Getting Started with MyBatis: Writing a Complete Program Example

MyBatis Getting Started: Writing a Complete Program Example
Introduction:
MyBatis is a very popular Java persistence layer framework. It can interact with the database and provides a flexible and efficient way to access the database. This article will introduce the basic usage and core functions of MyBatis through a complete program example.
- Environment setup
First of all, we need to introduce MyBatis related dependencies into the project. Add the following dependencies in the pom.xml file:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.7</version>
</dependency>
<!--其他依赖 -->
</dependencies>At the same time, we need to configure MyBatis related information, including database connection information, mapping files, etc. Create a configuration file named mybatis-config.xml in the src/main/resources directory and add the following content:
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_example"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="password"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/example/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>Note that the database connection information in the above configuration needs to be modified according to the actual situation.
- Write data model and mapping files
In order to demonstrate the functionality of MyBatis, we create a class named User and define the corresponding mapping in the UserMapper.xml file relation. Create the following two files in the src/main/java/com/example/model directory:
User.java:
package com.example.model;
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
// 省略构造函数、getter和setter方法
}UserMapper.xml:
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.UserMapper">
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="com.example.model.User">
INSERT INTO user (name, age) VALUES (#{name}, #{age})
</insert>
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.model.User">
SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>- Write Mapper interface
Create an interface named UserMapper in the src/main/java/com/example/mapper directory and define the corresponding methods, as shown below:
package com.example.mapper;
import com.example.model.User;
public interface UserMapper {
void insertUser(User user);
User getUserById(int id);
}- Write database operation code
Write database operation code in the main method, including obtaining SqlSessionFactory, creating SqlSession, performing database operations, etc. The specific code is as follows:
package com.example;
import com.example.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.example.model.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取MyBatis的配置文件流
Reader reader;
try {
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
// 创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
// 创建SqlSession
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 插入用户数据
User user = new User();
user.setName("Tom");
user.setAge(20);
userMapper.insertUser(user);
session.commit();
// 根据ID查询用户数据
user = userMapper.getUserById(user.getId());
System.out.println(user);
}
// 关闭输入流
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}- Example of running the program
Enter the project directory in the command line window and execute the following command to run the program:
mvn clean compile exec:java
After the program runs, a piece of user data will be inserted and the user's information will be queried based on the ID. If everything goes well, the console will output the user's information.
Summary:
Through the above complete program examples, we understand the basic usage and core functions of MyBatis. In actual development, we can write corresponding Mapper interfaces and mapping files according to specific needs, and create SqlSession through SqlSessionFactory for database operations. I believe that through learning and practice, we can better use MyBatis to build an efficient Java persistence layer.
The above is the detailed content of Getting Started with MyBatis: Writing a Complete Program Example. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 A Diffusion Model Tutorial Worth Your Time, from Purdue University
Apr 07, 2024 am 09:01 AM
A Diffusion Model Tutorial Worth Your Time, from Purdue University
Apr 07, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Diffusion can not only imitate better, but also "create". The diffusion model (DiffusionModel) is an image generation model. Compared with the well-known algorithms such as GAN and VAE in the field of AI, the diffusion model takes a different approach. Its main idea is a process of first adding noise to the image and then gradually denoising it. How to denoise and restore the original image is the core part of the algorithm. The final algorithm is able to generate an image from a random noisy image. In recent years, the phenomenal growth of generative AI has enabled many exciting applications in text-to-image generation, video generation, and more. The basic principle behind these generative tools is the concept of diffusion, a special sampling mechanism that overcomes the limitations of previous methods.
