 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 GitHub's latest AI tool helps users automatically fix bugs and vulnerabilities in their code
GitHub's latest AI tool helps users automatically fix bugs and vulnerabilities in their code
GitHub's latest AI tool helps users automatically fix bugs and vulnerabilities in their code

Today, GitHub launched a new "Code Scan" feature (preview) for all Advanced Security (GHAS) licensed users, designed to help users discover in GitHub code Potential security vulnerabilities and coding errors.

This new feature leverages Copilot and CodeQL to detect potential vulnerabilities or errors in your code, classify them, and prioritize remediation. It's important to note that Code Scan will consume GitHub Actions minutes.
According to the introduction, "code scanning" can not only prevent developers from introducing new problems, but can also trigger scanning based on specific dates and times, or when specific events (such as pushes) occur in the repository.
If AI discovers that there may be a vulnerability or error in your code, GitHub will issue an alert in the repository and cancel the alert after the user fixes the code that triggered the alert.
To monitor the code scanning results of your repository or organization, you can take advantage of web hooks and the code scanning API. Additionally, code scanning can interoperate with third-party code scanning tools by exchanging output in the Static Analysis Results Data Format (SARIF).
Currently, there are three main ways to use CodeQL analysis for CodeScan:
- Quickly configure CodeQL analysis for CodeScan on your repository using default settings. The default settings automatically select the languages to analyze, the query suites to run, and the events that trigger the scan, but you can manually select the query suites to run and the languages to analyze if needed. When CodeQL is enabled, GitHub Actions will perform a workflow run to scan your code.
- Add a CodeQL workflow to the repository using advanced settings. This generates a customizable workflow file that uses github/codeql-action to run the CodeQL CLI.
- Run the CodeQL CLI directly in an external CI system and upload the results to GitHub.
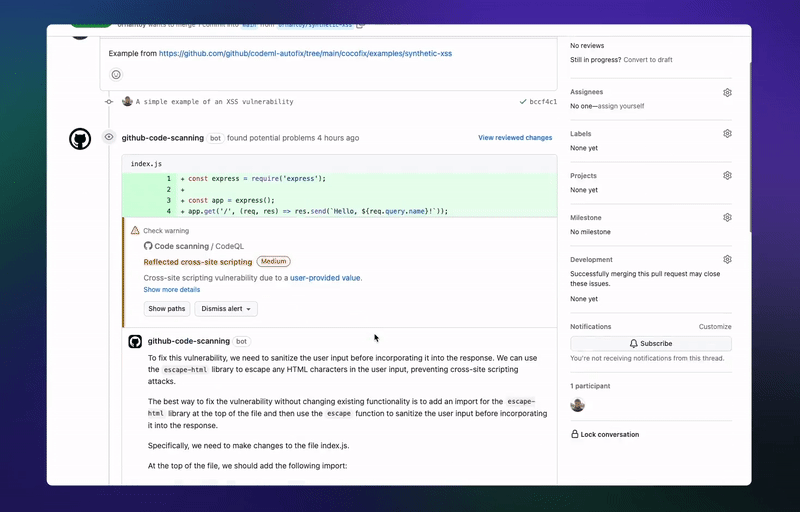
GitHub promises that this AI system can fix more than two-thirds of the vulnerabilities it finds, so developers generally don't need to actively edit the code. The company also promises that code scanning automatic remediation will cover more than 90% of alert types in its supported languages, which currently includes JavaScript, Typescript, Java, and Python.
Reference materials:
The above is the detailed content of GitHub's latest AI tool helps users automatically fix bugs and vulnerabilities in their code. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C? Answer: Use loop statements. Steps: 1. Define the variable n and store the countdown number to output; 2. Use the while loop to continuously print n until n is less than 1; 3. In the loop body, print out the value of n; 4. At the end of the loop, subtract n by 1 to output the next smaller reciprocal.
 How to play picture sequences smoothly with CSS animation?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
How to play picture sequences smoothly with CSS animation?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
How to achieve the playback of pictures like videos? Many times, we need to implement similar video player functions, but the playback content is a sequence of images. direct...
 How to implement nesting effect of text annotations in Quill editor?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:21 PM
How to implement nesting effect of text annotations in Quill editor?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:21 PM
A solution to implement text annotation nesting in Quill Editor. When using Quill Editor for text annotation, we often need to use the Quill Editor to...
 Zustand asynchronous operation: How to ensure the latest state obtained by useStore?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Zustand asynchronous operation: How to ensure the latest state obtained by useStore?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Data update problems in zustand asynchronous operations. When using the zustand state management library, you often encounter the problem of data updates that cause asynchronous operations to be untimely. �...
 How to quickly build a foreground page in a React Vite project using AI tools?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 01:45 PM
How to quickly build a foreground page in a React Vite project using AI tools?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 01:45 PM
How to quickly build a front-end page in back-end development? As a backend developer with three or four years of experience, he has mastered the basic JavaScript, CSS and HTML...
 Electron rendering process and WebView: How to achieve efficient 'synchronous' communication?
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:45 AM
Electron rendering process and WebView: How to achieve efficient 'synchronous' communication?
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:45 AM
Electron rendering process and WebView...
 How to use CSS to achieve smooth playback effect of image sequences?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 04:57 PM
How to use CSS to achieve smooth playback effect of image sequences?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 04:57 PM
How to realize the function of playing pictures like videos? Many times, we need to achieve similar video playback effects in the application, but the playback content is not...
 How to achieve the effect of high input elements but high text at the bottom?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
How to achieve the effect of high input elements but high text at the bottom?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
How to achieve the height of the input element is very high but the text is located at the bottom. In front-end development, you often encounter some style adjustment requirements, such as setting a height...





