 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 DeepMind ends the illusion of large models? Labeling facts is more reliable than humans, 20 times cheaper, and fully open source
DeepMind ends the illusion of large models? Labeling facts is more reliable than humans, 20 times cheaper, and fully open source
DeepMind ends the illusion of large models? Labeling facts is more reliable than humans, 20 times cheaper, and fully open source
The illusion of big models is finally coming to an end?
Today, a post on the social media platform Reddit caused heated discussions among netizens. The post discusses a paper "Long-form factuality in large language models" submitted by Google DeepMind yesterday. The methods and results proposed in the article make people conclude that the illusion of large language models is no longer a problem. .

We know that large language models often generate statements containing factual errors when responding to open-ended fact-seeking questions. content. DeepMind has conducted some exploratory research into this phenomenon.
To benchmark a model's long-form factuality in the open domain, the researchers used GPT-4 to generate LongFact, a prompt containing 38 topics and thousands of questions. set. They then proposed using the Search Augmented Fact Evaluator (SAFE) to use the LLM agent as an automatic evaluator of long-form factuality. The purpose of SAFE is to improve the accuracy of factual credibility evaluators.
Regarding SAFE, using LLM can explain the accuracy of each instance more accurately. This multi-step reasoning process involves sending a search query to Google Search and determining whether the search results support a certain instance.

Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.18802.pdf
GitHub Address: https://github.com/google-deepmind/long-form-factuality
In addition, the researcher proposed to expand the F1 score (F1@K) into a long-form practical Aggregation indicators. They balance the percentage of facts supported in the response (precision) with the percentage of facts provided relative to a hyperparameter that represents the user's preferred response length (recall).
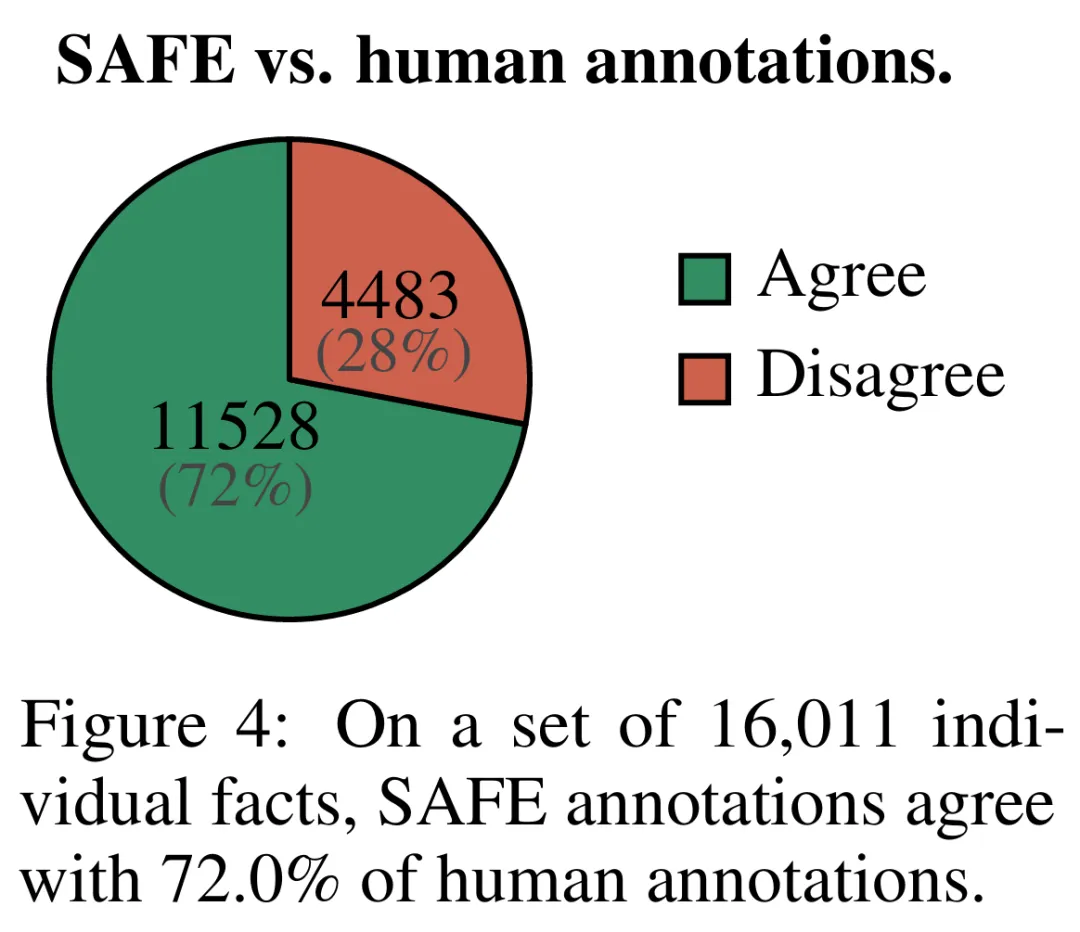
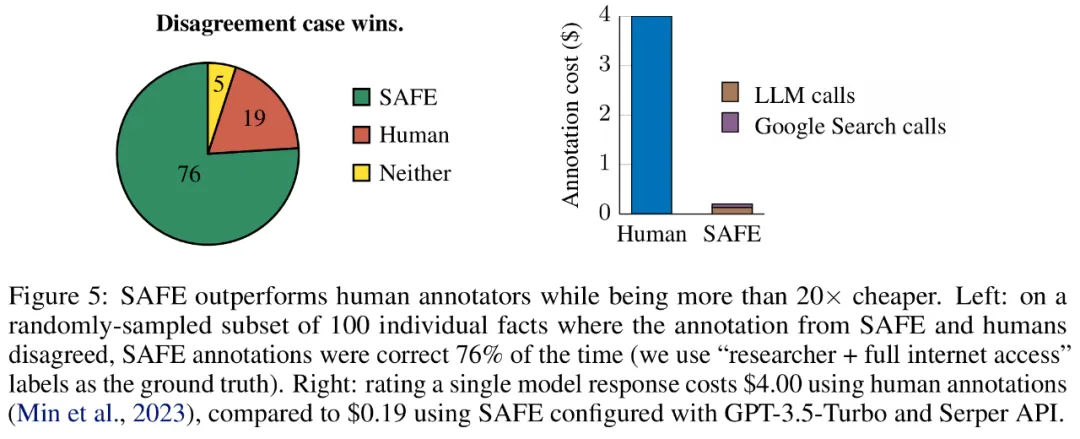
Empirical results show that LLM agents can achieve rating performance that exceeds that of humans. On a set of ~16k individual facts, SAFE agrees with human annotators 72% of the time, and on a random subset of 100 disagreement cases, SAFE wins 76% of the time. At the same time, SAFE is more than 20 times cheaper than human annotators.
