Upload multiple images in PHP
php Xiaobian Yuzai will introduce you how to upload multiple images in PHP. In website development, it is often necessary to implement the function of batch uploading images. In order to improve user experience and efficiency, uploading multiple images is a common requirement. PHP provides a wealth of functions and technologies to implement this function, including using forms, processing uploaded files, processing multiple files in a loop, etc. Through the guidance of this article, you will learn how to easily upload multiple images in PHP to add more interactive and creative elements to your website.
To make this possible, we need to specify the form action in our HTML file or section depending on how you structure your code base, and then use a built-in function to handle that action.
In this article, we will learn how to upload multiple images in PHP, which provides us with the ability to specify the required files from a form input, process all user-selected files, and upload or move to the desired location context.
Learn about form operations and $_FILES
for multiple file uploads in PHP
When the user puts any input into the HTML form, we use the POST method to send any input (from text to file) to the server side where our PHP application lives.
<fORM method='post' action='' enctype='multipart/form-data'>
enctype='multipart/form-data' part specifies the encoding method of the form data, which is required when we use file upload in the form.
For file upload we need to enter the type file and specify the name (can be any name you decide) for the file.
<input type="file" name="file" id="file">
For multiple file uploads, we still need the input type file, but now with a different specified name file[] and the added attribute multiple. Adding [] indicates that the input field can handle multiple files.
<input type="file" name="files[]" multiple/>
On the server side, the global variable $_FILES is an associative array that contains files uploaded via the Http POST method, allowing us to handle the files appropriately.
<?php $_FILES["files"]
Upload multiple images in PHP using move_uploaded_file()
Now that we understand the basics, we need to upload multiple files. Let's create a PHP form to upload multiple images.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Multiple Image Upload</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" name="formUploadFile">
<label>Select image(s) to upload:</label>
<input type="file" name="files[]" multiple="multiple" />
<input type="submit" value="Upload File" name="imgSubmit" />
</form>
<?php
if (isset($_POST["imgSubmit"])) {
$Upload multiple images in PHPs = [];
$uploadedFiles = [];
$extension = array("jpeg", "jpg", "png");
$UploadFolder = "images";
$counter = 0;
foreach ($_FILES["files"]["tmp_name"] as $key => $tmp_name) {
$temp = $_FILES["files"]["tmp_name"][$key];
$name = $_FILES["files"]["name"][$key];
if (empty($temp)) {
break;
}
$counter++;
$UploadOk = true;
$ext = pathinfo($name, PATHINFO_EXTENSION);
if (in_array($ext, $extension) == false) {
$UploadOk = false;
array_push($Upload multiple images in PHPs, $name . " isn't an image.");
}
if ($UploadOk == true) {
move_uploaded_file($temp, $UploadFolder . "/" . $name);
array_push($uploadedFiles, $name);
}
}
if ($counter > 0) {
if (count($Upload multiple images in PHPs) > 0) {
echo "<b>Errors:</b>";
echo "<br/><ul>";
foreach ($Upload multiple images in PHPs as $Upload multiple images in PHP) {
echo "<li>" . $Upload multiple images in PHP . "</li>";
}
echo "</ul><br/>";
}
if (count($uploadedFiles) > 0) {
echo "<b>Uploaded Files:</b>";
echo "<br/><ul>";
foreach ($uploadedFiles as $fileName) {
echo "<li>" . $fileName . "</li>";
}
echo "</ul><br/>";
echo count($uploadedFiles) . " iamge(s) are successfully uploaded.";
}
} else {
echo "Please, Select image(s) to upload.";
}
}
?>
</body>
</html>
Check whether the $_POST[] variable is set using the isset() function, initialize important variables, and set the extension required for file upload.
if (isset($_POST["imgSubmit"])) {
$Upload multiple images in PHPs = [];
$uploadedFiles = [];
$extension = array("jpeg", "jpg", "png");
$UploadFolder = "images";
After that we loop through the multiple images that have been processed via the $_FILES[] variable and then check the extension using pathinfo() and if true we move the image to the specified Folder $UploadFolder Use the move_uploaded_file() function and push the name of the image to the $uploadedFiles variable.
