Coinbase: Investment and Entrepreneurship Opportunities in AI Blockchain
Original title: "Blockchain for AI"
## Author: Rajarshi Gupta, Vijay Dialani
Over the past year, we have witnessed an explosion in the capabilities and applications of artificial intelligence. This includes significant improvements in the sophistication of text-to-image models, large language models, and their use in many business use cases such as search and recommendations, facilitating software development, and big data analytics. It is predicted that generative AI alone will form a $1.3 trillion market by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 42% over the next decade. When studying the intersection of blockchain and artificial intelligence, there are two main aspects to focus on. The first is the use of artificial intelligence/machine learning models and methods to enhance the transaction process of blockchain platforms, decentralized applications and digital assets. Secondly, focus on how to use blockchain technology to create value for developers and users of artificial intelligence/machine learning products and services. This cross-fertilization brings new possibilities to both fields, promoting innovation and progress. Fundamentals of Blockchain CapabilitiesBlockchain technology has a variety of basic capabilities that can be used to develop, deploy, and run artificial intelligence models. These capabilities include cryptographic primitives, blockchain protocols, and smart contracts. These properties are closely related to AI applications and we will explore them in detail in the following sections.Data Security: Helps AI store data in a tamper-proof and immutable manner and achieve high performance by using decentralized servers that are not vulnerable to attack, manipulation, censorship, and denial of service Availability.
Data testability, traceability, and auditability: Record transactions and assets in an immutable and transparent manner, making it easy to track the source, ownership, provenance of data, and data with numbers Signed and timestamped protocol. This also provides auditability and verifiable capabilities.
Decentralized decision-making: Enables decisions to be made by multiple entities or directly between two parties without a pre-existing trust relationship between them or with a central entity Make decisions.
Autonomous and transparent code execution: Enable programs to execute as smart contracts that are transparent to all parties involved and do not require reliance on trusted and centralized intermediaries It can run autonomously.
Decentralized Identity: Provides a secure digital identity mechanism that allows users to interact with services without revealing privacy.
Micro payment: Provide a safe and lightweight payment method to reduce friction in the payment process.
1. How blockchain can benefit artificial intelligence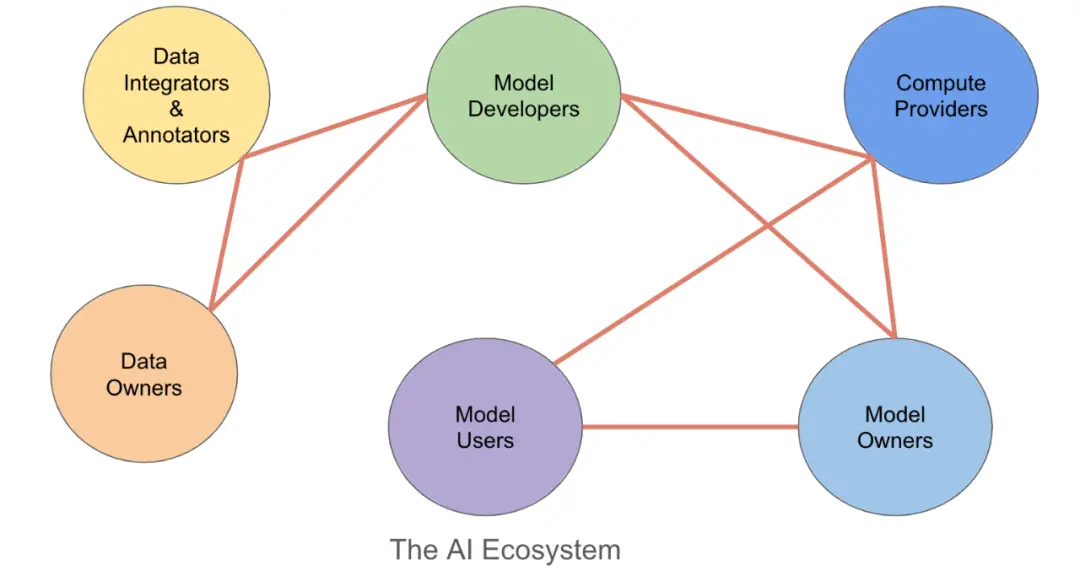
NFT will allow users or developers to maintain their ownership rights and further transfer ownership of the corresponding digital assets to others. It is also possible to envision a blockchain-based data and model access control mechanism, such as smart contracts that allow/restrict access based on a given list of user addresses. Alternatively, it could be integrated with a decentralized identity solution (perhaps using state-of-the-art cryptography such as zero-knowledge proofs) to allow access based on certain proven properties (e.g. allowing access based on proof that the user is old enough or only accessible from certain geographic locations) while protecting user privacy.
