How to use return statement in JavaScript

How to use return in JavaScript requires specific code examples
In JavaScript, return is a very important keyword, it is usually used to return values in functions or end the execution of the function. The return statement is used to return a value to the caller of the function and terminate the execution of the function.
The return statement can be used anywhere in a function and can return any JavaScript data type, including numbers, strings, booleans, objects, etc. When the return statement in a function is executed, the function immediately stops execution and returns the specified value. The following are some specific usage methods and sample codes about return:
- Return numeric value:
function calculateSum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
let sum = calculateSum(5, 3);
console.log(sum); // 输出 8The above code defines a function calculateSum, It takes two parameters a and b and returns their sum. When calling the function, the returned value is assigned to the variable sum, and the result is printed through console.log.
- Return string value:
function generateMessage(name) {
return "Hello, " + name + "! Welcome to our website.";
}
let message = generateMessage("John");
console.log(message); // 输出 "Hello, John! Welcome to our website."In this example, the function generateMessage accepts a parameter name, and in the character Returns a string with a welcome message. After calling the function, the returned value is assigned to the variable message and output through console.log.
- Returns a Boolean value:
function isEven(number) {
if (number % 2 === 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
let result = isEven(6);
console.log(result); // 输出 true In the above example, the function isEven accepts a parameter number and determines whether is an even number. If it is an even number, return true, otherwise return false. By calling the function, assign the result to the result variable and output it.
- Return object:
function createPerson(name, age, gender) {
return {
name: name,
age: age,
gender: gender
};
}
let person = createPerson("Alice", 25, "female");
console.log(person); // 输出 { name: 'Alice', age: 25, gender: 'female' }In this example, the function createPerson accepts three parameters and is used to create an object containing name, age and gender. properties object. By calling the function, assign the returned object to person and then output it.
- End the execution of the function early:
function checkInput(value) {
if (value === "") {
return;
}
// 执行其他逻辑
console.log("Input value is not empty!");
}
checkInput(""); // 没有输出
checkInput("Hello"); // 输出 "Input value is not empty!"In this example, if the value of value is an empty string, it will be returned directly. Subsequent logic will be executed. You can see the difference in output results by passing in different parameters of empty strings and non-empty strings when calling the function.
Through the above examples, we can see how to use the return statement and its importance in JavaScript functions. It returns a value to the caller of the function and terminates the function execution when appropriate. Combined with function parameters and logical processing, we can write more flexible and powerful JavaScript functions.
The above is the detailed content of How to use return statement in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
Tomato Novel is a very popular novel reading software. We often have new novels and comics to read in Tomato Novel. Every novel and comic is very interesting. Many friends also want to write novels. Earn pocket money and edit the content of the novel you want to write into text. So how do we write the novel in it? My friends don’t know, so let’s go to this site together. Let’s take some time to look at an introduction to how to write a novel. Share the Tomato novel tutorial on how to write a novel. 1. First open the Tomato free novel app on your mobile phone and click on Personal Center - Writer Center. 2. Jump to the Tomato Writer Assistant page - click on Create a new book at the end of the novel.
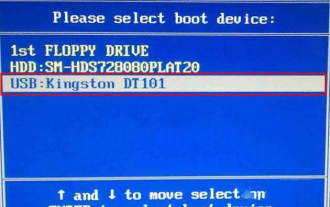 How to enter bios on Colorful motherboard? Teach you two methods
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
How to enter bios on Colorful motherboard? Teach you two methods
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Colorful motherboards enjoy high popularity and market share in the Chinese domestic market, but some users of Colorful motherboards still don’t know how to enter the bios for settings? In response to this situation, the editor has specially brought you two methods to enter the colorful motherboard bios. Come and try it! Method 1: Use the U disk startup shortcut key to directly enter the U disk installation system. The shortcut key for the Colorful motherboard to start the U disk with one click is ESC or F11. First, use Black Shark Installation Master to create a Black Shark U disk boot disk, and then turn on the computer. When you see the startup screen, continuously press the ESC or F11 key on the keyboard to enter a window for sequential selection of startup items. Move the cursor to the place where "USB" is displayed, and then
 How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
Unfortunately, people often delete certain contacts accidentally for some reasons. WeChat is a widely used social software. To help users solve this problem, this article will introduce how to retrieve deleted contacts in a simple way. 1. Understand the WeChat contact deletion mechanism. This provides us with the possibility to retrieve deleted contacts. The contact deletion mechanism in WeChat removes them from the address book, but does not delete them completely. 2. Use WeChat’s built-in “Contact Book Recovery” function. WeChat provides “Contact Book Recovery” to save time and energy. Users can quickly retrieve previously deleted contacts through this function. 3. Enter the WeChat settings page and click the lower right corner, open the WeChat application "Me" and click the settings icon in the upper right corner to enter the settings page.
