How to partition on Debian 12

In Debian 12, there are various graphical and command line tools available for partitioning disks. This article will introduce some common tools that you can use to partition storage devices such as hard drives/SSDs on Debian 12. These tools provide flexibility and control, allowing you to easily manage disk space according to your needs. With these tools, you can effectively divide disk space, create partitions for different purposes, and ensure the security and reliability of your data. Whether you prefer graphical interface or command line operation, Debian 12 provides suitable tools to allow you to perform disk partitioning operations according to your preferences and needs.
Content topic:
- Common disk partitioning programs for Debian 12
- Disk partitioning using GNOME Disk Utility
- Use GParted for disk partitioning
- Use Parted for disk partitioning
- Use Fdisk for disk partitioning
- Use CfDisk for disk partitioning
- in conclusion
- references
Common disk partitioning programs for Debian 12
Some common GUI (graphical user interface) disk partitioning programs on Debian 12 are:
- GNOME Disk Utility or GNOME NTFS
- GParted
Some common command line disk partitioning programs available on Debian 12 include:
- Detached
- FDisk
- cfdisk
In our list of disk partitioning programs, we consider the following beginner-friendly or easy-to-use disk partitioning programs:
- GNOME Disk Utility or GNOME NTFS (GUI)
- cfdisk (command line)
Use GNOME Disk Utility for disk partitioning
GNOME Disk Utility is the default disk partitioning tool for the GNOME desktop environment, providing a simple and easy-to-use user interface. You can easily use it to manage disk partitions when using the GNOME desktop environment on Debian 12. Through this article, you can learn how to use GNOME Disk to partition storage devices.
On the Debian 12 operating system, if the desktop environment you are using does not include GNOME Disk, you can execute the following command to install it.
$sudo apt update
$sudo apt install gnome—disk—utility
A screenshot of the GNOME Disks application looks like this:
Use GParted for disk partitioning
GParted is an advanced graphical partitioning tool built on the parted command line program. It offers many advanced features, although the user interface is not as user-friendly as GNOME Acrobat. For beginners, GParted's various features and options can be overwhelming.
If you need to do some advanced partitioning that GNOME NTFS cannot do, you may want to use GParted. To learn how to use GParted to partition a disk on Debian 12 operating system, read this article.
Debian 12 does not install GParted by default. To install GParted on Debian 12, run the following command:
$sudo apt update
$sudo apt install gparted
A screenshot of GParted looks like this:
Use Parted for disk partitioning
Parted is an advanced terminal-based partitioning program. It's packed with advanced features and targeted at advanced users (who like the Linux command line).
If you need to perform some advanced partitioning from the command line, check out Parted. To learn how to partition a disk from the command line using Parted on Debian 12 operating system, read this article.
Parted is not installed on Debian 12 by default. To install Parted on Debian 12, run the following command:
$sudo apt update
$sudo apt install parted
A screenshot of running Parted from the command line is shown below:
Use Fdisk for disk partitioning
fdisk is also an advanced terminal-based partitioning program. Its text-based user interface is easier for beginners to understand and use than Parted. Although it has fewer features than Parted/GParted, it is still capable of performing many disk partitioning tasks.
To learn how to partition a disk from the command line using fdisk on Debian 12 operating system, read this article.
By default, fdisk is installed on Debian 12 server and desktop operating systems. So you don't have to install it manually.
A screenshot of running fdisk from the command line is as follows:
Use CfDisk for disk partitioning
cfdisk is a terminal-based partitioning program. This is a stripped down version of fdisk. It doesn't have many features, but it's enough to do basic disk partitioning. cfdisk has an easy-to-use text-based user interface. This is a great disk partitioning program for beginners as well as advanced users.
To learn how to partition a disk from the command line using cfdisk on Debian 12 operating system, read this article.
Cfdisk is part of fdisk. Therefore, it is installed by default on Debian 12 server and desktop operating systems. No manual installation required.
A screenshot of running cfdisk from the command line is shown below:
in conclusion
In this article, we discussed some of the graphical user interface and command line disk partitioning programs available on Debian 12 that can be used to partition computer disks. Among these disk partitioning programs, GNOME Disk Utility or GNOME Disk and cfdisk has a very simple and clear user interface (UI). GParted, Parted and fDisk have many advanced features and are mainly aimed at advanced users. fDisk is easier to use than GParted and Parted.
