 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Anything in Any Scene: Realistic object insertion (to assist in the synthesis of various driving data)
Anything in Any Scene: Realistic object insertion (to assist in the synthesis of various driving data)
Anything in Any Scene: Realistic object insertion (to assist in the synthesis of various driving data)
Original title: Anything in Any Scene: Photorealistic Video Object Insertion
Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.17509.pdf
Code link: https ://github.com/AnythingInAnyScene/anything_in_anyscene
Author affiliation: Xpeng Motors

##Thesis idea
Realistic video simulation shows huge potential in applications ranging from virtual reality to film production. Especially when capturing video in the real world is impractical or expensive. Existing methods in video simulation often fail to accurately model lighting environments, represent object geometry, or achieve high levels of photorealism. This paper proposesAnything in Any Scene, a novel and versatile real video simulation framework that can seamlessly insert any object into existing dynamic videos and emphasize physical realism. The overall framework proposed in this paper contains three key processes: 1) integrating real objects into a given scene video and placing them in appropriate locations to ensure geometric realism; 2) estimating sky and ambient illumination distribution and Simulate real shadows and enhance light realism; 3) Use a style transfer network to refine the final video output to maximize photo realism. This article experimentally proves that the Anything in Any Scene framework can generate simulation videos with excellent geometric realism, lighting realism, and photo realism. By significantly mitigating the challenges associated with video data generation, our framework provides an efficient and cost-effective solution for obtaining high-quality videos. Furthermore, its applications extend far beyond video data enhancement, showing promising potential in virtual reality, video editing, and various other video-centric applications.
Main Contribution
This paper introduces a novel and extensible Anything in Any Scene video simulation framework, capable of integrating any object into any dynamic scene video. This article is uniquely structured and focuses on maintaining geometry, lighting, and photorealism in video simulations to ensure high quality and authenticity of the output results. After extensive verification, the results show that the framework has the ability to produce highly realistic video simulations, thus significantly expanding the application scope and development potential of this field.Thesis Design
Image and video simulation have found success in a variety of applications, from virtual reality to film production. The ability to generate diverse and high-quality visual content through photorealistic image and video simulation has the potential to advance these fields, introducing new possibilities and applications. While the authenticity of images and videos captured in the real world is invaluable, they are often limited by long-tail distributions. This leads to over-representation of common scenarios and under-representation of rare but critical situations, presenting a challenge known as the out-of-distribution problem. Traditional methods of addressing these limitations through video capture and editing proved impractical or cost-prohibitive because it was difficult to cover all possible scenarios. The importance of video simulation, especially by integrating existing videos with newly inserted objects, becomes crucial to overcome these challenges. By generating large-scale, diverse, and realistic visual content, video simulation helps augment applications in virtual reality, video editing, and video data augmentation. However, generating realistic simulation videos considering physical realism is still a challenging open problem. Existing methods often exhibit limitations by focusing on specific settings, especially indoor environments [9, 26, 45, 46, 57]. These methods may not adequately address the complexity of outdoor scenes, including varying lighting conditions and fast-moving objects. Methods relying on 3D model registration are limited to integrating limited classes of objects [12, 32, 40, 42]. Many methods ignore important factors such as lighting environment modeling, correct object placement, and achieving realism [12, 36]. The failed case is shown in Figure 1. Therefore, these limitations greatly limit their application in areas that require highly scalable, geometrically consistent, and realistic scene video simulations, such as autonomous driving and robotics. This paper proposes a comprehensive framework for photorealistic video object insertion in Anything in Any Scene that addresses these challenges. The framework is designed to be versatile and suitable for indoor and outdoor scenes, ensuring physical accuracy in terms of geometric realism, lighting realism, and photorealism. The goal of this paper is to create video simulations that are not only useful for visual data augmentation in machine learning, but also suitable for various video applications such as virtual reality and video editing.The overview of the Anything in Any Scene framework of this article is shown in Figure 2. This paper details our novel and scalable pipeline for building a diverse asset library of scene videos and object meshes in Section 3. This paper introduces a visual data query engine designed to efficiently retrieve relevant video clips from visual queries using descriptive keywords. Next, this paper proposes two methods for generating 3D meshes, leveraging existing 3D assets as well as multi-view image reconstruction. This allows unrestricted insertion of any desired object, even if it is highly irregular or semantically weak. In Section 4, the paper details methods for integrating objects into dynamic scene videos, focusing on maintaining physical realism. This paper designs the object placement and stabilization method described in Section 4.1 to ensure that the inserted object is stably anchored on consecutive video frames. To address the challenge of creating realistic lighting and shadow effects, this paper estimates sky and environment lighting and generates realistic shadows during rendering, as described in Section 4.2. The generated simulated video frames inevitably contain unrealistic artifacts that differ from real-world captured video, such as imaging quality differences in noise levels, color fidelity, and sharpness. This paper uses a style transfer network to enhance photo realism in Section 4.3.
