What is PQ3, Apple's new iMessage security protocol?
What is the PQ3 protocol?
Currently, communication security is measured by three security levels.
- Level 0: In this level, messages remain unencrypted.
- Level 1: Here messages are end-to-end encrypted, but there is no additional authentication or quantum security.
- Level 2: This includes authentication and quantum security, but they are limited to initial key establishment. This means that quantum security can only be provided if the conversation key material can never be compromised.
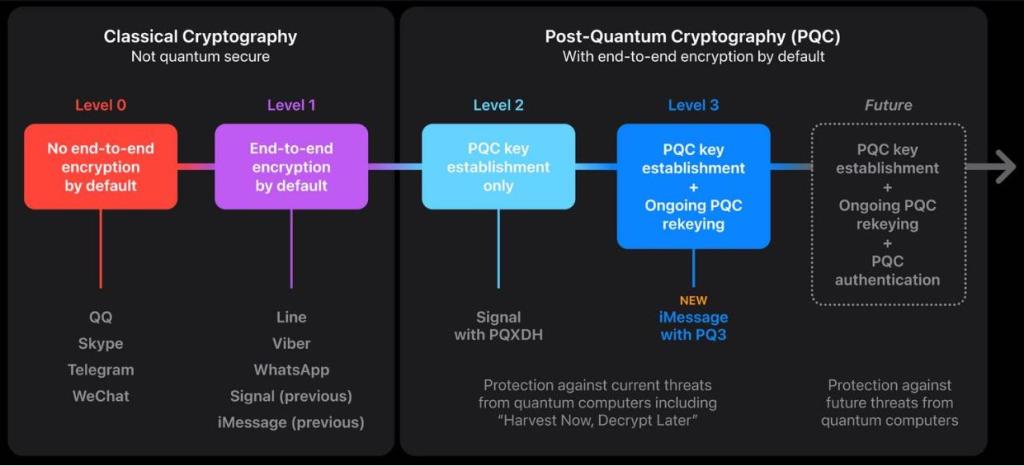
The new iMessage security protocol PQ3 is the first to be deemed to achieve what Apple calls “Level 3 Security” Messaging protocol. The protocol uses quantum encryption technology to secure key generation and message exchange. Level 3 PQC automatically restores the confidentiality of conversations even if keys are compromised. Therefore, PQ3 is claimed to surpass other widely used protocols in messaging applications.
Why is Apple moving to PQ3 protocol for iMessage?
Since its launch in 2011, Apple’s iMessage has supported end-to-end encryption and is enabled by default. Over the years, Apple has continuously improved its cryptography technology to ensure the security of user data. Although existing encryption algorithms are considered secure in the current environment, increased quantum computing capabilities may pose challenges to these algorithms as the technology develops. Therefore, in order to deal with potential threats in the future, the field of cryptography continues to conduct research and innovation to ensure the reliability and security of encryption technology.
Such a quantum computer does not exist today. However, a resourceful attacker can do their homework before arriving in the future. Such attackers can manage to collect large amounts of encrypted data and store it for future reference. While they can't decrypt any of the collected data today, they could use quantum computers to do so in the future. This attack scheme is called "Harvest now, decrypt later".
iMessage’s new security protocol, PQ3, is designed to protect users from “harvest now, decrypt later” attacks. Apple says that because PQ3 implements "Level 3" security, it ensures "initial key establishment and ongoing message exchange."
How does the PQ3 protocol work?
The new PQ3 protocol brings new post-quantum encryption keys to the public key set. Each device generates these public keys locally and then transmits them to Apple servers as part of the iMessage registration process. To do this, Apple uses the Modular Lattice-based Key Encapsulation Mechanism standard, or ML-KEM, which enables the sender device to obtain the recipient's public key and generate a post-quantum encryption key for the first message. This works even if the receiver is offline.
Apple then includes a periodic post-quantum rekeying mechanism in the conversation. This mechanism can self-heal from key compromise and protect future messages.