The above is the detailed content of How to partition on Debian 12. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to install Snap on Debian 12
Mar 20, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
How to install Snap on Debian 12
Mar 20, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Snap is an external package manager designed for Linux systems that provides you with a convenient way to install containerized applications. Snap allows you to easily download and install packages without worrying about installing additional dependencies. The manager automatically resolves the dependencies required by the package, ensuring that the package runs smoothly on your system. Snap complements the native apt package manager, giving you another option for installing and running applications on your system. In this guide, you will find a complete guide on how to install Snap on Debian12. Outline: How to install Snap on Debian12 How to find package availability on Snap How to find information about packages on Snap
 How to install Steam on Debian 12
Mar 21, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
How to install Steam on Debian 12
Mar 21, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
STEAM is a popular gaming platform developed by Valve Corporation that allows you to buy, download, install and play games. It provides features such as automatic updates, matchmaking, and a community forum to resolve software-related issues. In addition to this, you can also use Steam to interact with other players and developers as it has extensive community support. In this guide you will learn: How to install Steam on Debian12 How to run Steam on Debian12 How to remove Steam from Debian12 Conclusion How to install Steam on Debian12 You can install Steam on Debian12: Debian Official Repository deb packages
 Debian installation of Wine and Debian installation of Wine tutorial
Feb 12, 2024 am 10:36 AM
Debian installation of Wine and Debian installation of Wine tutorial
Feb 12, 2024 am 10:36 AM
Wine is a compatibility layer that can run Windows applications on Linux systems. It allows users to seamlessly run Windows applications on Linux systems without the need for dual-system installation or virtual machine setup. This article will introduce how to run Windows applications on Debian systems. Install Wine and provide some related tutorials. Installing Wine Installing Wine on a Debian system is very simple, just use the apt command, open a terminal, and enter the following command: ```shellsudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallwine```This will update your package list and install Wine , after the installation is complete, you can
 win11 disk partition tutorial
Jan 10, 2024 am 08:57 AM
win11 disk partition tutorial
Jan 10, 2024 am 08:57 AM
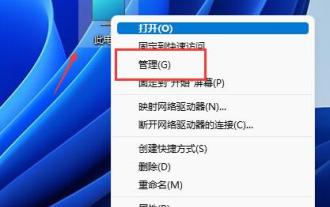
Sometimes the system's default partition cannot meet our needs. At this time, we need to manually partition the win11 disk. We only need to open the disk manager to easily modify the partition. How to partition a win11 disk: 1. First, right-click "This Computer" and open Computer "Management" 2. Then enter "Disk Management" under the storage option on the left 3. Then check the disk status on the right to see if there is available space. (If there is free space, skip to step 6) 4. If there is no free space, right-click the disk with space and select "Compress Volume" 5. Then select the amount of space that needs to be freed and click "Compress" 6. When the compression is completed The available space will appear. Right-click it and select "New Simple Volume" 7. Then enter the desired simple volume size and click "Next Page" 8.
 A complete guide to installing Debian and deb files under Windows
Feb 14, 2024 pm 11:03 PM
A complete guide to installing Debian and deb files under Windows
Feb 14, 2024 pm 11:03 PM
Installing Debian in Windows systems and installing deb files directly in Windows are ways for many Linux enthusiasts to explore dual systems or try new software. This article will detail the steps and precautions for these two installation methods. Installing Debian under Windows To install Debian in a Windows system, you usually need to use virtual machine software, such as VirtualBox. The following are the specific steps: 1. Download and install VirtualBox, which is a free virtualization software that can run on the same computer. Multiple operating systems. 2. Download the Debian ISO image file. You can find the download link on the Debian official website. 3. in
 Ubuntu system disk partition scheme design and practical experience sharing
Feb 12, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
Ubuntu system disk partition scheme design and practical experience sharing
Feb 12, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
As an open source operating system, Ubuntu is very popular on both servers and personal computers. Disk partitioning is a very important step when installing Ubuntu. A reasonable disk partitioning scheme can improve the performance and stability of the system, and at the same time To better manage data and files, this article will share some experience in the design and practice of Ubuntu system disk partitioning scheme, and how to partition the disk on Ubuntu20.04. Ubuntu20.04 disk partition Ubuntu20.04 is the latest long-term support version, which introduces many new features and improvements. Before doing disk partitioning, we first need to understand some basic concepts. 1. Primary partition and extended partition: The primary partition is used to install
 Detailed guide to installing GCC and GCC10 on Debian
Feb 10, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Detailed guide to installing GCC and GCC10 on Debian
Feb 10, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Debian is a popular Linux distribution, widely used in servers and desktop systems. GCC (GNUCompilerCollection) is an open source compiler suite used to compile C, C++, Fortran and other programming languages. In the Debian system, Installing GCC and GCC10 is very simple. This article will provide you with a detailed installation guide. Install GCC1. Open Terminal and use the following command to update the package list: ```shellsudoaptupdate``` 2. Install GCC and its related tools: sudoaptinstallbuild-essential This command will install
 How to add desktop shortcut icon on Debian11
Jan 09, 2024 am 10:06 AM
How to add desktop shortcut icon on Debian11
Jan 09, 2024 am 10:06 AM
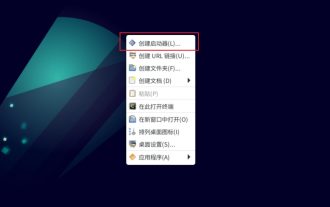
How to create application shortcuts on the desktop in Debian11? Windows system installation programs generally create application shortcuts on the desktop. How to create them in Debian11? Let’s take a look at the detailed tutorial below. Right-click on a blank space on the desktop and select [Create Launcher]. In the pop-up interface, set the program to create a shortcut in [Command]. The editor takes the terminal emulator as an example. The user can set the icon by himself. After the setting is completed, click [Create]. Then you can see the shortcut, as shown in the picture below. When the shortcut is no longer needed, right-click on the icon and select [Delete].






