How to use LSOF to monitor ports in real time
LSOF (List Open Files) is a command line tool mainly used to monitor system resources similar to Linux/Unix operating systems. Through the LSOF command, users can get detailed information about the active files in the system and the processes that are accessing these files. LSOF can help users identify the processes currently occupying file resources, thereby better managing system resources and troubleshooting possible problems. LSOF is powerful and flexible, and can help system administrators quickly locate file-related problems, such as file leaks, unclosed file descriptors, etc. Via LSOF command
The LSOF command line tool allows system administrators and developers to:
- Determine the process currently using a specific file or port, especially important in the case of port conflicts
- Detect files that have been deleted but are still open by the process, which may cause unnecessary space consumption; the LSOF command is used to identify and resolve such situations
- Helps efficiently troubleshoot errors such as "Port is already in use"
- Track network activity and open network connections for monitoring
- Investigate file access patterns to help identify potential security vulnerabilities
In this tutorial, you will learn how to monitor a live port using the LSOF command.
Basic syntax of LSOF command
The syntax of the LSOF command is as follows:
$lsof [options][name]
The options of the LSOF command are flags used to specify the file-related information to be displayed. These options typically include the filename, process ID, username, or IP address of the network file (IPv4, IPv6). By selecting different options, the LSOF command can list the open files associated with these identifiers.
Use the LSOF command to monitor the port in real time
LSOF is usually preinstalled on many Linux systems. If your system does not have it installed, you may need to manually download and install an available package. You can check the installation of LSOF on your system and see the installed version by running the following command:
$lsof-v
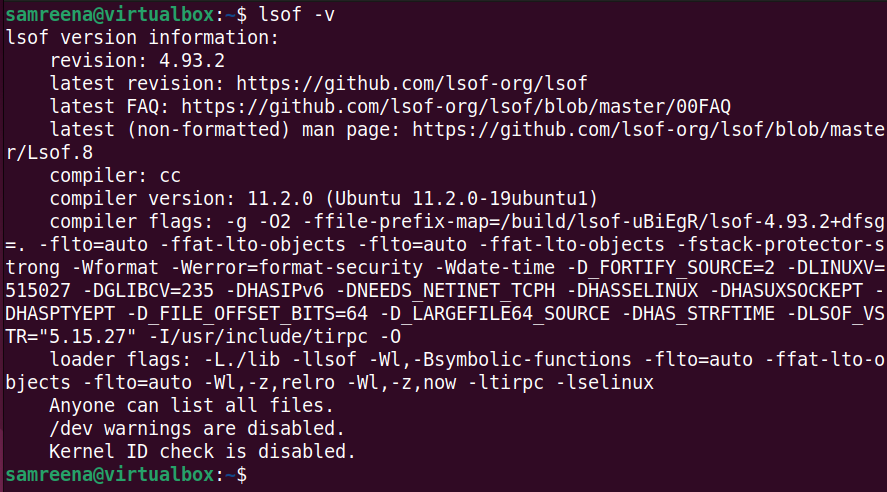
It is important to note that to run LSOF commands with appropriate permissions, you may need to elevate to superuser privileges to obtain specific information about the process and network connections, and you may need to use "sudo" with administrator privileges. Execute this command.
List network files
When you run the LSOF command with the "-i" option, it will display information about processes that have network connections, such as listening sockets or established connections.