foreach ($_FILES["files"]["tmp_name"] as $key => $tmp_name) {
$temp = $_FILES["files"]["tmp_name"][$key];
$name = $_FILES["files"]["name"][$key];
if (empty($temp)) {
break;
}
$counter++;
$UploadOk = true;
$ext = pathinfo($name, PATHINFO_EXTENSION);
if (in_array($ext, $extension) == false) {
$UploadOk = false;
array_push($Upload multiple images in PHPs, $name . " isn't an image.");
}
if ($UploadOk == true) {
move_uploaded_file($temp, $UploadFolder . "/" . $name);
array_push($uploadedFiles, $name);
}
}
Finally, we show the existing Upload multiple images in PHPs and the uploaded files.
if ($counter > 0) {
if (count($Upload multiple images in PHPs) > 0) {
echo "<b>Errors:</b>";
echo "<br/><ul>";
foreach ($Upload multiple images in PHPs as $Upload multiple images in PHP) {
echo "<li>" . $Upload multiple images in PHP . "</li>";
}
echo "</ul><br/>";
}
if (count($uploadedFiles) > 0) {
echo "<b>Uploaded Files:</b>";
echo "<br/><ul>";
foreach ($uploadedFiles as $fileName) {
echo "<li>" . $fileName . "</li>";
}
echo "</ul><br/>";
echo count($uploadedFiles) . " image(s) are successfully uploaded.";
}
} else {
echo "Please, Select image(s) to upload.";
}
PHP file served to the browser.
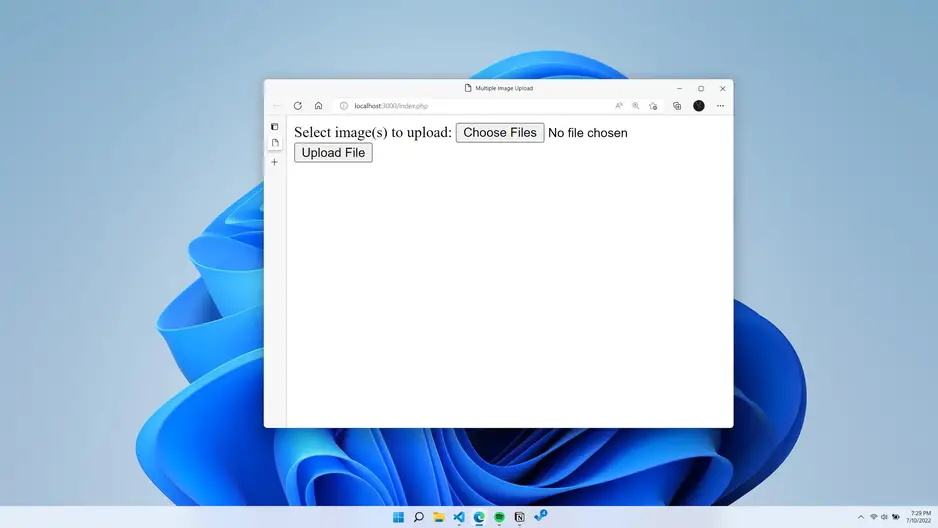
Select an image and upload the image.

Then, the uploaded file is displayed.

Uploaded image:

If the file you select is not an image, an Upload multiple images in PHP will appear.

