 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Golang
Golang
 Detailed explanation of function parameter passing method in Go language
Detailed explanation of function parameter passing method in Go language
Detailed explanation of function parameter passing method in Go language
Mar 09, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
The Go language is an open source programming language developed by Google and is designed to improve developer productivity and code reliability. In the Go language, the way function parameters are passed is very important, as it can affect the performance and memory usage of the program.
1. Value passing
Value passing refers to copying the value of the parameter and passing it to the function. Operations on parameters inside the function will not affect the values of external variables. Here is a simple value passing example:
package main
import "fmt"
func modifyValue(x int) {
x = x * 2
fmt.Println("Inside function:", x)
}
func main() {
num := 10
modifyValue(num)
fmt.Println("Outside function:", num)
}In the above example, the modifyValue function receives an integer parameter and multiplies the parameter by 2. After the function call, the value of the external variable num has not changed.
2. Passing by reference
Passing by reference means passing the address of the parameter to the function, and the function can modify the value of the external variable through the address. In the Go language, reference types such as slices, maps, and channels are passed by reference by default. Here is an example of passing by reference:
package main
import "fmt"
func modifySlice(s []int) {
s[0] = 100
fmt.Println("Inside function:", s)
}
func main() {
slice := []int{1, 2, 3}
modifySlice(slice)
fmt.Println("Outside function:", slice)
} In the above example, the modifySlice function receives a slice parameter and modifies the first element to 100. After the function call, the value of the outer slice slice has also changed.
3. Pass pointer
By passing the pointer of the parameter, the function can directly operate the value in the memory address pointed to by the parameter. This method can reduce the overhead of copying parameters, and is especially suitable for large data structures and situations that require frequent modifications. Here is an example of passing a pointer:
package main
import "fmt"
func modifyPointer(x *int) {
*x = *x * 2
fmt.Println("Inside function:", *x)
}
func main() {
num := 10
modifyPointer(&num)
fmt.Println("Outside function:", num)
}In the above example, the modifyPointer function receives an integer pointer parameter and multiplies the value pointed to by the pointer by 2. After the function call, the value of the external variable num has also changed.
Through the above examples, we can see the application and impact of different parameter passing methods in the Go language. In actual development, choosing the appropriate delivery method can improve the performance and maintainability of the program. I hope this article is helpful to readers, thank you for reading!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of function parameter passing method in Go language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot Article

Hot tools Tags

Hot Article

Hot Article Tags

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What to do if your Huawei phone has insufficient memory (Practical methods to solve the problem of insufficient memory)
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:34 PM
What to do if your Huawei phone has insufficient memory (Practical methods to solve the problem of insufficient memory)
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:34 PM
What to do if your Huawei phone has insufficient memory (Practical methods to solve the problem of insufficient memory)
 How to use reflection to access private fields and methods in golang
May 03, 2024 pm 12:15 PM
How to use reflection to access private fields and methods in golang
May 03, 2024 pm 12:15 PM
How to use reflection to access private fields and methods in golang
 What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory
May 09, 2024 am 11:10 AM
What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory
May 09, 2024 am 11:10 AM
What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory
 For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
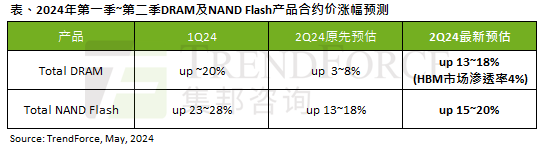 The impact of the AI wave is obvious. TrendForce has revised up its forecast for DRAM memory and NAND flash memory contract price increases this quarter.
May 07, 2024 pm 09:58 PM
The impact of the AI wave is obvious. TrendForce has revised up its forecast for DRAM memory and NAND flash memory contract price increases this quarter.
May 07, 2024 pm 09:58 PM
The impact of the AI wave is obvious. TrendForce has revised up its forecast for DRAM memory and NAND flash memory contract price increases this quarter.
 The difference between performance testing and unit testing in Go language
May 08, 2024 pm 03:09 PM
The difference between performance testing and unit testing in Go language
May 08, 2024 pm 03:09 PM
The difference between performance testing and unit testing in Go language
 What pitfalls should we pay attention to when designing distributed systems with Golang technology?
May 07, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
What pitfalls should we pay attention to when designing distributed systems with Golang technology?
May 07, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
What pitfalls should we pay attention to when designing distributed systems with Golang technology?