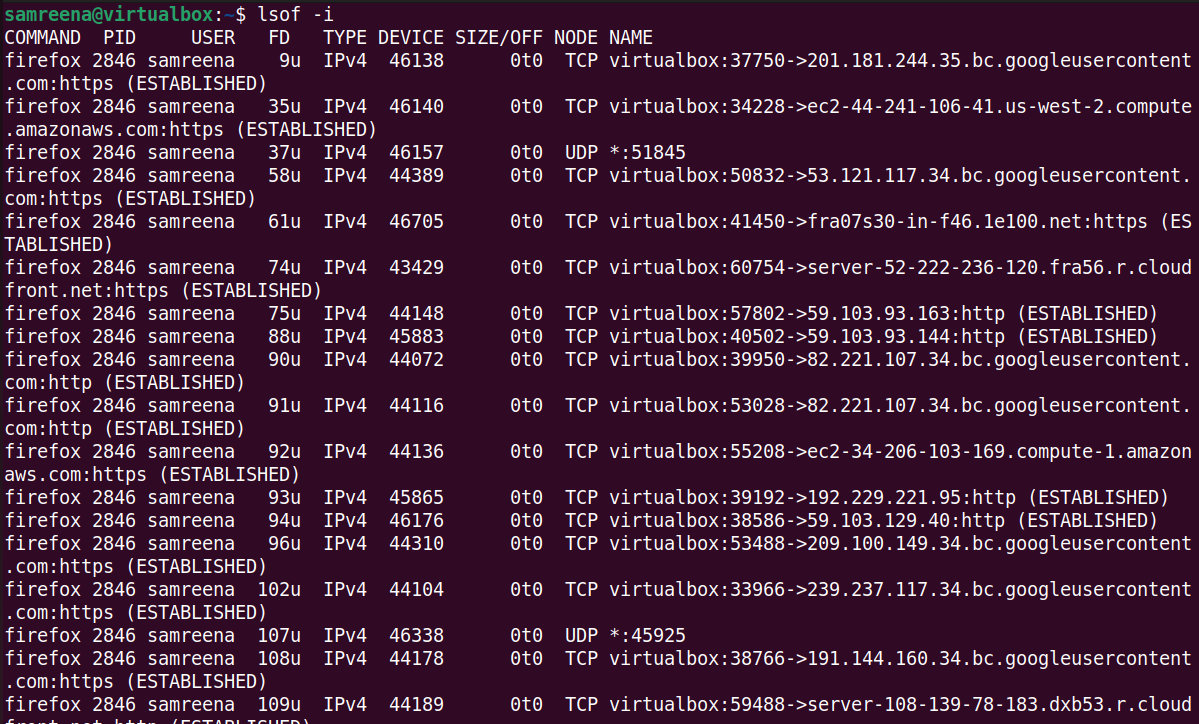
$lsof-i
The previous command displays information about the process name (COMMAND), process ID (PID), user (USER), file descriptor (FD), connection type (TYPE), local and remote addresses, and connection status. You should see the following output:
List TCP connections
You can filter the output based on specific criteria, such as specific types of connections or ports. For example, you can use "lsof --itcp" to list only processes associated with TCP connections.
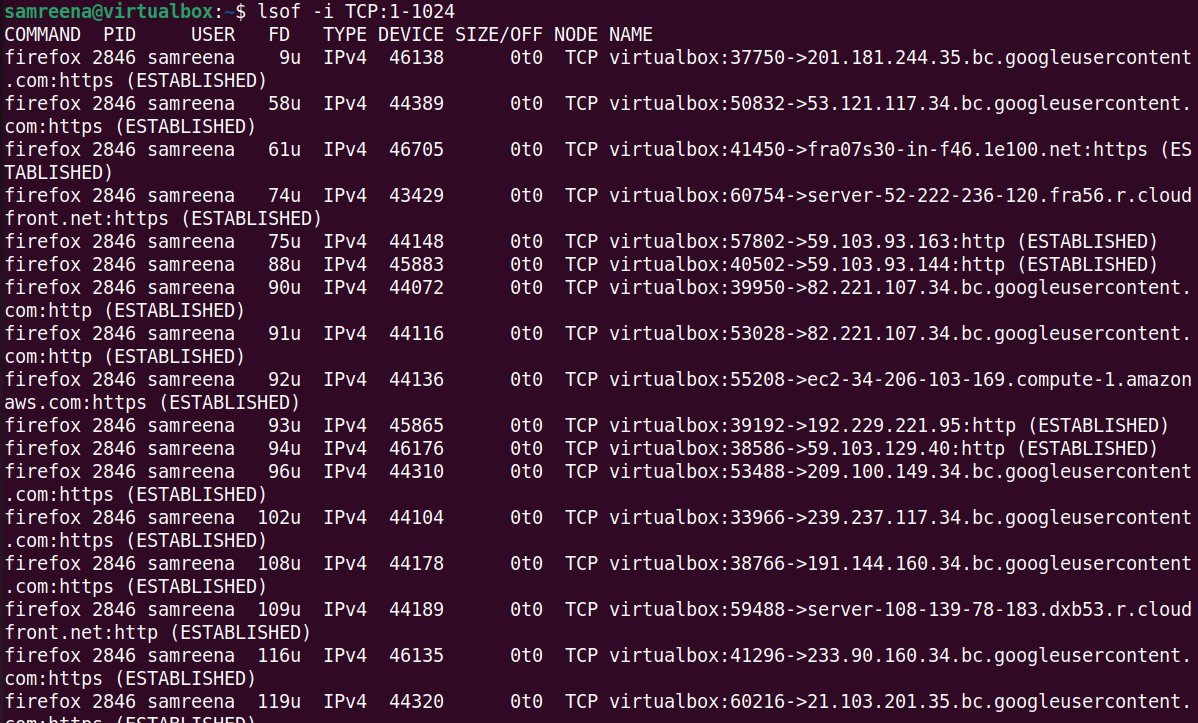
$lsof—i tcp: 1—1024
The previous command filters information about processes opening TCP connections within the specified port range 1 to 1024. This is useful for identifying which processes are using well-known ports associated with public services.
