Memory frequency depends on motherboard or CPU
Does the memory frequency depend on the motherboard or the CPU?
In the process of assembling a computer, memory frequency has always been a very important topic. Many people are troubled by some questions when purchasing memory. For example, is the frequency of the memory determined by the motherboard or the CPU? In order to solve this problem, we need to understand the impact of motherboard and CPU on memory frequency.
First of all, we need to clarify the concept of memory frequency. Memory frequency refers to the operating frequency of the memory chip, usually in MHz or GT/s. It represents the amount of data a memory module can transfer per second. A higher memory frequency means better memory module performance and faster data transfer speeds.
The impact of motherboard and CPU on memory frequency is different. The motherboard's impact on memory frequency is mainly reflected in two aspects: the memory frequency range supported by the motherboard's chipset and the motherboard's power supply capability. The chipset determines the highest frequency the motherboard can support, while the power supply determines the stability and reliability of the memory module.
Generally speaking, the motherboard's chipset will clearly indicate the supported memory frequency range in the product specifications. For example, a certain motherboard may support DDR4 memory with a frequency range of 2133MHz to 3200MHz. If you select memory that is outside the range supported by your motherboard, it may not function properly or may only run at the highest frequency supported by your motherboard.
In addition, the power supply capability of the motherboard will also have an impact on the stability of the memory module. Some high-frequency memory modules require a higher voltage supply to maintain stable operation. If the motherboard's power supply capability is insufficient, the memory module may not work properly or errors may occur frequently.
Compared with the motherboard, the CPU has a more direct impact on the memory frequency. Modern CPUs have integrated memory controllers that communicate directly with memory. Therefore, the CPU's memory controller determines the memory frequency range that the CPU can support.
Different models of CPUs also have limited support for memory frequencies. For example, a certain CPU may support DDR4 memory, but the maximum frequency can only reach 2666MHz. Even if the motherboard supports higher memory frequencies, the CPU still cannot exceed its own limits.
In addition, overclocking is also a factor that affects memory frequency. Some CPUs and motherboards support overclocking, and users can increase the memory frequency by adjusting the CPU multiplier and voltage. However, overclocking will also increase the power consumption and heat dissipation problems of the computer, so it needs to be treated with caution.
To sum up, the choice of memory frequency should take into account the motherboard and CPU factors. When purchasing memory, you must first understand the specifications of the motherboard and CPU to ensure that the frequency of the memory is within the support range of both. At the same time, you should also pay attention to the power supply capability of the motherboard to ensure that it can provide sufficient voltage for the memory.
Finally, if users have overclocking needs, they also need to consider whether the CPU and motherboard support overclocking. Overclocking requires higher power supply and cooling capabilities, and users should be prepared accordingly when installing overclocked memory.
In short, the choice of memory frequency is not only affected by the motherboard's support range and power supply capabilities, but also limited by the CPU's memory controller. These factors should be carefully considered when purchasing memory to ensure the stability and performance of the memory.
The above is the detailed content of Memory frequency depends on motherboard or CPU. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
1. First, we right-click the blank space of the taskbar and select the [Task Manager] option, or right-click the start logo, and then select the [Task Manager] option. 2. In the opened Task Manager interface, we click the [Services] tab on the far right. 3. In the opened [Service] tab, click the [Open Service] option below. 4. In the [Services] window that opens, right-click the [InternetConnectionSharing(ICS)] service, and then select the [Properties] option. 5. In the properties window that opens, change [Open with] to [Disabled], click [Apply] and then click [OK]. 6. Click the start logo, then click the shutdown button, select [Restart], and complete the computer restart.