 Generate PPT with one click! Kimi: Let the 'PPT migrant workers' become popular first
Aug 01, 2024 pm 03:28 PM
Generate PPT with one click! Kimi: Let the 'PPT migrant workers' become popular first
Aug 01, 2024 pm 03:28 PM
Kimi: In just one sentence, in just ten seconds, a PPT will be ready. PPT is so annoying! To hold a meeting, you need to have a PPT; to write a weekly report, you need to have a PPT; to make an investment, you need to show a PPT; even when you accuse someone of cheating, you have to send a PPT. College is more like studying a PPT major. You watch PPT in class and do PPT after class. Perhaps, when Dennis Austin invented PPT 37 years ago, he did not expect that one day PPT would become so widespread. Talking about our hard experience of making PPT brings tears to our eyes. "It took three months to make a PPT of more than 20 pages, and I revised it dozens of times. I felt like vomiting when I saw the PPT." "At my peak, I did five PPTs a day, and even my breathing was PPT." If you have an impromptu meeting, you should do it
 Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Interpretation of MyBatis dynamic SQL tags: Detailed explanation of Set tag usage MyBatis is an excellent persistence layer framework. It provides a wealth of dynamic SQL tags and can flexibly construct database operation statements. Among them, the Set tag is used to generate the SET clause in the UPDATE statement, which is very commonly used in update operations. This article will explain in detail the usage of the Set tag in MyBatis and demonstrate its functionality through specific code examples. What is Set tag Set tag is used in MyBati
 All CVPR 2024 awards announced! Nearly 10,000 people attended the conference offline, and a Chinese researcher from Google won the best paper award
Jun 20, 2024 pm 05:43 PM
All CVPR 2024 awards announced! Nearly 10,000 people attended the conference offline, and a Chinese researcher from Google won the best paper award
Jun 20, 2024 pm 05:43 PM
In the early morning of June 20th, Beijing time, CVPR2024, the top international computer vision conference held in Seattle, officially announced the best paper and other awards. This year, a total of 10 papers won awards, including 2 best papers and 2 best student papers. In addition, there were 2 best paper nominations and 4 best student paper nominations. The top conference in the field of computer vision (CV) is CVPR, which attracts a large number of research institutions and universities every year. According to statistics, a total of 11,532 papers were submitted this year, and 2,719 were accepted, with an acceptance rate of 23.6%. According to Georgia Institute of Technology’s statistical analysis of CVPR2024 data, from the perspective of research topics, the largest number of papers is image and video synthesis and generation (Imageandvideosyn
 From bare metal to a large model with 70 billion parameters, here is a tutorial and ready-to-use scripts
Jul 24, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
From bare metal to a large model with 70 billion parameters, here is a tutorial and ready-to-use scripts
Jul 24, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
We know that LLM is trained on large-scale computer clusters using massive data. This site has introduced many methods and technologies used to assist and improve the LLM training process. Today, what we want to share is an article that goes deep into the underlying technology and introduces how to turn a bunch of "bare metals" without even an operating system into a computer cluster for training LLM. This article comes from Imbue, an AI startup that strives to achieve general intelligence by understanding how machines think. Of course, turning a bunch of "bare metal" without an operating system into a computer cluster for training LLM is not an easy process, full of exploration and trial and error, but Imbue finally successfully trained an LLM with 70 billion parameters. and in the process accumulate
 AI in use | AI created a life vlog of a girl living alone, which received tens of thousands of likes in 3 days
Aug 07, 2024 pm 10:53 PM
AI in use | AI created a life vlog of a girl living alone, which received tens of thousands of likes in 3 days
Aug 07, 2024 pm 10:53 PM
Editor of the Machine Power Report: Yang Wen The wave of artificial intelligence represented by large models and AIGC has been quietly changing the way we live and work, but most people still don’t know how to use it. Therefore, we have launched the "AI in Use" column to introduce in detail how to use AI through intuitive, interesting and concise artificial intelligence use cases and stimulate everyone's thinking. We also welcome readers to submit innovative, hands-on use cases. Video link: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2hX_i7li3RqdE4u016yGhQ Recently, the life vlog of a girl living alone became popular on Xiaohongshu. An illustration-style animation, coupled with a few healing words, can be easily picked up in just a few days.
 A must-read for technical beginners: Analysis of the difficulty levels of C language and Python
Mar 22, 2024 am 10:21 AM
A must-read for technical beginners: Analysis of the difficulty levels of C language and Python
Mar 22, 2024 am 10:21 AM
Title: A must-read for technical beginners: Difficulty analysis of C language and Python, requiring specific code examples In today's digital age, programming technology has become an increasingly important ability. Whether you want to work in fields such as software development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, or just learn programming out of interest, choosing a suitable programming language is the first step. Among many programming languages, C language and Python are two widely used programming languages, each with its own characteristics. This article will analyze the difficulty levels of C language and Python
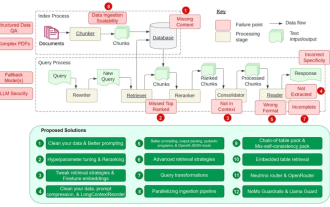 Counting down the 12 pain points of RAG, NVIDIA senior architect teaches solutions
Jul 11, 2024 pm 01:53 PM
Counting down the 12 pain points of RAG, NVIDIA senior architect teaches solutions
Jul 11, 2024 pm 01:53 PM
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is a technique that uses retrieval to boost language models. Specifically, before a language model generates an answer, it retrieves relevant information from an extensive document database and then uses this information to guide the generation process. This technology can greatly improve the accuracy and relevance of content, effectively alleviate the problem of hallucinations, increase the speed of knowledge update, and enhance the traceability of content generation. RAG is undoubtedly one of the most exciting areas of artificial intelligence research. For more details about RAG, please refer to the column article on this site "What are the new developments in RAG, which specializes in making up for the shortcomings of large models?" This review explains it clearly." But RAG is not perfect, and users often encounter some "pain points" when using it. Recently, NVIDIA’s advanced generative AI solution