Real-time monitoring of specific ports
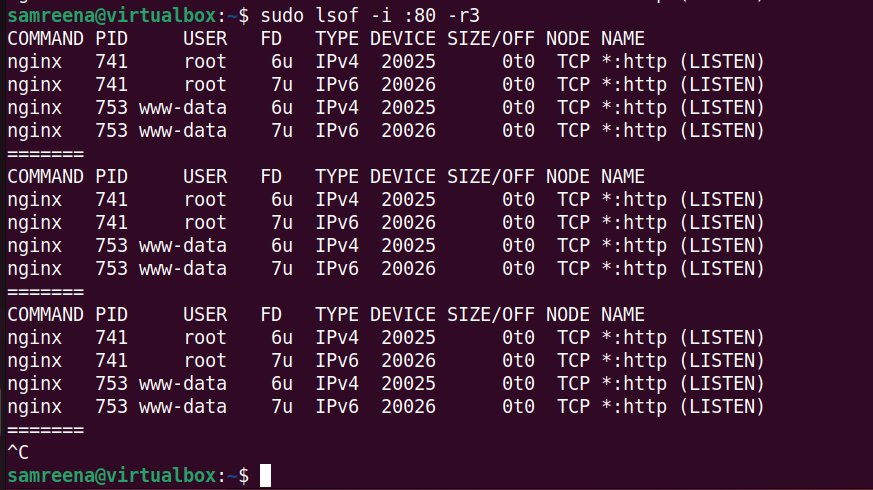
Using LSOF, you can monitor specific ports in real time. For example, you want to monitor processes related to "HTTP" on port 80, which is updated every 3 seconds. To do this, use the following command to monitor port 80 in real time:
$lsof—i:80—r3
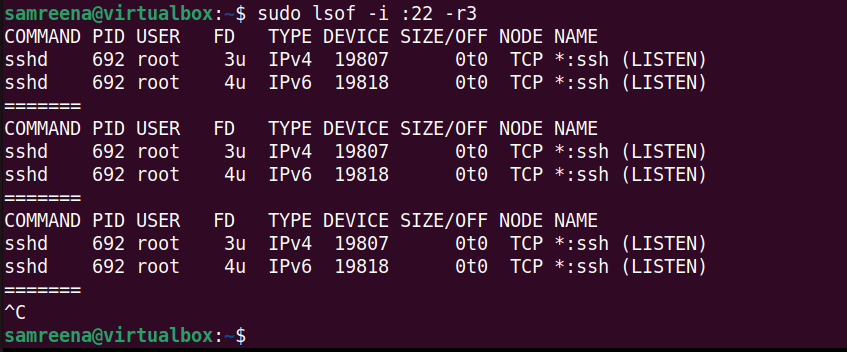
Real-time monitoring of SSHD port 22
To monitor all SSHD connections running on port 22, run the following command:
$sudo lsof -i:22-r3
This command continuously monitors and displays real-time information about network connections on port 22 every 3 seconds. This is especially useful for tracking changes that occur in real time, such as new SSH connections or disconnections.