The simulation videos generated from the framework proposed in this paper achieve a high degree of lighting realism, geometric realism, and photo realism, outperforming other videos in both quality and quantity, as shown in Section 5.3. This article further demonstrates the application of this article's simulation video in training perception algorithms in Section 5.4 to verify its practical value. The Anything in Any Scene framework enables the creation of large-scale, low-cost video datasets for data augmentation with time-efficiency and realistic visual quality, thereby easing the burden of video data generation and potentially improving long-tail and out-of-distribution challenges . With its general framework design, the Anything in Any Scene framework can easily integrate improved models and new modules, such as improved 3D mesh reconstruction methods, to further enhance video simulation performance.
 Figure 1. Examples of simulated video frames with incorrect lighting environment estimation, incorrect object placement, and unrealistic texture styles. These problems make the image lack physical realism.
Figure 1. Examples of simulated video frames with incorrect lighting environment estimation, incorrect object placement, and unrealistic texture styles. These problems make the image lack physical realism. 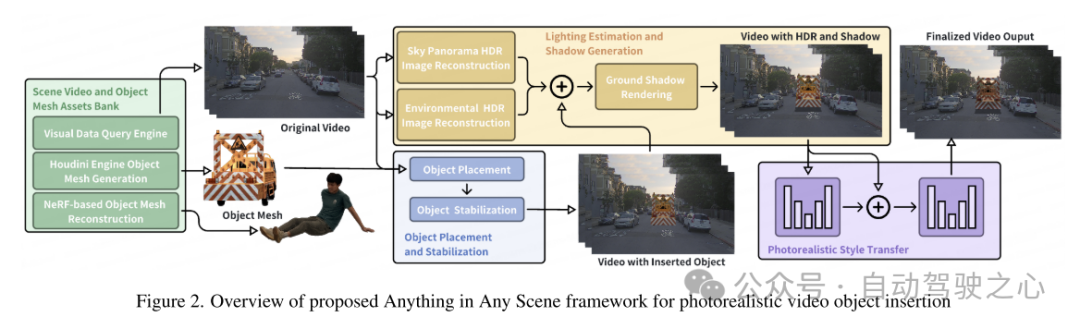 Figure 2. Overview of the Anything in Any Scene framework for photorealistic video object insertion
Figure 2. Overview of the Anything in Any Scene framework for photorealistic video object insertion Figure 3. Example of a driving scene video for object placement. The red dots in each image are where the objects were inserted.
Figure 3. Example of a driving scene video for object placement. The red dots in each image are where the objects were inserted.