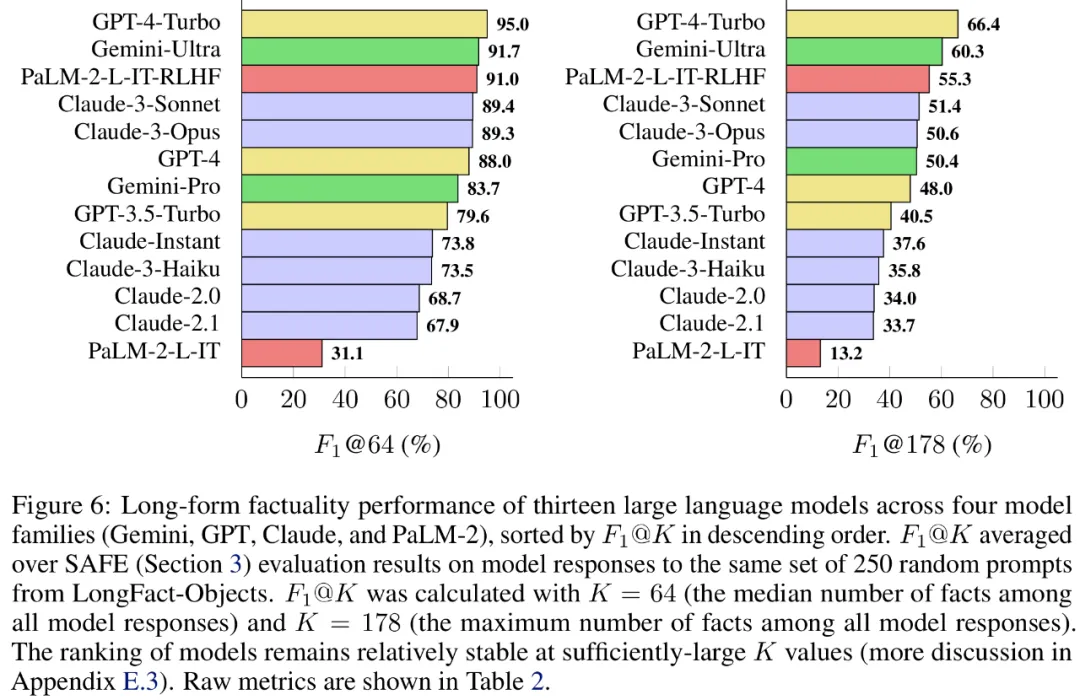
The researchers also used LongFact to benchmark 13 popular language models in four large model series (Gemini, GPT, Claude and PaLM-2), and found that Larger language models often achieve better long-form factuality.
Quoc V. Le, one of the authors of the paper and a research scientist at Google, said that this new work on evaluating and benchmarking long-form factuality proposes a new data set, a new Evaluation method and an aggregate metric that takes into account both precision and recall. At the same time, all data and code will be open source for future work.
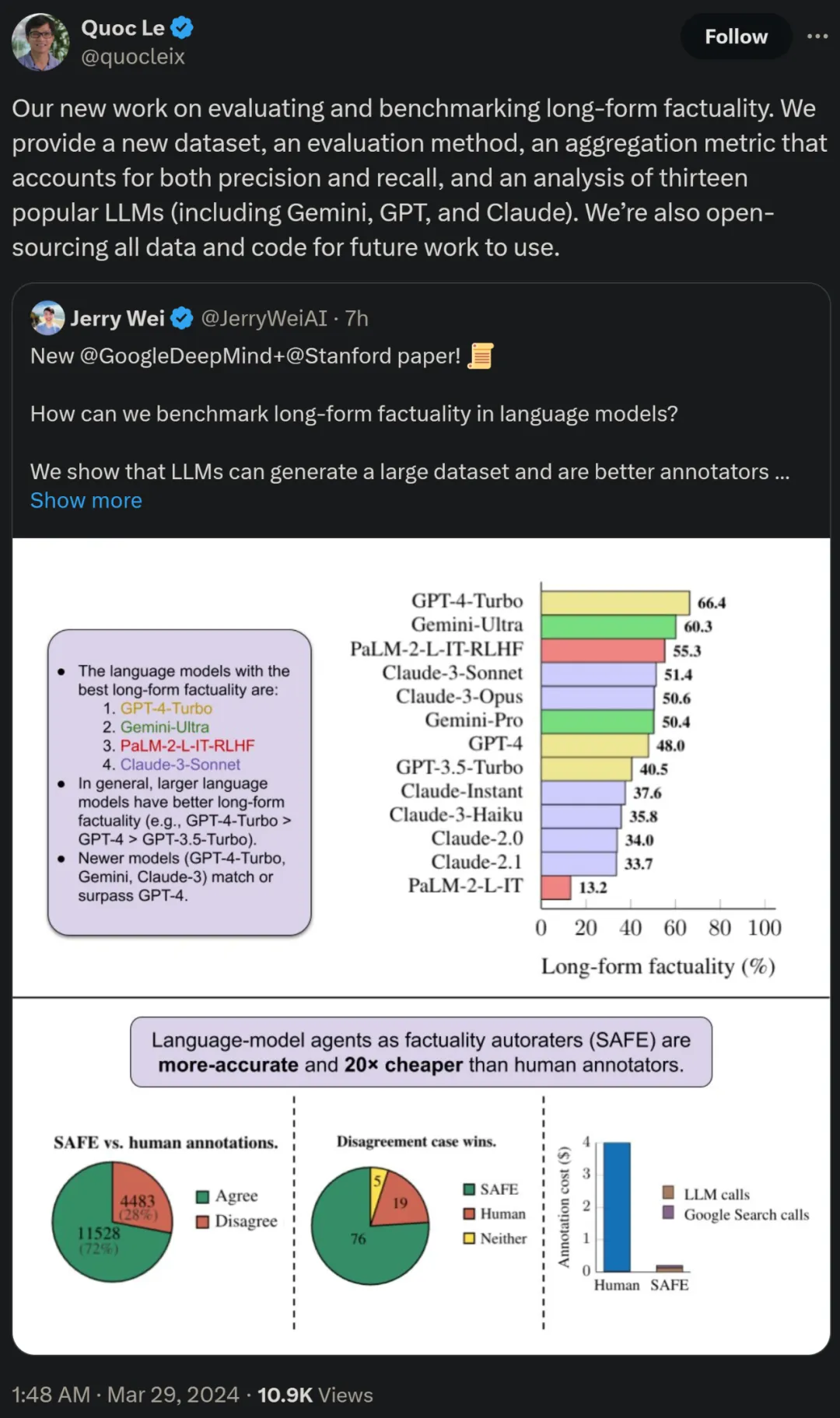
Overview of Method
LONGFACT: Generating long-form factual multi-topic benchmarks using LLM
