How to create and use MySQL views

How to create and use MySQL views?
MySQL is a popular relational database management system that allows users to create views to simplify complex query operations and improve query efficiency. Views are virtual tables created through query statements and can be used like ordinary tables. In this article, we'll cover how to create and use MySQL views and provide specific code examples.
1. Create a MySQL view
To create a MySQL view, you need to use the CREATE VIEW statement. The syntax is as follows:
CREATE VIEW view_name AS SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE condition;
view_name: The name of the viewcolumn1, column2, ...: The columns to be included in the viewtable_name: Which table the view will obtain data fromcondition: Optional conditions for filtering view data
For example, we create a simple view to display the names and salaries in the employee table:
CREATE VIEW employee_view AS SELECT name, salary FROM employee;
2. Using MySQL views
Once the view is created, it can be used like a normal table. The following are some common operations using views:
- Query the data of the view:
SELECT * FROM employee_view;
- Perform on the view Filter:
SELECT * FROM employee_view WHERE salary > 5000;
- Update the data in the view:
Since the view is a virtual Tables are not where the data is actually stored, so there are some limitations. Normally, views are not updatable, but you can allow updates to the view data by using the WITH CHECK OPTION option in the CREATE VIEW statement. In this way, the update operation will be checked to ensure that it meets the conditions defined by the view.
3. Example
Suppose we have a student tablestudent:
CREATE TABLE student (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50),
age INT,
gender VARCHAR(10)
);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, age, gender) VALUES
(1, 'Alice', 20, 'Female'),
(2, 'Bob', 22, 'Male'),
(3, 'Cathy', 21, 'Female');Now we create a view female_student that only contains information about female students:
CREATE VIEW female_student AS SELECT id, name, age FROM student WHERE gender = 'Female';
Query the data of view female_student:
SELECT * FROM female_student;
In this way, we can easily Obtain data under specific conditions in the view without having to write complex query statements every time.
Conclusion
By creating and using MySQL views, we can simplify complex query operations and improve the efficiency of database operations. Views can help us organize and manage data more conveniently, reduce duplication of work, and improve programming efficiency. I hope that through the introduction of this article, you can become more proficient in using MySQL views to perform database operations.
The above is the detailed content of How to create and use MySQL views. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to fix Blizzard Battle.net update stuck at 45%?
Mar 16, 2024 pm 06:52 PM
How to fix Blizzard Battle.net update stuck at 45%?
Mar 16, 2024 pm 06:52 PM
Blizzard Battle.net update keeps stuck at 45%, how to solve it? Recently, many people have been stuck at the 45% progress bar when updating software. They will still get stuck after restarting multiple times. So how to solve this situation? We can reinstall the client, switch regions, and delete files. To deal with it, this software tutorial will share the operation steps, hoping to help more people. Blizzard Battle.net update keeps stuck at 45%, how to solve it? 1. Client 1. First, you need to confirm that your client is the official version downloaded from the official website. 2. If not, users can enter the Asian server website to download. 3. After entering, click Download in the upper right corner. Note: Be sure not to select Simplified Chinese when installing.