Real-time monitoring port range
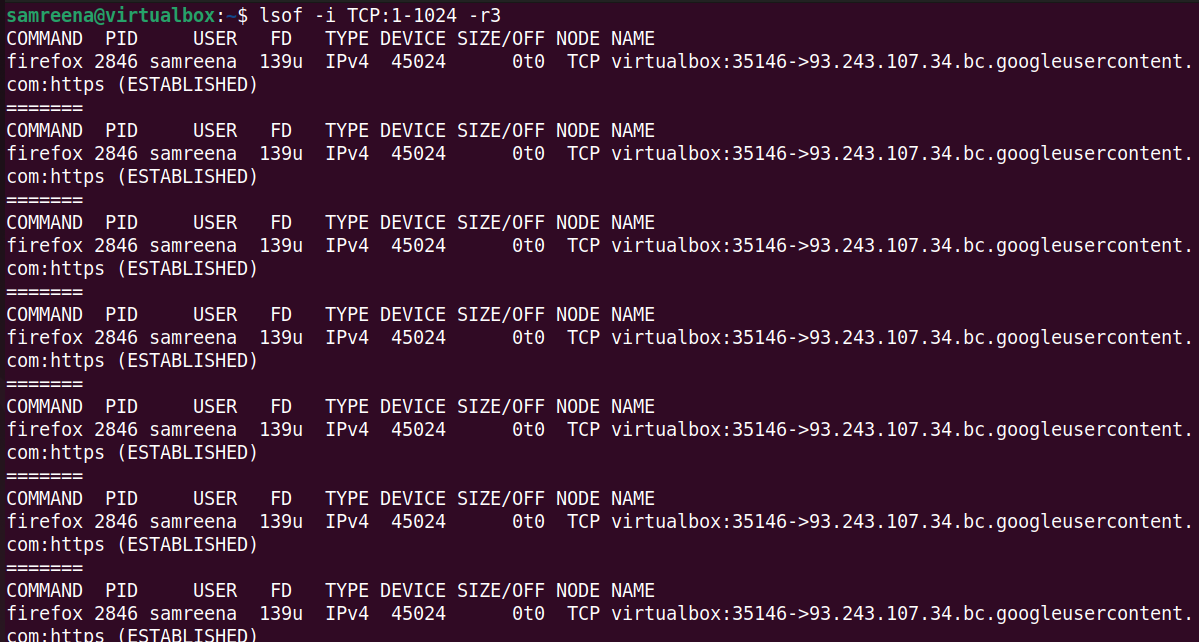
To monitor the information of processes with open TCP connections in the specified port range 1 to 1024 in real time, you can use the following command:
$lsof-i tcp:1-1024-r3
Real-time monitoring of all ports
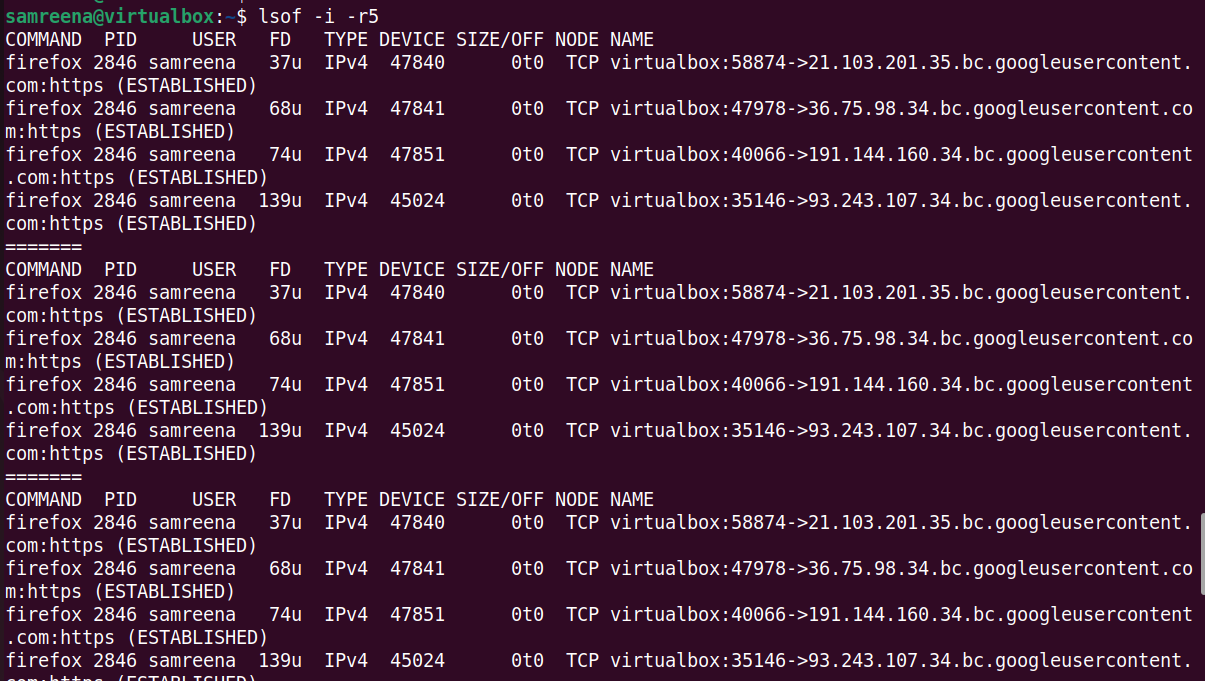
You can use the LSOF command to monitor all network connections in real time. For example, you want to run monitoring continuously and display real-time information about network connections every 5 seconds.
