimize compilation speed: Take advantage of parallel compilation and incremental compilation. Optimize dependencies: Analyze dependency trees and use BOM (bill of materials) to manage transitive dependencies. Practical case: illustrate optimizing compilation speed and dependency management through examples.
 How to Install Java on Debian 12: A Step-by-Step Guide
Mar 20, 2024 pm 03:40 PM
How to Install Java on Debian 12: A Step-by-Step Guide
Mar 20, 2024 pm 03:40 PM
Java is a powerful programming language that enables users to create a wide range of applications, such as building games, creating web applications, and designing embedded systems. Debian12 is a powerful newly released Linux-based operating system that provides a stable and reliable foundation for Java applications to flourish. Together with Java and Debian systems you can open up a world of possibilities and innovations that can definitely help people a lot. This is only possible if Java is installed on your Debian system. In this guide, you will learn: How to install Java on Debian12 How to install Java on Debian12 How to remove Java from Debian12
 JUnit unit testing framework: advantages and limitations of using it
Apr 18, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
JUnit unit testing framework: advantages and limitations of using it
Apr 18, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
The JUnit unit testing framework is a widely used tool whose main advantages include automated testing, fast feedback, improved code quality, and portability. But it also has limitations, including limited scope, maintenance costs, dependencies, memory consumption, and lack of continuous integration support. For unit testing of Java applications, JUnit is a powerful framework that offers many benefits, but its limitations need to be considered when using it.
 Oracle API Usage Guide: Exploring Data Interface Technology
Mar 07, 2024 am 11:12 AM
Oracle API Usage Guide: Exploring Data Interface Technology
Mar 07, 2024 am 11:12 AM
Oracle is a world-renowned database management system provider, and its API (Application Programming Interface) is a powerful tool that helps developers easily interact and integrate with Oracle databases. In this article, we will delve into the Oracle API usage guide, show readers how to utilize data interface technology during the development process, and provide specific code examples. 1.Oracle
 Detailed explanation of VSCode functions: How does it help you improve work efficiency?
Mar 25, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
Detailed explanation of VSCode functions: How does it help you improve work efficiency?
Mar 25, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
Detailed explanation of VSCode functions: How does it help you improve work efficiency? With the continuous development of the software development industry, developers' pursuit of work efficiency and code quality have become important goals in their work. In this process, the choice of code editor becomes a key decision. Among many editors, Visual Studio Code (VSCode for short) is loved by the majority of developers for its powerful functions and flexible scalability. This article will introduce some functions of VSCode in detail and discuss