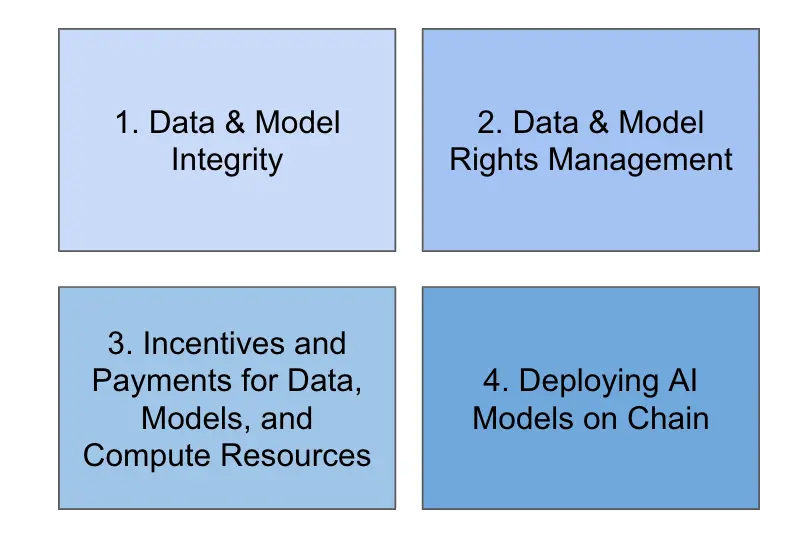
2.3. Incentives and payments for data, models, and computing resources
Blockchains can use stablecoins to facilitate low-rate micropayments using generative AI models. Smart contracts can allow revenue to be shared among multiple co-owners of a model in a decentralized manner. This co-ownership model is actually a “decentralized Hugging Face” that may allow small and medium-sized model developers to join forces and compete with the larger companies in the field. It can also be used to incentivize data providers, data annotators, model developers or human feedback providers around the world to join a new decentralized project to develop new generative AI models or solutions, and at the same time, have appropriate Mechanism to track contributions so that incentives can be distributed equitably.
Blockchain can also be used to create a decentralized data/model/computation market, enabling calculation providers, training data providers, model developers and users to easily search and match each other, providing incentives , payment and signing of contracts and agreements. A decentralized blockchain-based review system implemented using smart contracts can incorporate automated and human-based reviewers into the same system to incentivize high-throughput, thorough, high-quality review of data and models.
2.4. Deploying AI on-chain
This category involves running certain AI models directly on the blockchain for greater transparency and trust. AI models may provide some inference or generation use cases directly to end users, giving them confidence that only the model they intend to provide input to can receive said input and produce the output they see without any manipulation, falsification or censorship. Alternatively, AI models can be deployed to help smart contracts adjust and optimize their own parameters in response to user transactions.
The AI model may also be a smart contract that uses historical and current transaction data on the chain to make buy/sell/trade decisions on digital assets for profit. These models can be deployed on Layer1 chains as smart contracts or through Layer2 systems such as zk-rollups. These models may be privately owned or decentralized in the form of a DAO, allowing multiple individuals and entities to own a “stake” in a given on-chain model.
In the long term, for such applications, there may be interest in researching and developing a completely new platform to support AI workflows, given the high data and computing requirements of AI applications.