"In PQ3, the new key sent with the conversation is used to create a new message encryption key that cannot be calculated from past message encryption keys, thereby returning the conversation to a secure state , even if the previous key is extracted or compromised by an adversary."
Impressively, PQ3 is the first large-scale cryptographic messaging protocol to deploy this post-quantum rekeying property .
Advantages of the PQ3 protocol
For PQ3, Apple has not replaced or modified the existing algorithm. Instead, it rebuilt the iMessage encryption protocol from the ground up to provide the following benefits:
- Protect the entire communication from current and future adversaries.
- It limits the number of past and future messages that can be decrypted using a single compromised key. This mitigates the impact of critical intrusions.
- Amortize the message size to prevent any excessive overhead.
- PQ3 is based on a hybrid design that combines new post-quantum algorithms with current elliptic curve algorithms. This ensures that PQ3 will never be less secure than existing protocols.
- Formal verification methods to high-level security assurance.
PQ3 Protocol Availability in iMessage
Apple will gradually begin rolling out PQ3 for support of iMessage conversations with iOS 17.4, iPadOS 17.4, macOS 14.4, and watchOS 10.4. The giant said the latest beta versions of these software updates already feature this security protocol. Apple also confirmed that visionOS will not have a PQ3 protocol when it initially launches.
The above is the detailed content of What is PQ3, Apple's new iMessage security protocol?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 What is the use of Apple iOS 17.5's 'repair mode”?
May 06, 2024 pm 02:34 PM
What is the use of Apple iOS 17.5's 'repair mode”?
May 06, 2024 pm 02:34 PM
In order to use iPhones more safely, Apple has introduced the "Lost Device Protection" function since iOS 17.3. When we send our iPhone to an Apple repair center for repair, the engineer will ask us to turn off the "Find My iPhone" function. This step is to ensure that the user is confirmed as the owner of the device and that it is not lost or stolen. Although it is for safety reasons, a delay time is set for each operation to turn off this function, usually one hour. Therefore, some customers who are not familiar with such settings can only wait in the store for a short period of time before turning off "Search". My iPhone" feature. In order to solve this problem, Apple plans to add a "repair mode" in iOS 17.5. "dimension
 Apple iOS 17.5 RC version released: allows EU iPhone users to download apps from the website
May 08, 2024 am 09:30 AM
Apple iOS 17.5 RC version released: allows EU iPhone users to download apps from the website
May 08, 2024 am 09:30 AM
[Click here to go directly to the upgrade tutorial] According to news on May 8, Apple pushed the iOS17.5RC update (internal version number: 21F79) to iPhone users today. This update is 70 days away from the last release. How to upgrade iOS/iPadOS/watchOS/macOS development version and public beta version? To upgrade the iOS/iPadOS17 developer preview version and public beta version, you can refer to the experience shared by friends: Experience Post 1||Experience Post 2||Experience Post 3||Experience Post 4. Starting from the iOS/iPadOS 16.4 Developer Preview Beta 1, you need to register for the Apple Developer Program. After registration, open the system [Settings] [Software Update] to see the upgrade option. Please note that your iPhone or IP
 iOS 17 Tips: Notes supports adding jump links
Mar 27, 2024 pm 10:26 PM
iOS 17 Tips: Notes supports adding jump links
Mar 27, 2024 pm 10:26 PM
For friends who are accustomed to using iPhone memos to record things, this new improvement in iOS17 should not be missed: in memos, you can add links to jump to other memos. The operation method is as follows: 1. Tap in the memo input area and select "Add Link". 2. Enter the memo title keyword to search, and then select the memo you want to jump to to complete the addition. 3. Tap the link to jump.
 Should iPhone12 ios16 be updated to ios17.5beta3? How is the experience of ios17.5beta3?
Apr 25, 2024 pm 04:52 PM
Should iPhone12 ios16 be updated to ios17.5beta3? How is the experience of ios17.5beta3?