$lsof—i—r5
The following output includes real-time details of the process and its associated network sockets, every 5 seconds:
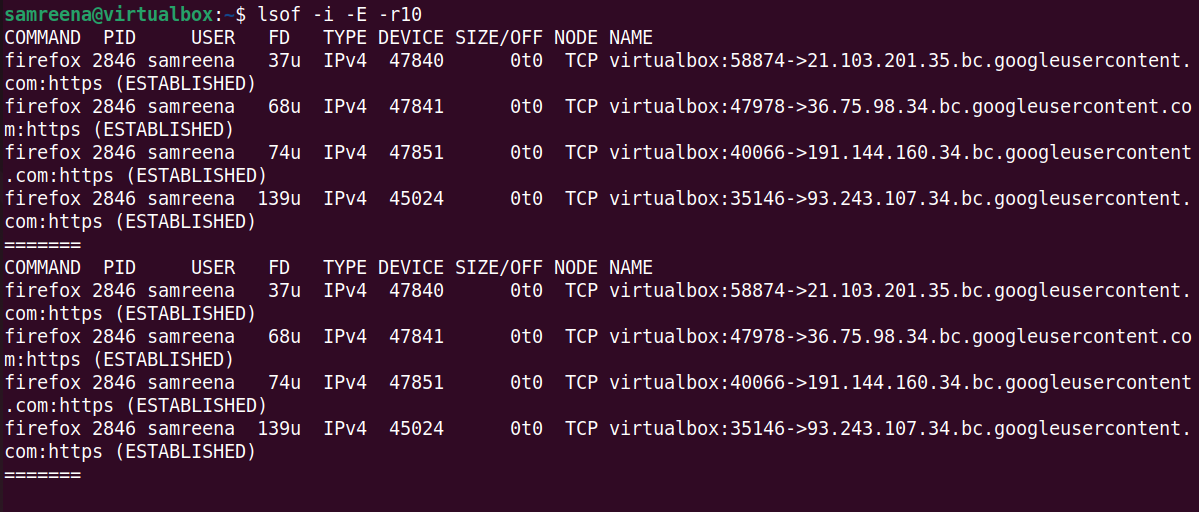
Similarly, you can also use the LSOF command to monitor only "established" connections:
$lsof—i—E—r10
in conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to monitor ports in real time using the LSOF command. This command can also help system administrators and other Linux users monitor network connections, including all active or open ports. We hope this guide will help you understand how to use the LSOF command with different options and monitor different ports and processes in real time.
The above is the detailed content of How to use LSOF to monitor ports in real time. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
![Soundbar detected as monitor screen on Windows PC [Fix]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/170835733166289.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) Soundbar detected as monitor screen on Windows PC [Fix]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:42 PM
Soundbar detected as monitor screen on Windows PC [Fix]
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:42 PM
On Windows PCs, some users have discovered that the Soundbar is recognized as a monitor when connected to the HDMI port. This may cause some confusion, but the solution is not the only one. How to Connect a Soundbar to a PC via HDMI Most soundbars use HDMI, optical, or 3.5mm audio connections. If your soundbar only supports HDMI connections, it must be connected to an HDMI port labeled HDMIARC. Many TVs or monitors are usually equipped with multiple HDMI ports, one of which should support the ARC protocol that complies with the HDMI standard. In other words, HDMI is an interface used to transmit audio and video. If the device does not have an HDMI port, consider using a monitor.