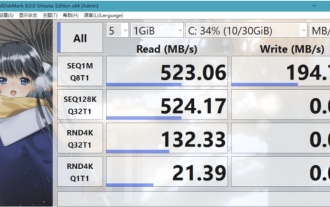 What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark is a small HDD benchmark tool for hard drives that quickly measures sequential and random read/write speeds. Next, let the editor introduce CrystalDiskMark to you and how to use crystaldiskmark~ 1. Introduction to CrystalDiskMark CrystalDiskMark is a widely used disk performance testing tool used to evaluate the read and write speed and performance of mechanical hard drives and solid-state drives (SSD). Random I/O performance. It is a free Windows application and provides a user-friendly interface and various test modes to evaluate different aspects of hard drive performance and is widely used in hardware reviews
 How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000 is a software that can listen to music resources at any time. It brings you all kinds of music with lossless sound quality. The enhanced version of the music player allows you to get a more comprehensive and comfortable music experience. Its design concept is to play the advanced audio on the computer The device is transplanted to mobile phones to provide a more convenient and efficient music playback experience. The interface design is simple, clear and easy to use. It adopts a minimalist design style without too many decorations and cumbersome operations to get started quickly. It also supports a variety of skins and Theme, personalize settings according to your own preferences, and create an exclusive music player that supports the playback of multiple audio formats. It also supports the audio gain function to adjust the volume according to your own hearing conditions to avoid hearing damage caused by excessive volume. Next, let me help you
 How to set font size on mobile phone (easily adjust font size on mobile phone)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
How to set font size on mobile phone (easily adjust font size on mobile phone)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Setting font size has become an important personalization requirement as mobile phones become an important tool in people's daily lives. In order to meet the needs of different users, this article will introduce how to improve the mobile phone use experience and adjust the font size of the mobile phone through simple operations. Why do you need to adjust the font size of your mobile phone - Adjusting the font size can make the text clearer and easier to read - Suitable for the reading needs of users of different ages - Convenient for users with poor vision to use the font size setting function of the mobile phone system - How to enter the system settings interface - In Find and enter the "Display" option in the settings interface - find the "Font Size" option and adjust it. Adjust the font size with a third-party application - download and install an application that supports font size adjustment - open the application and enter the relevant settings interface - according to the individual
 How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox, as an email address widely used by Chinese netizens, has always won the trust of users with its stable and efficient services. NetEase Mailbox Master is an email software specially created for mobile phone users. It greatly simplifies the process of sending and receiving emails and makes our email processing more convenient. So how to use NetEase Mailbox Master, and what specific functions it has. Below, the editor of this site will give you a detailed introduction, hoping to help you! First, you can search and download the NetEase Mailbox Master app in the mobile app store. Search for "NetEase Mailbox Master" in App Store or Baidu Mobile Assistant, and then follow the prompts to install it. After the download and installation is completed, we open the NetEase email account and log in. The login interface is as shown below
 How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Cloud storage has become an indispensable part of our daily life and work nowadays. As one of the leading cloud storage services in China, Baidu Netdisk has won the favor of a large number of users with its powerful storage functions, efficient transmission speed and convenient operation experience. And whether you want to back up important files, share information, watch videos online, or listen to music, Baidu Cloud Disk can meet your needs. However, many users may not understand the specific use method of Baidu Netdisk app, so this tutorial will introduce in detail how to use Baidu Netdisk app. Users who are still confused can follow this article to learn more. ! How to use Baidu Cloud Network Disk: 1. Installation First, when downloading and installing Baidu Cloud software, please select the custom installation option.