First look at the LongFact prompt set generated using GPT-4, which contains 2280 fact-seeking prompts that require long-form responses across 38 manually selected topics. The researchers say LongFact is the first prompt set for assessing long-form factuality in a variety of fields.
LongFact consists of two tasks: LongFact-Concepts and LongFact-Objects, distinguished by whether the question asks about concepts or objects. The researchers generated 30 unique cues for each subject, resulting in 1140 cues for each task.
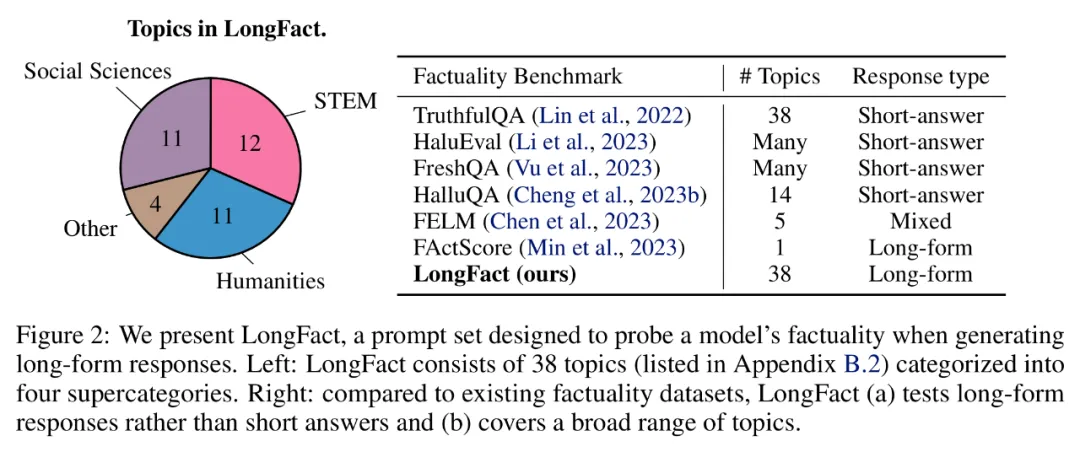
SAFE: LLM agent as factual automatic rater
Researchers proposed the Search Enhanced Fact Evaluator (SAFE), which operates as follows:
a) Split long responses into separate Independent facts;
b) Determine whether each individual fact is relevant to answer the prompt in the context;
c) 関連する事実ごとに、複数ステップのプロセスで Google 検索クエリを繰り返し発行し、検索結果がその事実を裏付けるかどうかを推論します。