The above is the detailed content of Upload multiple images in PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 PHP format rows to CSV and write file pointer
Mar 22, 2024 am 09:00 AM
PHP format rows to CSV and write file pointer
Mar 22, 2024 am 09:00 AM
This article will explain in detail how PHP formats rows into CSV and writes file pointers. I think it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. Format rows to CSV and write to file pointer Step 1: Open file pointer $file=fopen("path/to/file.csv","w"); Step 2: Convert rows to CSV string using fputcsv( ) function converts rows to CSV strings. The function accepts the following parameters: $file: file pointer $fields: CSV fields as an array $delimiter: field delimiter (optional) $enclosure: field quotes (
 PHP changes current umask
Mar 22, 2024 am 08:41 AM
PHP changes current umask
Mar 22, 2024 am 08:41 AM
This article will explain in detail about changing the current umask in PHP. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. Overview of PHP changing current umask umask is a php function used to set the default file permissions for newly created files and directories. It accepts one argument, which is an octal number representing the permission to block. For example, to prevent write permission on newly created files, you would use 002. Methods of changing umask There are two ways to change the current umask in PHP: Using the umask() function: The umask() function directly changes the current umask. Its syntax is: intumas
 PHP creates a file with a unique file name
Mar 21, 2024 am 11:22 AM
PHP creates a file with a unique file name
Mar 21, 2024 am 11:22 AM
This article will explain in detail how to create a file with a unique file name in PHP. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. Creating files with unique file names in PHP Introduction Creating files with unique file names in PHP is essential for organizing and managing your file system. Unique file names ensure that existing files are not overwritten and make it easier to find and retrieve specific files. This guide will cover several ways to generate unique filenames in PHP. Method 1: Use the uniqid() function The uniqid() function generates a unique string based on the current time and microseconds. This string can be used as the basis for the file name.
 PHP calculates MD5 hash of file
Mar 21, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
PHP calculates MD5 hash of file
Mar 21, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
This article will explain in detail about PHP calculating the MD5 hash of files. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. PHP calculates the MD5 hash of a file MD5 (MessageDigest5) is a one-way encryption algorithm that converts messages of arbitrary length into a fixed-length 128-bit hash value. It is widely used to ensure file integrity, verify data authenticity and create digital signatures. Calculating the MD5 hash of a file in PHP PHP provides multiple methods to calculate the MD5 hash of a file: Use the md5_file() function. The md5_file() function directly calculates the MD5 hash value of the file and returns a 32-character
 PHP returns an array with key values flipped
Mar 21, 2024 pm 02:10 PM
PHP returns an array with key values flipped
Mar 21, 2024 pm 02:10 PM
This article will explain in detail how PHP returns an array after key value flipping. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. PHP Key Value Flip Array Key value flip is an operation on an array that swaps the keys and values in the array to generate a new array with the original key as the value and the original value as the key. Implementation method In PHP, you can perform key-value flipping of an array through the following methods: array_flip() function: The array_flip() function is specially used for key-value flipping operations. It receives an array as argument and returns a new array with the keys and values swapped. $original_array=[
 PHP truncate file to given length
Mar 21, 2024 am 11:42 AM
PHP truncate file to given length
Mar 21, 2024 am 11:42 AM
This article will explain in detail how PHP truncates files to a given length. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. Introduction to PHP file truncation The file_put_contents() function in PHP can be used to truncate files to a specified length. Truncation means removing part of the end of a file, thereby shortening the file length. Syntax file_put_contents($filename,$data,SEEK_SET,$offset);$filename: the file path to be truncated. $data: Empty string to be written to the file. SEEK_SET: designated as the beginning of the file
 PHP determines whether a specified key exists in an array
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
PHP determines whether a specified key exists in an array
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
This article will explain in detail how PHP determines whether a specified key exists in an array. The editor thinks it is very practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. PHP determines whether a specified key exists in an array: In PHP, there are many ways to determine whether a specified key exists in an array: 1. Use the isset() function: isset($array["key"]) This function returns a Boolean value, true if the specified key exists, false otherwise. 2. Use array_key_exists() function: array_key_exists("key",$arr
 PHP returns the numeric encoding of the error message in the previous MySQL operation
Mar 22, 2024 pm 12:31 PM
PHP returns the numeric encoding of the error message in the previous MySQL operation
Mar 22, 2024 pm 12:31 PM
This article will explain in detail the numerical encoding of the error message returned by PHP in the previous Mysql operation. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. . Using PHP to return MySQL error information Numeric Encoding Introduction When processing mysql queries, you may encounter errors. In order to handle these errors effectively, it is crucial to understand the numerical encoding of error messages. This article will guide you to use php to obtain the numerical encoding of Mysql error messages. Method of obtaining the numerical encoding of error information 1. mysqli_errno() The mysqli_errno() function returns the most recent error number of the current MySQL connection. The syntax is as follows: $erro




