999999Two simple ways to create an account in one week, did you know?
There are three types of users under Linux: 1. Super user: root has all permissions to the operating system uid0
2. Ordinary users: Ordinary users have limited permissions of the operating system uid500-6000
3. Pseudo user: This is to facilitate system management and meet the requirements of the corresponding system process file owner. It cannot log in to the system uid1--499
Manage user files and basic user information are placed here/etc/passwd. Any user has read permission to it. Only the account is defined and the password is not defined
One line represents a user divided into seven parts
Account name: Password: uid: gid: Related information: User home directory: Class library
The user’s password file /etc/shadow is only readable by root
Username: Password: Last changed: Maximum interval: Minimum interval: Warning time: Inactivity time: Expiration time
0can be changed at any time to 999999 for one week
Two easy ways to create an account
1Add a record in /etc/passwd
2#ueradd user#passwd password (lee user’s affiliated group is admin)
View user information:
Common options for the useradd command are as follows:
-dhome-dir: Specify the home directory.
-edate: The date the account was disabled, in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.
-fdays: The number of days after the password expires before the account is disabled.
-ggroup-name: The group name or GID of the main group to which the user belongs.

-Ggroup-list: A list of affiliated groups to which the user belongs. Multiple items are separated by colons.
-m: If the home directory does not exist, create it.
-M: Do not create the user directory.
-n: Do not create user private groups for users.
-r: Create a system account without a home directory with a UID greater than 500.
-p: Encrypted password.
-s: Specify the user to log in to the Shell, the default is /bin/bash.
-uUID: UID of the specified userlinux sets user group permissionssuse linux, it must be uniquelinux sets user group permissions, and is less than 499
Deletion of user:
User disablement:
User’s Unlock:
Change of user login name:
(If a user is locked, the password will be locked. Linux server configuration and management are all strictly prohibiting users from logging into the system. This method is not only mentioned in the above, so I will not give examples one by one)
Group configuration file/etc/group
Group name group password group id other users
Creation and deletion of groups (deletion of groups is different from that of users)
Creation and deletion of group password
What to do if you really don’t know? View help. Man or --help
The above is the detailed content of 999999Two simple ways to create an account in one week, did you know?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
Tomato Novel is a very popular novel reading software. We often have new novels and comics to read in Tomato Novel. Every novel and comic is very interesting. Many friends also want to write novels. Earn pocket money and edit the content of the novel you want to write into text. So how do we write the novel in it? My friends don’t know, so let’s go to this site together. Let’s take some time to look at an introduction to how to write a novel. Share the Tomato novel tutorial on how to write a novel. 1. First open the Tomato free novel app on your mobile phone and click on Personal Center - Writer Center. 2. Jump to the Tomato Writer Assistant page - click on Create a new book at the end of the novel.
