 Computer Tutorials
Computer Tutorials
 Computer Knowledge
Computer Knowledge
 Super practical! Sar commands that will make you a Linux master
Super practical! Sar commands that will make you a Linux master
Super practical! Sar commands that will make you a Linux master

I. Overview
The sar command presents a system usage report using data collected from system activity. These reports are made up of different sections, each containing the type of data and when the data was collected. The default mode of the sar command displays CPU usage at different time increments for various resources accessing the CPU (such as user, system, I/O scheduler, etc.). Additionally, it displays the percentage of idle CPU for a given time period. The average value for each data point is listed at the bottom of the report. sar reports collected data every 10 minutes by default, but you can use various options to filter and adjust these reports.
Similar to the uptime command, the sar command can also help you monitor the CPU load. sar allows you to understand when excessive load occurs and the specific details that may be causing it. sar provides more detailed data to help you better analyze system performance and deal with potential problems in a timely manner.
The syntax of the sar command is:
# sar [选项]
2. sar command example
1. Install sar command
To install the sar command, you need the "sysstat" package.
# yum install sysstat # rpm -ivh sysstat-2.3.4
Configure sar to retain logs beyond the default 7 days.
# vi /etc/sysconfig/sysstat
Change the "HISTORY" parameter.
2.CPU usage
Get the current CPU usage.
# sar 2 10 # sar -p 2 10 # sar-P ALL 2 10
To get the CPU usage of the previous date, such as the 14th:
# sar -P ALL -f /var/log/sa/sa14
c. To get the CPU usage from 7am to 3pm on the 10th of the month (that is, at a specified time):
# sar -P ALL -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
3.Memory usage
Get current memory usage:
# sar -r 2 10
To get the memory usage of the previous date, such as the 14th:
# sar -r -f /var/log/sa/sa14
To get the memory usage from 7am to 3pm on the 10th of the month (that is, the specified time):
# sar -r -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
4. Exchange usage
To get current swap usage:
# sar -S 2 10
To get the swap usage of the previous date, such as the 14th:
# sar -S -f /var/log/sa/sa14
To get swap usage from 7am to 3pm on the 10th of the month:
# sar -S -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
5.Load average
To get current load average statistics:
# sar -q 2 10
To get the load average statistics of the previous date, such as the 14th:
# sar -q -f /var/log/sa/sa14
To get load average statistics for the 10th of the month (7am to 3pm):
# sar -q -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
6. Use paging
To get the current paging usage:
# sar -B 2 10
To get the pagination usage of the previous date, such as the 14th:
# sar -B -f /var/log/sa/sa14
To get usage from 7am to 3pm on the 10th of the month:
# sar -B -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
7.IO usage
Get current IO usage:
# sar -B 2 10
To get the IO usage of the previous date, such as the 14th:
# sar -B -f /var/log/sa/sa14
To get IO usage from 7am to 3pm on the 10th of the month:
# sar -B -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
8. Disk IO usage
Get current disk IO usage:
# sar -d -p 2 10
To get the disk IO usage of the previous date, such as the 14th:
# sar -d -p -f /var/log/sa/sa14
To get the disk IO usage from 7am to 3pm on the 10th of the month:
# sar -d -p -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
9.Network statistics
To obtain current network device statistics:
# sar -n DEV 2 10
To obtain the network device statistics of the previous date, such as the 14th:
# sar -n DEV -f /var/log/sa/sa14
To get network device statistics from 7am to 3pm on the 10th of the month:
# sar -n DEV -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
10. Power management statistics
To get current power management usage:
# sar -m 2 10
To get the power management usage of the previous date, such as the 14th day:
# sar -m -f /var/log/sa/sa14
To get power management usage from 7am to 3pm on the 10th of the month:
# sar -m ALL -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
11.Memory Statistics (Page Activity)
To get current memory statistics:
# sar -r 2 10
To get the memory statistics of the previous date, such as the 14th day:
# sar -r -f /var/log/sa/sa14
To get memory statistics for the 10th of this month (7am to 3pm):
# sar -R ALL -f /var/log/sa/sa10 -s 07:00:00 -e 15:00:00
The above is the detailed content of Super practical! Sar commands that will make you a Linux master. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to run SUDO commands in Windows 11/10
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:50 AM
How to run SUDO commands in Windows 11/10
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:50 AM
The sudo command allows users to run commands in elevated privilege mode without switching to superuser mode. This article will introduce how to simulate functions similar to sudo commands in Windows systems. What is the Shudao Command? Sudo (short for "superuser do") is a command-line tool that allows users of Unix-based operating systems such as Linux and MacOS to execute commands with elevated privileges typically held by administrators. Running SUDO commands in Windows 11/10 However, with the launch of the latest Windows 11 Insider preview version, Windows users can now experience this feature. This new feature enables users to
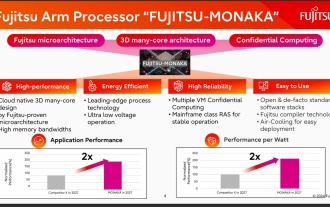 144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
According to news from this website on July 28, foreign media TechRader reported that Fujitsu introduced in detail the FUJITSU-MONAKA (hereinafter referred to as MONAKA) processor planned to be shipped in 2027. MONAKACPU is based on the "cloud native 3D many-core" architecture and adopts the Arm instruction set. It is oriented to the data center, edge and telecommunications fields. It is suitable for AI computing and can realize mainframe-level RAS1. Fujitsu said that MONAKA will achieve a leap in energy efficiency and performance: thanks to technologies such as ultra-low voltage (ULV) technology, the CPU can achieve 2 times the energy efficiency of competing products in 2027, and cooling does not require water cooling; in addition, the application performance of the processor It can also reach twice as much as your opponent. In terms of instructions, MONAKA is equipped with vector
 The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
1. First, we right-click the blank space of the taskbar and select the [Task Manager] option, or right-click the start logo, and then select the [Task Manager] option. 2. In the opened Task Manager interface, we click the [Services] tab on the far right. 3. In the opened [Service] tab, click the [Open Service] option below. 4. In the [Services] window that opens, right-click the [InternetConnectionSharing(ICS)] service, and then select the [Properties] option. 5. In the properties window that opens, change [Open with] to [Disabled], click [Apply] and then click [OK]. 6. Click the start logo, then click the shutdown button, select [Restart], and complete the computer restart.