 12306 How to check historical ticket purchase records How to check historical ticket purchase records
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:11 PM
12306 How to check historical ticket purchase records How to check historical ticket purchase records
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:11 PM
Download the latest version of 12306 ticket booking app. It is a travel ticket purchasing software that everyone is very satisfied with. It is very convenient to go wherever you want. There are many ticket sources provided in the software. You only need to pass real-name authentication to purchase tickets online. All users You can easily buy travel tickets and air tickets and enjoy different discounts. You can also start booking reservations in advance to grab tickets. You can book hotels or special car transfers. With it, you can go where you want to go and buy tickets with one click. Traveling is simpler and more convenient, making everyone's travel experience more comfortable. Now the editor details it online Provides 12306 users with a way to view historical ticket purchase records. 1. Open Railway 12306, click My in the lower right corner, and click My Order 2. Click Paid on the order page. 3. On the paid page
 How to install Angular on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
How to install Angular on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Angular.js is a freely accessible JavaScript platform for creating dynamic applications. It allows you to express various aspects of your application quickly and clearly by extending the syntax of HTML as a template language. Angular.js provides a range of tools to help you write, update and test your code. Additionally, it provides many features such as routing and form management. This guide will discuss how to install Angular on Ubuntu24. First, you need to install Node.js. Node.js is a JavaScript running environment based on the ChromeV8 engine that allows you to run JavaScript code on the server side. To be in Ub
 How to check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com
Mar 28, 2024 pm 04:31 PM
How to check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com
Mar 28, 2024 pm 04:31 PM
How to check my academic qualifications on Xuexin.com? You can check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com, but many users don’t know how to check their academic qualifications on Xuexin.com. Next, the editor brings you a graphic tutorial on how to check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com. Interested users come and take a look! Xuexin.com usage tutorial: How to check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com 1. Xuexin.com entrance: https://www.chsi.com.cn/ 2. Website query: Step 1: Click on the Xuexin.com address above to enter the homepage Click [Education Query]; Step 2: On the latest webpage, click [Query] as shown by the arrow in the figure below; Step 3: Then click [Login Academic Credit File] on the new page; Step 4: On the login page Enter the information and click [Login];
 Windows cannot access the specified device, path, or file
Jun 18, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Windows cannot access the specified device, path, or file
Jun 18, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
A friend's computer has such a fault. When opening "This PC" and the C drive file, it will prompt "Explorer.EXE Windows cannot access the specified device, path or file. You may not have the appropriate permissions to access the project." Including folders, files, This computer, Recycle Bin, etc., double-clicking will pop up such a window, and right-clicking to open it is normal. This is caused by a system update. If you also encounter this situation, the editor below will teach you how to solve it. 1. Open the registry editor Win+R and enter regedit, or right-click the start menu to run and enter regedit; 2. Locate the registry "Computer\HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\PackagedCom\ClassInd"
 Linux Deploy operation steps and precautions
Mar 14, 2024 pm 03:03 PM
Linux Deploy operation steps and precautions
Mar 14, 2024 pm 03:03 PM
LinuxDeploy operating steps and precautions LinuxDeploy is a powerful tool that can help users quickly deploy various Linux distributions on Android devices, allowing users to experience a complete Linux system on their mobile devices. This article will introduce the operating steps and precautions of LinuxDeploy in detail, and provide specific code examples to help readers better use this tool. Operation steps: Install LinuxDeploy: First, install
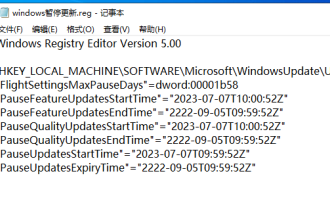 Windows permanently pauses updates, Windows turns off automatic updates
Jun 18, 2024 pm 07:04 PM
Windows permanently pauses updates, Windows turns off automatic updates
Jun 18, 2024 pm 07:04 PM
Windows updates may cause some of the following problems: 1. Compatibility issues: Some applications, drivers, or hardware devices may be incompatible with new Windows updates, causing them to not work properly or crash. 2. Performance issues: Sometimes, Windows updates may cause the system to become slower or experience performance degradation. This may be due to new features or improvements requiring more resources to run. 3. System stability issues: Some users reported that after installing Windows updates, the system may experience unexpected crashes or blue screen errors. 4. Data loss: In rare cases, Windows updates may cause data loss or file corruption. This is why before making any important updates, back up your
 How to update MSI graphics card driver? MSI graphics card driver download and installation steps
Mar 13, 2024 pm 08:49 PM
How to update MSI graphics card driver? MSI graphics card driver download and installation steps
Mar 13, 2024 pm 08:49 PM
MSI graphics cards are the mainstream graphics card brand on the market. We know that graphics cards need to install drivers to achieve performance and ensure compatibility. So how to update the MSI graphics card driver to the latest version? Generally, MSI graphics card drivers can be downloaded and installed from the official website. Let’s find out more below. Graphics card driver update method: 1. First, we enter the "MSI official website". 2. After entering, click the "Search" button in the upper right corner and enter your graphics card model. 3. Then find the corresponding graphics card and click on the details page. 4. Then enter the "Technical Support" option above. 5.Finally go to “Driver & Download”