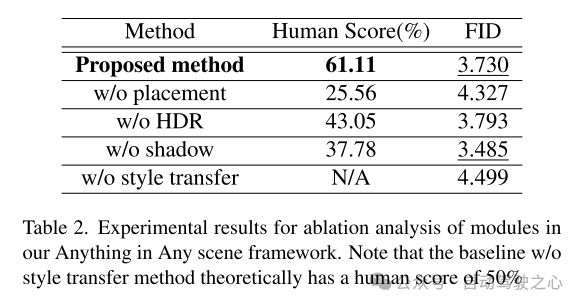
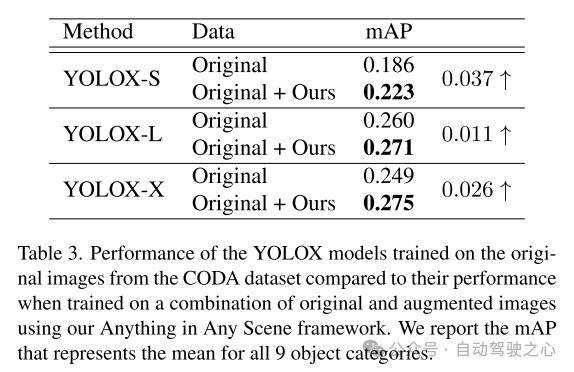
Experimental results
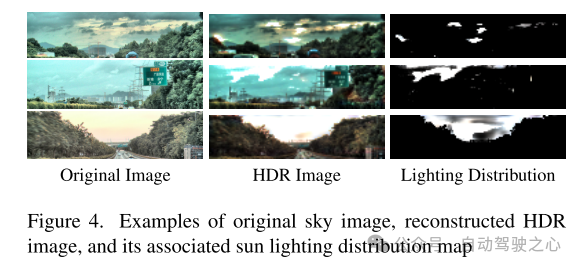
Figure 4. Examples of original sky images, reconstructed HDR images, and their associated solar illumination distribution maps

Figure 5. Examples of original and reconstructed HDR environment panoramic images
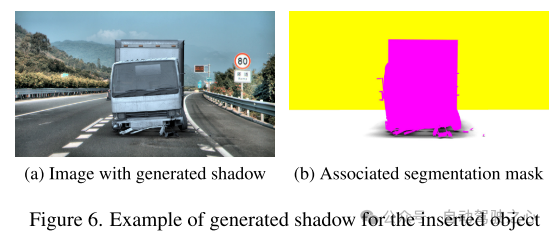
Figure 6. For inserted objects Example of shadow generation

# Figure 7. Qualitative comparison of simulated video frames from the PandaSet dataset using different style transfer networks.

Figure 8. Qualitative comparison of simulated video frames from the PandaSet dataset under various rendering conditions.
Summary:
This paper proposes an innovative and extensible framework, "Anything in Any Scene", designed for realistic video simulation And design. The framework proposed in this paper seamlessly integrates various objects into different dynamic videos, ensuring that geometric realism, lighting realism, and photo realism are preserved. Through extensive demonstrations, this paper demonstrates its efficacy in mitigating challenges associated with video data collection and generation, providing a cost-effective and time-saving solution for a variety of scenarios. The application of our framework shows significant improvements in downstream perception tasks, especially in solving the long-tail distribution problem in object detection. The flexibility of our framework allows direct integration of improved models for each module, and our framework lays a solid foundation for future exploration and innovation in the field of realistic video simulation.
Citation:
Bai C, Shao Z, Zhang G, et al. Anything in Any Scene: Photorealistic Video Object Insertion[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.17509 , 2024.
The above is the detailed content of Anything in Any Scene: Realistic object insertion (to assist in the synthesis of various driving data). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to record screen video with OPPO phone (simple operation)
May 07, 2024 pm 06:22 PM
How to record screen video with OPPO phone (simple operation)
May 07, 2024 pm 06:22 PM
Game skills or teaching demonstrations, in daily life, we often need to use mobile phones to record screen videos to show some operating steps. Its function of recording screen video is also very good, and OPPO mobile phone is a powerful smartphone. Allowing you to complete the recording task easily and quickly, this article will introduce in detail how to use OPPO mobile phones to record screen videos. Preparation - Determine recording goals You need to clarify your recording goals before you start. Do you want to record a step-by-step demonstration video? Or want to record a wonderful moment of a game? Or want to record a teaching video? Only by better arranging the recording process and clear goals. Open the screen recording function of OPPO mobile phone and find it in the shortcut panel. The screen recording function is located in the shortcut panel.