 Leak reveals key specs of Intel Arrow Lake-U, -H, -HX and -S
Jun 15, 2024 pm 09:49 PM
Leak reveals key specs of Intel Arrow Lake-U, -H, -HX and -S
Jun 15, 2024 pm 09:49 PM
IntelArrowLakeisexpectedtobebasedonthesameprocessorarchitectureasLunarLake,meaningthatIntel'sbrandnewLionCoveperformancecoreswillbecombinedwiththeeconomicalSkymontefficiencycores.WhileLunarLakeisonlyavailableasava
 AM4 refuses to die, news says AMD will launch Ryzen 9 5900XT/7 5800XT: clocked at up to 4.8GHz
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:43 PM
AM4 refuses to die, news says AMD will launch Ryzen 9 5900XT/7 5800XT: clocked at up to 4.8GHz
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:43 PM
According to news from this website on June 1st, the source @CodeCommando tweeted today, sharing some screenshots of AMD’s upcoming presentation documents at the Computex2024 event. The content of the tweet was “AM4 will never die”, and the accompanying picture showed two new Ryzen5000XT series processors. The screenshots show the following two products: Ryzen 95900 Ryzen75800XT It is a faster variant of AMD's existing Ryzen75800X processor. Both processors are clocked up to 4.8G
 How to check the MAC address of the network card in Win11? How to use the command to obtain the MAC address of the network card in Win11
Feb 29, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
How to check the MAC address of the network card in Win11? How to use the command to obtain the MAC address of the network card in Win11
Feb 29, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
This article will introduce readers to how to use the command prompt (CommandPrompt) to find the physical address (MAC address) of the network adapter in Win11 system. A MAC address is a unique identifier for a network interface card (NIC), which plays an important role in network communications. Through the command prompt, users can easily obtain the MAC address information of all network adapters on the current computer, which is very helpful for network troubleshooting, configuring network settings and other tasks. Method 1: Use "Command Prompt" 1. Press the [Win+X] key combination, or [right-click] click the [Windows logo] on the taskbar, and in the menu item that opens, select [Run]; 2. Run the window , enter the [cmd] command, and then
 Super practical! Sar commands that will make you a Linux master
Mar 01, 2024 am 08:01 AM
Super practical! Sar commands that will make you a Linux master
Mar 01, 2024 am 08:01 AM
1. Overview The sar command displays system usage reports through data collected from system activities. These reports are made up of different sections, each containing the type of data and when the data was collected. The default mode of the sar command displays the CPU usage at different time increments for various resources accessing the CPU (such as users, systems, I/O schedulers, etc.). Additionally, it displays the percentage of idle CPU for a given time period. The average value for each data point is listed at the bottom of the report. sar reports collected data every 10 minutes by default, but you can use various options to filter and adjust these reports. Similar to the uptime command, the sar command can also help you monitor the CPU load. Through sar, you can understand the occurrence of excessive load
 2024 latest CPU ladder chart sharing (detailed high-definition)
Mar 13, 2024 pm 08:19 PM
2024 latest CPU ladder chart sharing (detailed high-definition)
Mar 13, 2024 pm 08:19 PM
The level of game performance has a great relationship with the CPU. For game-loving users, CPU performance is the focus of computer configuration, especially for LOL and CS:GO. It is more accurate and objective to directly look at the single-core performance for some large-scale 3D games. It mainly depends on the graphics card + CPU scheduling, so which CPU has better performance? This article will introduce you to the celestial map. The latest high-definition full version of the CPU ladder diagram