 How to delete WeChat friends? How to delete WeChat friends
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
How to delete WeChat friends? How to delete WeChat friends
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
WeChat is one of the mainstream chat tools. We can meet new friends, contact old friends and maintain the friendship between friends through WeChat. Just as there is no such thing as a banquet that never ends, disagreements will inevitably occur when people get along with each other. When a person extremely affects your mood, or you find that your views are inconsistent when you get along, and you can no longer communicate, then we may need to delete WeChat friends. How to delete WeChat friends? The first step to delete WeChat friends: tap [Address Book] on the main WeChat interface; the second step: click on the friend you want to delete and enter [Details]; the third step: click [...] in the upper right corner; Step 4: Click [Delete] below; Step 5: After understanding the page prompts, click [Delete Contact]; Warm
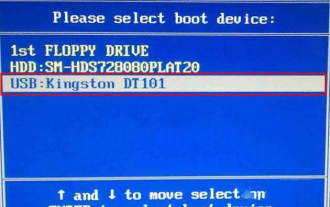 How to enter bios on Colorful motherboard? Teach you two methods
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
How to enter bios on Colorful motherboard? Teach you two methods
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Colorful motherboards enjoy high popularity and market share in the Chinese domestic market, but some users of Colorful motherboards still don’t know how to enter the bios for settings? In response to this situation, the editor has specially brought you two methods to enter the colorful motherboard bios. Come and try it! Method 1: Use the U disk startup shortcut key to directly enter the U disk installation system. The shortcut key for the Colorful motherboard to start the U disk with one click is ESC or F11. First, use Black Shark Installation Master to create a Black Shark U disk boot disk, and then turn on the computer. When you see the startup screen, continuously press the ESC or F11 key on the keyboard to enter a window for sequential selection of startup items. Move the cursor to the place where "USB" is displayed, and then
 How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
Unfortunately, people often delete certain contacts accidentally for some reasons. WeChat is a widely used social software. To help users solve this problem, this article will introduce how to retrieve deleted contacts in a simple way. 1. Understand the WeChat contact deletion mechanism. This provides us with the possibility to retrieve deleted contacts. The contact deletion mechanism in WeChat removes them from the address book, but does not delete them completely. 2. Use WeChat’s built-in “Contact Book Recovery” function. WeChat provides “Contact Book Recovery” to save time and energy. Users can quickly retrieve previously deleted contacts through this function. 3. Enter the WeChat settings page and click the lower right corner, open the WeChat application "Me" and click the settings icon in the upper right corner to enter the settings page.
 Summary of methods to obtain administrator rights in Win11
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
Summary of methods to obtain administrator rights in Win11
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
A summary of how to obtain Win11 administrator rights. In the Windows 11 operating system, administrator rights are one of the very important permissions that allow users to perform various operations on the system. Sometimes, we may need to obtain administrator rights to complete some operations, such as installing software, modifying system settings, etc. The following summarizes some methods for obtaining Win11 administrator rights, I hope it can help you. 1. Use shortcut keys. In Windows 11 system, you can quickly open the command prompt through shortcut keys.
 Quickly master: How to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones revealed!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
Quickly master: How to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones revealed!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
In today's society, mobile phones have become an indispensable part of our lives. As an important tool for our daily communication, work, and life, WeChat is often used. However, it may be necessary to separate two WeChat accounts when handling different transactions, which requires the mobile phone to support logging in to two WeChat accounts at the same time. As a well-known domestic brand, Huawei mobile phones are used by many people. So what is the method to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones? Let’s reveal the secret of this method. First of all, you need to use two WeChat accounts at the same time on your Huawei mobile phone. The easiest way is to
 Detailed explanation of Oracle version query method
Mar 07, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
Detailed explanation of Oracle version query method
Mar 07, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
Detailed explanation of Oracle version query method Oracle is one of the most popular relational database management systems in the world. It provides rich functions and powerful performance and is widely used in enterprises. In the process of database management and development, it is very important to understand the version of the Oracle database. This article will introduce in detail how to query the version information of the Oracle database and give specific code examples. Query the database version of the SQL statement in the Oracle database by executing a simple SQL statement
 The secret of hatching mobile dragon eggs is revealed (step by step to teach you how to successfully hatch mobile dragon eggs)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
The secret of hatching mobile dragon eggs is revealed (step by step to teach you how to successfully hatch mobile dragon eggs)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Mobile games have become an integral part of people's lives with the development of technology. It has attracted the attention of many players with its cute dragon egg image and interesting hatching process, and one of the games that has attracted much attention is the mobile version of Dragon Egg. To help players better cultivate and grow their own dragons in the game, this article will introduce to you how to hatch dragon eggs in the mobile version. 1. Choose the appropriate type of dragon egg. Players need to carefully choose the type of dragon egg that they like and suit themselves, based on the different types of dragon egg attributes and abilities provided in the game. 2. Upgrade the level of the incubation machine. Players need to improve the level of the incubation machine by completing tasks and collecting props. The level of the incubation machine determines the hatching speed and hatching success rate. 3. Collect the resources required for hatching. Players need to be in the game