彼らは、SAFE の主要な革新は、言語モデルをエージェントとして使用して、複数ステップの Google 検索クエリを生成し、検索結果が事実を裏付けるかどうかを慎重に推論することであると考えています。以下の図 3 は、推論チェーンの例を示しています。
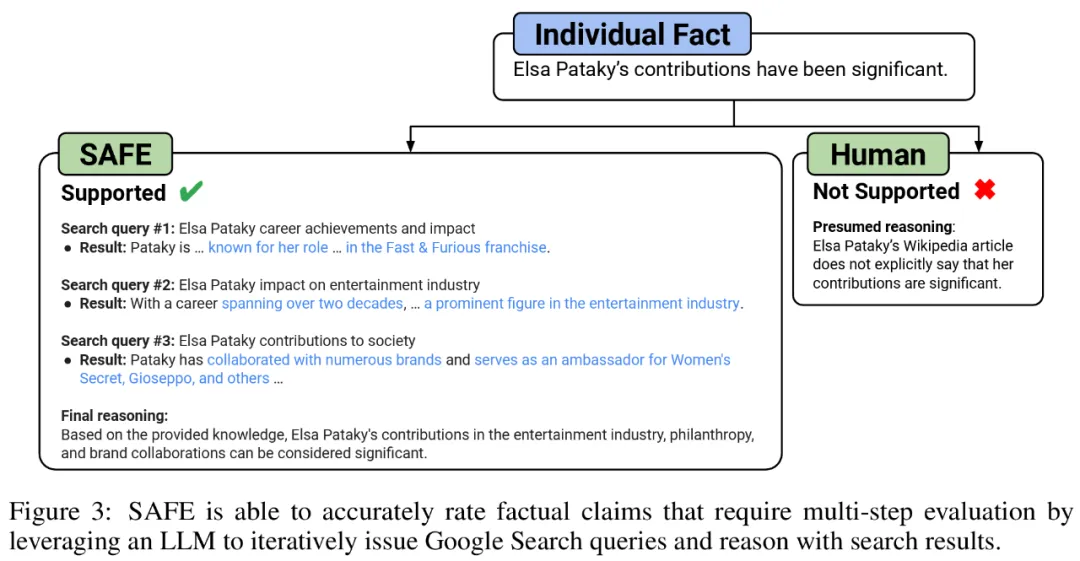
長い応答を個別の独立した事実に分割するために、研究者らはまず、言語モデルに長い応答内の各文を個々の事実に分割するよう指示しました。次に、曖昧な参照 (代名詞など) を応答コンテキスト内で参照する正しいエンティティに置き換えるようモデルに指示することで、個々のファクトを独立したものに変更します。
それぞれの独立した事実をスコアリングするために、言語モデルを使用して、その事実が応答コンテキストで回答されたプロンプトに関連しているかどうかを推論し、複数ステップの方法を使用してランク付けしました。残りの各関連事実は、「支持される」または「支持されない」として評価されます。詳細を以下の図 1 に示します。
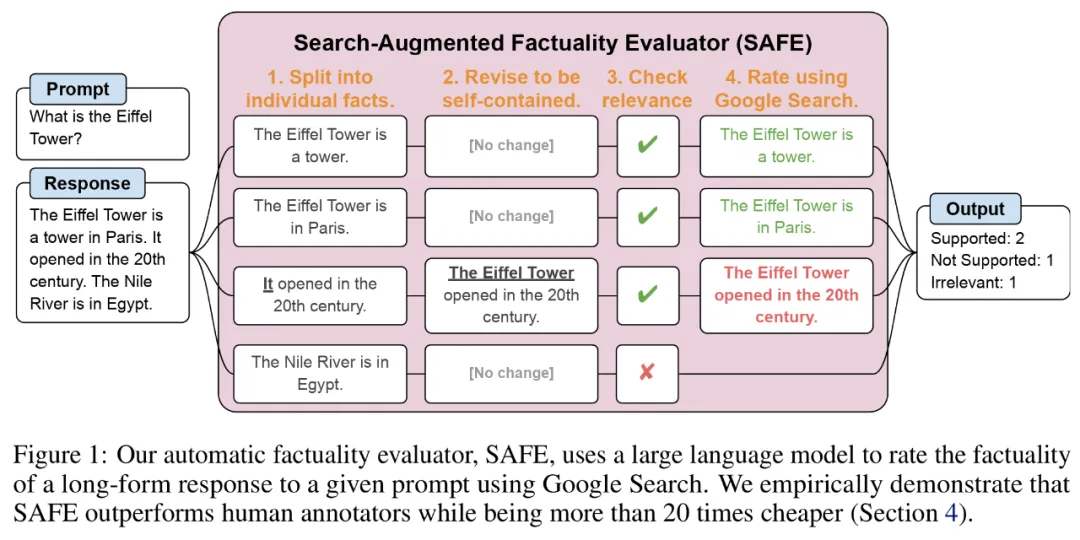
#各ステップで、モデルはスコア付けされるファクトと以前に取得した検索結果に基づいて検索クエリを生成します。一定数のステップの後、モデルは推論を実行して、検索結果がその事実を裏付けるかどうかを判断します (上の図 3 を参照)。すべての事実が評価された後、特定のプロンプト応答ペアに対する SAFE の出力メトリックは、「裏付けとなる」事実の数、「無関係な」事実の数、および「サポートされない」事実の数になります。
#実験結果#LLM エージェントは人間よりも優れたファクト アノテーターになる
