 Computer Tutorials
Computer Tutorials
 Computer Knowledge
Computer Knowledge
 JWT, Session, SSO, OAuth2.0 comparison: analysis of scenarios, advantages and disadvantages
JWT, Session, SSO, OAuth2.0 comparison: analysis of scenarios, advantages and disadvantages
JWT, Session, SSO, OAuth2.0 comparison: analysis of scenarios, advantages and disadvantages
In modern web applications and distributed systems, identity authentication and authorization are key links to ensure system security. JWT (JSON Web Tokens), Session, SSO (Single Sign-On, single sign-on) and OAuth2.0 are four common identity authentication and authorization mechanisms, each of which has different application scenarios, advantages and disadvantages. This article will conduct a comparative analysis of these four mechanisms so that readers can better understand and choose an authentication and authorization solution that suits their business needs.

1. JWT (JSON Web Tokens)
JWT is an open standard (RFC 7519) for securely transmitting information between two parties. These messages can be verified and trusted because they are digitally signed. JWT can be signed using the HMAC algorithm or RSA public and private key pairs to ensure the integrity and security of the information.
Scenario: JWT is often used for stateless authentication, authentication between different services in distributed systems, and as an API key for API authentication and authorization.
advantage:
- Stateless: The server does not save any session information, so it can be easily expanded horizontally.
- Cross-domain: JWT can be easily transmitted between different domain names without additional CORS configuration.
- Security: JWT can ensure the integrity and authenticity of data through digital signatures.
shortcoming:
- Validity management: Once a JWT is issued, its validity is usually controlled by the client, and it is difficult for the server to actively invalidate it.
- Sensitive information leakage: If the JWT contains sensitive information and is not encrypted, there may be a risk of information leakage.
2. Session
Session is a server-based authentication method. After the user logs in, the server will create a unique Session ID and store it on the server and client (usually through cookies). In subsequent requests, the client passes the Session ID, which the server can use to identify the user. In this way, the server is able to track the user's session state to ensure that the user remains logged in during the same session. The use of Session helps to enhance the security of the system because each Session ID is unique, providing an effective method to authenticate the user's identity and restrict access to protected resources. At the same time, through the Session mechanism, the server can also clear session information in time after the user activity ends, improving the efficiency and security of the system.
Scenario: Session is suitable for traditional web applications, especially those that need to maintain user status.
advantage:
- State management: The server can easily manage the user's session state.
- Security: Session IDs are usually shorter and can be encrypted for transmission via HTTPS, reducing the risk of interception.
shortcoming:
- Scalability: The Session mechanism relies on server-side storage, so there may be challenges in horizontal expansion.
- Cross-domain problem: Session ID is usually bound to a specific domain name, making cross-domain use difficult.
3. SSO (Single Sign-On, single sign-on)
SSO is an identity authentication method that allows users to access all mutually trusted applications or services by logging in once across multiple applications or services.
Scenario: SSO is suitable for the integration of multiple applications or services within the enterprise, as well as the integration of third-party applications.
advantage:
- Improve user experience: Users only need to log in once to access multiple applications.
- Reduce management costs: Unified identity management reduces the cost of maintaining multiple user accounts.
shortcoming:
- Complex architecture: Implementing SSO requires building a unified authentication center and handling trust relationships between different applications.
- Security challenges: SSO involves data sharing between multiple applications, which may increase security risks.
4. OAuth2.0
OAuth2.0 is an open standard that allows third-party applications to use the resource owner's authorization to obtain limited access to resources owned by the resource owner.
Scenario: OAuth2.0 is often used by third-party applications to access user resources (such as WeChat login, Weibo sharing, etc.).
advantage:
- Authorization flexibility: OAuth2.0 supports a variety of authorization processes, including authorization code mode, password mode, client mode, etc., to meet the needs of different scenarios.
- Security: OAuth2.0 implements resource access through access tokens. The tokens are time-sensitive and can limit the access scope.
shortcoming:
- Complexity: The authorization process of OAuth2.0 is relatively complex, and errors and exceptions in various authorization processes need to be correctly handled.
- Security Challenges: If tokens are not managed properly, there may be a risk of misuse or theft.
5. Summary
JWT, Session, SSO and OAuth2.0 each have different application scenarios, advantages and disadvantages. When selecting an identity authentication and authorization solution, comprehensive considerations need to be made based on business needs, system architecture, and security requirements. At the same time, no matter which solution is adopted, security issues should be taken seriously and appropriate security measures should be taken to protect user data and system security.