 The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Imagine an artificial intelligence model that not only has the ability to surpass traditional computing, but also achieves more efficient performance at a lower cost. This is not science fiction, DeepSeek-V2[1], the world’s most powerful open source MoE model is here. DeepSeek-V2 is a powerful mixture of experts (MoE) language model with the characteristics of economical training and efficient inference. It consists of 236B parameters, 21B of which are used to activate each marker. Compared with DeepSeek67B, DeepSeek-V2 has stronger performance, while saving 42.5% of training costs, reducing KV cache by 93.3%, and increasing the maximum generation throughput to 5.76 times. DeepSeek is a company exploring general artificial intelligence
 How to switch language in Adobe After Effects cs6 (Ae cs6) Detailed steps for switching between Chinese and English in Ae cs6 - ZOL download
May 09, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
How to switch language in Adobe After Effects cs6 (Ae cs6) Detailed steps for switching between Chinese and English in Ae cs6 - ZOL download
May 09, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
1. First find the AMTLanguages folder. We found some documentation in the AMTLanguages folder. If you install Simplified Chinese, there will be a zh_CN.txt text document (the text content is: zh_CN). If you installed it in English, there will be a text document en_US.txt (the text content is: en_US). 3. Therefore, if we want to switch to Chinese, we need to create a new text document of zh_CN.txt (the text content is: zh_CN) under the AdobeAfterEffectsCCSupportFilesAMTLanguages path. 4. On the contrary, if we want to switch to English,
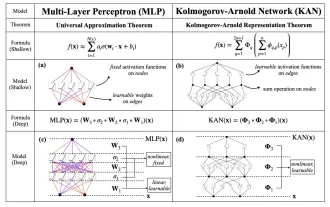 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 How to shoot videos on Douyin? How to turn on the microphone for video shooting?
May 09, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
How to shoot videos on Douyin? How to turn on the microphone for video shooting?
May 09, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
As one of the most popular short video platforms today, the quality and effect of Douyin’s videos directly affect the user’s viewing experience. So, how to shoot high-quality videos on Douyin? 1. How to shoot videos on Douyin? 1. Open the Douyin APP and click the "+" button in the middle at the bottom to enter the video shooting page. 2. Douyin provides a variety of shooting modes, including normal shooting, slow motion, short video, etc. Choose the appropriate shooting mode according to your needs. 3. On the shooting page, click the "Filter" button at the bottom of the screen to choose different filter effects to make the video more personalized. 4. If you need to adjust parameters such as exposure and contrast, you can click the "Parameters" button in the lower left corner of the screen to set it. 5. During shooting, you can click on the left side of the screen
 Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
In order to align large language models (LLMs) with human values and intentions, it is critical to learn human feedback to ensure that they are useful, honest, and harmless. In terms of aligning LLM, an effective method is reinforcement learning based on human feedback (RLHF). Although the results of the RLHF method are excellent, there are some optimization challenges involved. This involves training a reward model and then optimizing a policy model to maximize that reward. Recently, some researchers have explored simpler offline algorithms, one of which is direct preference optimization (DPO). DPO learns the policy model directly based on preference data by parameterizing the reward function in RLHF, thus eliminating the need for an explicit reward model. This method is simple and stable
 No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
At the forefront of software technology, UIUC Zhang Lingming's group, together with researchers from the BigCode organization, recently announced the StarCoder2-15B-Instruct large code model. This innovative achievement achieved a significant breakthrough in code generation tasks, successfully surpassing CodeLlama-70B-Instruct and reaching the top of the code generation performance list. The unique feature of StarCoder2-15B-Instruct is its pure self-alignment strategy. The entire training process is open, transparent, and completely autonomous and controllable. The model generates thousands of instructions via StarCoder2-15B in response to fine-tuning the StarCoder-15B base model without relying on expensive manual annotation.
 How to create a shaking effect when cutting footage? How to make the camera follow the characters?
May 07, 2024 am 08:16 AM
How to create a shaking effect when cutting footage? How to make the camera follow the characters?
May 07, 2024 am 08:16 AM
In the digital age, short videos have become an important way for more and more people to express themselves, share their lives, and convey information. As a popular video editing software, Jianying provides users with rich editing functions. This article will give you a detailed introduction to how to create a camera shake effect and how to make the camera follow the characters. 1. How to create a shaking effect in the cut shot? 1. Open the clipping APP: - Open the clipping APP and enter the video editing interface. 2. Select video material: - Select the video material to be edited in the video material library. 3. Add effects: - Click the "Special Effects" button to enter the special effects library. -In the special effects library, find the "shake shake" effect and add it to the video. 4. Adjust effect parameters: - In the effect parameter interface, you can adjust