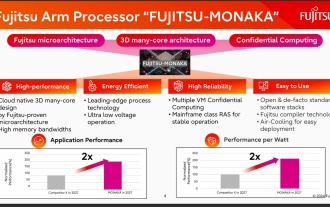 144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
According to news from this website on July 28, foreign media TechRader reported that Fujitsu introduced in detail the FUJITSU-MONAKA (hereinafter referred to as MONAKA) processor planned to be shipped in 2027. MONAKACPU is based on the "cloud native 3D many-core" architecture and adopts the Arm instruction set. It is oriented to the data center, edge and telecommunications fields. It is suitable for AI computing and can realize mainframe-level RAS1. Fujitsu said that MONAKA will achieve a leap in energy efficiency and performance: thanks to technologies such as ultra-low voltage (ULV) technology, the CPU can achieve 2 times the energy efficiency of competing products in 2027, and cooling does not require water cooling; in addition, the application performance of the processor It can also reach twice as much as your opponent. In terms of instructions, MONAKA is equipped with vector
 'Valkyrie' joins hands with 'Silver', Biostar displays two Intel Z890 motherboards
Jun 09, 2024 am 11:14 AM
'Valkyrie' joins hands with 'Silver', Biostar displays two Intel Z890 motherboards
Jun 09, 2024 am 11:14 AM
According to news from this website on June 5, according to foreign media TechPowerUp, Biostar exhibited two LGA1851 socket Z890 motherboards supporting Intel's next-generation desktop CPU at the 2024 Taipei International Computer Show. These two motherboards are the flagship Z890VALKYRIE "Valkyrie" and the mainstream Z890A-SILVER. Both are ATX specifications and do not have pre-installed wireless network cards. This website summarizes the detailed parameters of the two motherboards as follows: Z890VALKYRIE continues the gold-powder double-wing elements of the "Valkyrie" family, uses a 23-phase power supply design, and is equipped with 4 DDR5 memory slots. ▲Image source TechPowerUp, the same as below. This motherboard provides 3 alloy-reinforced PCIeG
 Close-up of LGA-1851 socket, Guangji showcases new embedded motherboard: supports Intel Core Ultra 200 series processors
Apr 11, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Close-up of LGA-1851 socket, Guangji showcases new embedded motherboard: supports Intel Core Ultra 200 series processors
Apr 11, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
According to the news from this site on April 11, according to the German technology media ComputeBase, Guangji Technology attended the EmbeddedWorld2024 conference and publicly demonstrated a motherboard using the LGA-1851 slot for the first time. This motherboard is compatible with Intel Meteor Lake processors and is mainly used in embedded systems. The media took an in-depth look and shared multiple photos, confirming that LGA-1851 is the same size as Intel’s existing LGA-1700 socket. The relevant pictures attached to this site are as follows: Not compatible with CPU, but compatible with CPU coolers but not LGA-1851 socket 151 additional pins were added and the CPU locking system was adjusted, so it is not compatible with existing LGA-1700 socket processors. But because LG
 Leak reveals key specs of Intel Arrow Lake-U, -H, -HX and -S
Jun 15, 2024 pm 09:49 PM
Leak reveals key specs of Intel Arrow Lake-U, -H, -HX and -S
Jun 15, 2024 pm 09:49 PM
IntelArrowLakeisexpectedtobebasedonthesameprocessorarchitectureasLunarLake,meaningthatIntel'sbrandnewLionCoveperformancecoreswillbecombinedwiththeeconomicalSkymontefficiencycores.WhileLunarLakeisonlyavailableasava
 AM4 refuses to die, news says AMD will launch Ryzen 9 5900XT/7 5800XT: clocked at up to 4.8GHz
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:43 PM
AM4 refuses to die, news says AMD will launch Ryzen 9 5900XT/7 5800XT: clocked at up to 4.8GHz
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:43 PM
According to news from this website on June 1st, the source @CodeCommando tweeted today, sharing some screenshots of AMD’s upcoming presentation documents at the Computex2024 event. The content of the tweet was “AM4 will never die”, and the accompanying picture showed two new Ryzen5000XT series processors. The screenshots show the following two products: Ryzen 95900 Ryzen75800XT It is a faster variant of AMD's existing Ryzen75800X processor. Both processors are clocked up to 4.8G
 Sapphire launches NITRO+ B650I WIFI ultra-platinum motherboard, 1679 yuan
Apr 22, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
Sapphire launches NITRO+ B650I WIFI ultra-platinum motherboard, 1679 yuan
Apr 22, 2024 pm 01:58 PM
According to news from this site on April 22, Sapphire (Sapphire Technology) recently launched the NITRO+B650IWIFI ultra-platinum motherboard. The e-commerce platform sells it for 1,689 yuan. You can get a 10 yuan coupon, and the price is 1,679 yuan. According to inquiries on this site, Sapphire released a NITRO+B550I motherboard in 2021, and this new product can be regarded as the successor of that product. Sapphire NITRO+B650IWIFI adopts 8-layer PCB+8-phase digital power supply design, uses PowerStage70ADr.MOS, and supports DDR5-6000+ memory overclocking. In terms of storage, it is equipped with 2 Gen4x4 M.2 interfaces and 4 SATA3 interfaces. This motherboard is covered with MOS power supply and front M.2 bay.
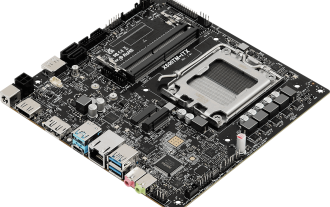 'The world's first Thin Mini ITX motherboard supporting AM5', ASRock releases X600TM-ITX: up to 96GB memory, 4 external monitors
Jul 27, 2024 am 10:37 AM
'The world's first Thin Mini ITX motherboard supporting AM5', ASRock releases X600TM-ITX: up to 96GB memory, 4 external monitors
Jul 27, 2024 am 10:37 AM
According to news from this site on July 27, ASRock recently announced the launch of the X600TM-ITX motherboard, claiming to be "the world's first ThinMiniITX motherboard that supports AM5". The motherboard size is 17*17 cm and supports AMD Ryzen 9000/8000/7000 series processing. device. ASRock said that this motherboard is suitable for products such as mini computers, all-in-one computers, smart mirrors, educational tools, and home theater computers, and can handle various tasks in daily offices, presentations, and work. X600TM-ITX supports the latest AM5 processor, which improves performance by up to 1.33 times compared to the previous generation. This means faster speeds, increased multitasking capabilities, better gaming experiences, faster data processing, and