The above is the detailed content of JWT, Session, SSO, OAuth2.0 comparison: analysis of scenarios, advantages and disadvantages. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Three secrets for deploying large models in the cloud
Apr 24, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Three secrets for deploying large models in the cloud
Apr 24, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Compilation|Produced by Xingxuan|51CTO Technology Stack (WeChat ID: blog51cto) In the past two years, I have been more involved in generative AI projects using large language models (LLMs) rather than traditional systems. I'm starting to miss serverless cloud computing. Their applications range from enhancing conversational AI to providing complex analytics solutions for various industries, and many other capabilities. Many enterprises deploy these models on cloud platforms because public cloud providers already provide a ready-made ecosystem and it is the path of least resistance. However, it doesn't come cheap. The cloud also offers other benefits such as scalability, efficiency and advanced computing capabilities (GPUs available on demand). There are some little-known aspects of deploying LLM on public cloud platforms
 What are web standards?
Oct 18, 2023 pm 05:24 PM
What are web standards?
Oct 18, 2023 pm 05:24 PM
Web standards are a set of specifications and guidelines developed by W3C and other related organizations. It includes standardization of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, DOM, Web accessibility and performance optimization. By following these standards, the compatibility of pages can be improved. , accessibility, maintainability and performance. The goal of web standards is to enable web content to be displayed and interacted consistently on different platforms, browsers and devices, providing better user experience and development efficiency.
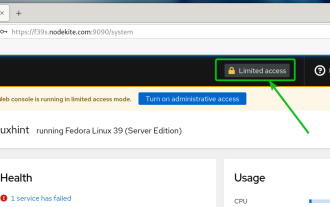 How to enable administrative access from the cockpit web UI
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
How to enable administrative access from the cockpit web UI
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
Cockpit is a web-based graphical interface for Linux servers. It is mainly intended to make managing Linux servers easier for new/expert users. In this article, we will discuss Cockpit access modes and how to switch administrative access to Cockpit from CockpitWebUI. Content Topics: Cockpit Entry Modes Finding the Current Cockpit Access Mode Enable Administrative Access for Cockpit from CockpitWebUI Disabling Administrative Access for Cockpit from CockpitWebUI Conclusion Cockpit Entry Modes The cockpit has two access modes: Restricted Access: This is the default for the cockpit access mode. In this access mode you cannot access the web user from the cockpit
 PHP 401 response: Resolve Unauthorized errors and enhance security
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
PHP 401 response: Resolve Unauthorized errors and enhance security
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:15 PM
In web development, a 401 Unauthorized error means that the client is not authorized to access a specific resource. PHP provides multiple processing methods: 1. Use 401 HTTP status code; 2. Output JSON response; 3. Redirect to the login page. To enhance security, you can take the following measures: 1. Use HTTPS; 2. Enable CSRF protection; 3. Implement input validation; 4. Use an authorization framework.
 what does web mean
Jan 09, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
what does web mean
Jan 09, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
The web is a global wide area network, also known as the World Wide Web, which is an application form of the Internet. The Web is an information system based on hypertext and hypermedia, which allows users to browse and obtain information by jumping between different web pages through hyperlinks. The basis of the Web is the Internet, which uses unified and standardized protocols and languages to enable data exchange and information sharing between different computers.
 Is PHP front-end or back-end in web development?
Mar 24, 2024 pm 02:18 PM
Is PHP front-end or back-end in web development?
Mar 24, 2024 pm 02:18 PM
PHP belongs to the backend in web development. PHP is a server-side scripting language, mainly used to process server-side logic and generate dynamic web content. Compared with front-end technology, PHP is more used for back-end operations such as interacting with databases, processing user requests, and generating page content. Next, specific code examples will be used to illustrate the application of PHP in back-end development. First, let's look at a simple PHP code example for connecting to a database and querying data:
 Azure JWT validation in Go not working
Feb 09, 2024 am 11:12 AM
Azure JWT validation in Go not working
Feb 09, 2024 am 11:12 AM
I have a gohttp server. I want to secure my routes using azurejwt token. I am able to generate the token but cannot verify it. This is what I do: packagemainimport("context""errors""fmt""github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go""github.com/lestrrat-go/jwx/jwa""github.com/lestrrat-go/ jwx/jwk"njwt"github.com
 How to use TLS 1.2 with MySql Go driver?
Feb 10, 2024 am 09:40 AM
How to use TLS 1.2 with MySql Go driver?
Feb 10, 2024 am 09:40 AM
We have to use tls1.2 to connect to our mysql server. In our java application we use the following jdbcurl-jdbc:mysql://xxxx-001-dev.cluster-xx-2.rds.amazonaws.com/bats?**enabledtlsprotocols=tlsv1.2** in our When connecting to mysql in my go application, I cannot achieve a similar configuration - cfg1:=mysql.config{user:"adm