 How to run SUDO commands in Windows 11/10
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:50 AM
How to run SUDO commands in Windows 11/10
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:50 AM
The sudo command allows users to run commands in elevated privilege mode without switching to superuser mode. This article will introduce how to simulate functions similar to sudo commands in Windows systems. What is the Shudao Command? Sudo (short for "superuser do") is a command-line tool that allows users of Unix-based operating systems such as Linux and MacOS to execute commands with elevated privileges typically held by administrators. Running SUDO commands in Windows 11/10 However, with the launch of the latest Windows 11 Insider preview version, Windows users can now experience this feature. This new feature enables users to
 How to check the MAC address of the network card in Win11? How to use the command to obtain the MAC address of the network card in Win11
Feb 29, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
How to check the MAC address of the network card in Win11? How to use the command to obtain the MAC address of the network card in Win11
Feb 29, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
This article will introduce readers to how to use the command prompt (CommandPrompt) to find the physical address (MAC address) of the network adapter in Win11 system. A MAC address is a unique identifier for a network interface card (NIC), which plays an important role in network communications. Through the command prompt, users can easily obtain the MAC address information of all network adapters on the current computer, which is very helpful for network troubleshooting, configuring network settings and other tasks. Method 1: Use "Command Prompt" 1. Press the [Win+X] key combination, or [right-click] click the [Windows logo] on the taskbar, and in the menu item that opens, select [Run]; 2. Run the window , enter the [cmd] command, and then
 Super practical! Sar commands that will make you a Linux master
Mar 01, 2024 am 08:01 AM
Super practical! Sar commands that will make you a Linux master
Mar 01, 2024 am 08:01 AM
1. Overview The sar command displays system usage reports through data collected from system activities. These reports are made up of different sections, each containing the type of data and when the data was collected. The default mode of the sar command displays the CPU usage at different time increments for various resources accessing the CPU (such as users, systems, I/O schedulers, etc.). Additionally, it displays the percentage of idle CPU for a given time period. The average value for each data point is listed at the bottom of the report. sar reports collected data every 10 minutes by default, but you can use various options to filter and adjust these reports. Similar to the uptime command, the sar command can also help you monitor the CPU load. Through sar, you can understand the occurrence of excessive load
 Where is hyperv enhanced session mode? Tips for enabling or disabling Hyper-V enhanced session mode using commands in Win11
Feb 29, 2024 pm 05:52 PM
Where is hyperv enhanced session mode? Tips for enabling or disabling Hyper-V enhanced session mode using commands in Win11
Feb 29, 2024 pm 05:52 PM
In Win11 system, you can enable or disable Hyper-V enhanced session mode through commands. This article will introduce how to use commands to operate and help users better manage and control Hyper-V functions in the system. Hyper-V is a virtualization technology provided by Microsoft. It is built into Windows Server and Windows 10 and 11 (except Home Edition), allowing users to run virtual operating systems in Windows systems. Although virtual machines are isolated from the host operating system, they can still use the host's resources, such as sound cards and storage devices, through settings. One of the key settings is to enable Enhanced Session Mode. Enhanced session mode is Hyper
 Fix AHCI Port 0 Device Error on Windows Computer
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
Fix AHCI Port 0 Device Error on Windows Computer
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
If you encounter an AHCI port 0 device error every time you start your computer, you need to follow the methods provided in this article to solve the problem. What is AHCI port 0 device error? AHCI device errors are reported by the BIOS. SMART has indicated that the hard drive on port 0 is faulty and may not be accessible. The hard drive may have problems at any time. If it is a desktop computer, it is recommended to try changing the hard drive connection port. If the problem persists, it may be a problem with the hard drive itself. You can run a disk check tool, disable the failed hard drive and check the ports to resolve this issue. Fixing AHCI Port 0 Device Errors on Windows Computers Typically, AHCI Port0 device errors do not originate from operating system issues, but rather from the hard drive failing on port 0.
 What is the correct way to restart a service in Linux?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:09 AM
What is the correct way to restart a service in Linux?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:09 AM
What is the correct way to restart a service in Linux? When using a Linux system, we often encounter situations where we need to restart a certain service, but sometimes we may encounter some problems when restarting the service, such as the service not actually stopping or starting. Therefore, it is very important to master the correct way to restart services. In Linux, you can usually use the systemctl command to manage system services. The systemctl command is part of the systemd system manager
 Artifact in Linux: Principles and Applications of eventfd
Feb 13, 2024 pm 08:30 PM
Artifact in Linux: Principles and Applications of eventfd
Feb 13, 2024 pm 08:30 PM
Linux is a powerful operating system that provides many efficient inter-process communication mechanisms, such as pipes, signals, message queues, shared memory, etc. But is there a simpler, more flexible, and more efficient way to communicate? The answer is yes, that is eventfd. eventfd is a system call introduced in Linux version 2.6. It can be used to implement event notification, that is, to deliver events through a file descriptor. eventfd contains a 64-bit unsigned integer counter maintained by the kernel. The process can read/change the counter value by reading/writing this file descriptor to achieve inter-process communication. What are the advantages of eventfd? It has the following features