Apr 25, 2024 pm 04:52 PM
Practical sharing... As Apple continues to launch new iOS versions, many iPhone users are faced with the choice of whether to upgrade the system. The release of the latest iOS17.5Beta3 has attracted widespread attention, especially for iPhone12 users. Whether they should abandon the existing iOS16 and try the new Beta version has become a question worth discussing. Based on actual experience, this article analyzes the pros and cons of upgrading iPhone 12 to iOS 17.5 Beta 3 to provide a reference for the majority of Apple fans. First of all, we need to make it clear that Beta versions are usually used by developers or early adopters who are willing to take a certain risk. This means that compared to the official version, the Beta version may contain
 Does iPhone 15 need to be downgraded to iOS 17.3.1?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 04:10 PM
Does iPhone 15 need to be downgraded to iOS 17.3.1?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 04:10 PM
In the early morning of February 9, Apple pushed the official version of iOS 17.3.1 update to iPhone users! The size of the iOS17.3.1 official version installation package is about 281MB, and the internal version number is 21D61. The official version of iOS 17.3.1 is a simple minor repair, but its reputation has been very good since its release. Users say that this version is smooth, stable, and does not generate heat. It is suitable for elderly care and is recognized as the version with the best reputation. With the release of the new version, Apple closed the verification channel for the official version of iOS 17.3.1 on March 13. Generally speaking, after Apple closes the system verification channel, it is impossible to open it again. Surprisingly, Apple has quietly opened the iOS17.3.1 system verification channel recently. Query in iOS verification channel
 iOS 17 Tips: Forgot the password you just set? Can be unlocked with old password
Apr 08, 2024 pm 08:10 PM
iOS 17 Tips: Forgot the password you just set? Can be unlocked with old password
Apr 08, 2024 pm 08:10 PM
Some users will want to update their iPhone's lock screen password for security reasons. However, you may encounter a situation where you just set a new password and then forget the new password. To solve this problem, Apple has optimized the system in iOS17, iPadOS17 and newer versions. If the lock screen password is suddenly forgotten after changing the lock screen password, the user can still use the old password to unlock the device within 72 hours after changing the password. . The specific method is as follows: 1. In the lock screen interface, click "Forgot Password" in the lower right corner: 2. Select "Enter Previous Password", use the old password to unlock the device, and set a new password again according to the prompts. If you want to make the old password invalid: Make sure you have memorized the new password, if you need to make the old password invalid immediately
 What is the iOS 17 Stolen Device Protection feature? How to enable?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 04:04 PM
What is the iOS 17 Stolen Device Protection feature? How to enable?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 04:04 PM
In iOS 17.3 or later, you can enable Stolen Device Protection on your iPhone to add a layer of security to your device. After successful enablement, certain features and operations require additional security requirements before they can be used. How Stolen Device Protection works: Stolen Device Protection adds a layer of security when you take your iPhone away from a familiar location, like home or the office; it also helps protect your account if your iPhone is stolen. and personal information. For example, when this feature is turned on, when performing certain operations (such as accessing stored passwords and credit cards), the system will require a biometric authentication using Face ID or Touch ID, and password substitution or return cannot be used. retreat, thereby ensuring that only
 What should I do if the iPad camera cannot scan QR codes?
Mar 26, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
What should I do if the iPad camera cannot scan QR codes?
Mar 26, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
Previously, some iPads in the Aisi backend reported that they could not scan application QR codes after upgrading to iOS 17.4. This problem was caused by a vulnerability in the iOS 17.4 system. Last Friday, Apple pushed iOS17.4.1 and iPadOS17.4.1 updates to users. According to the instructions released by Apple, this update mainly contains important security updates and bug fixes. It is reported that iPadOS 17.4.1 has fixed the vulnerability in which the camera application cannot scan QR codes. This update is intended to improve system stability and security and provide users with a better experience. The launch of this update shows Apple’s emphasis on user data security and product quality, and is also a reflection of Apple’s continuous improvement of products and services. Users should update their