3. How to Help
Coinbase’s mission is to empower more than 1 billion people with economic freedom. As Crypto usage grows, we are focused on building the most trustworthy, compliant products and services and supporting other builders. It’s clear that AI blockchain fits the strategy of enabling those individuals and organizations that are part of the emerging AI ecosystem (which is currently almost entirely based on the centralized and less transparent Web2 framework) to benefit from blockchain and AI-based Benefiting from chain-based Crypto solutions, this is broadly defined.
We believe Coinbase is particularly well-suited to become a major contributor in this space because, a) it has significant visibility and brand power among both retail customers and institutional users of those blockchain assets and services; b) ) it has a proven track record of success in helping bridge the gap between the emerging Web3 world and existing Web2 systems; c) it has a team with an understanding of the growing generative AI ecosystem and the needs of developers and other stakeholders Deep understanding and strong ML development team.
Coinbase is deeply interested in exploring partnerships and integrations with like-minded companies, such as those with expertise in artificial intelligence solutions and ecosystem services, and are committed to turning ideas into reality.
The above is the detailed content of Coinbase: Investment and Entrepreneurship Opportunities in AI Blockchain. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C? Answer: Use loop statements. Steps: 1. Define the variable n and store the countdown number to output; 2. Use the while loop to continuously print n until n is less than 1; 3. In the loop body, print out the value of n; 4. At the end of the loop, subtract n by 1 to output the next smaller reciprocal.
 How to play picture sequences smoothly with CSS animation?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
How to play picture sequences smoothly with CSS animation?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
How to achieve the playback of pictures like videos? Many times, we need to implement similar video player functions, but the playback content is a sequence of images. direct...
 Integers in C: a little history
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:09 AM
Integers in C: a little history
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:09 AM
Integers are the most basic data type in programming and can be regarded as the cornerstone of programming. The job of a programmer is to give these numbers meanings. No matter how complex the software is, it ultimately comes down to integer operations, because the processor only understands integers. To represent negative numbers, we introduced two's complement; to represent decimal numbers, we created scientific notation, so there are floating-point numbers. But in the final analysis, everything is still inseparable from 0 and 1. A brief history of integers In C, int is almost the default type. Although the compiler may issue a warning, in many cases you can still write code like this: main(void){return0;} From a technical point of view, this is equivalent to the following code: intmain(void){return0;}
 How to implement nesting effect of text annotations in Quill editor?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:21 PM
How to implement nesting effect of text annotations in Quill editor?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:21 PM
A solution to implement text annotation nesting in Quill Editor. When using Quill Editor for text annotation, we often need to use the Quill Editor to...
 What does the return value of 56 or 65 mean by C language function?
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:15 AM
What does the return value of 56 or 65 mean by C language function?
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:15 AM
When a C function returns 56 or 65, it indicates a specific event. These numerical meanings are defined by the function developer and may indicate success, file not found, or read errors. Replace these "magic numbers" with enumerations or macro definitions can improve readability and maintainability, such as: READ_SUCCESS, FILE_NOT_FOUND, and READ_ERROR.
 Zustand asynchronous operation: How to ensure the latest state obtained by useStore?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Zustand asynchronous operation: How to ensure the latest state obtained by useStore?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Data update problems in zustand asynchronous operations. When using the zustand state management library, you often encounter the problem of data updates that cause asynchronous operations to be untimely. �...
 What determines the return value type of C language function?
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:42 AM
What determines the return value type of C language function?
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:42 AM
The return value type of the function is determined by the return type specified when the function is defined. Common types include int, float, char, and void (indicating that no value is returned). The return value type must be consistent with the actual returned value in the function body, otherwise it will cause compiler errors or unpredictable behavior. When returning a pointer, you must make sure that the pointer points to valid memory, otherwise it may cause a segfault. When dealing with return value types, error handling and resource release (such as dynamically allocated memory) need to be considered to write robust and reliable code.
 Electron rendering process and WebView: How to achieve efficient 'synchronous' communication?
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:45 AM
Electron rendering process and WebView: How to achieve efficient 'synchronous' communication?
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:45 AM
Electron rendering process and WebView...