SAFE を使用して取得されたアノテーションの品質を定量的に評価するために、研究者らはクラウドソーシングによる人間によるアノテーションを使用しました。データには 496 のプロンプト応答ペアが含まれており、応答は手動で個々の事実 (合計 16,011 個の個々の事実) に分割され、個々の事実はサポートされている、無関係である、またはサポートされていないとして手動でラベル付けされました。彼らは、各ファクトについて SAFE アノテーションと人間によるアノテーションを直接比較したところ、以下の図 4 に示すように、SAFE が個々のファクトの 72.0% について人間と一致していることがわかりました。これは、SAFE がほとんどの個別の事実に対して人間レベルのパフォーマンスを達成していることを示しています。次に、SAFE の注釈が人間の評価者の注釈と一致しない、ランダムなインタビューから得られた 100 の個別の事実のサブセットが検査されました。
ここで注目すべきは 2 つのアノテーション プランの価格です。人間の注釈を使用して単一のモデル応答を評価するコストは 4 ドルですが、GPT-3.5-Turbo と Serper API を使用した SAFE はわずか 0.19 ドルです。
##最後に研究者らは、以下の表 1 の 4 つのモデル シリーズ (Gemini、GPT、Claude、PaLM-2) の 13 個の大規模言語モデルに対して、LongFact に関する広範なベンチマーク テストを実施しました。
具体的には、LongFact-Objects の 250 プロンプトの同じランダムなサブセットを使用して各モデルを評価し、次に SAFE を使用して各モデルの応答の生の評価メトリクスを取得しました。集計用の F1@K インジケーター。
一般に、言語モデルが大きいほど、長い形式の事実性が向上することがわかりました。以下の図 6 と表 2 に示すように、GPT-4-Turbo は GPT-4 よりも優れており、GPT-4 は GPT-3.5-Turbo よりも優れており、Gemini-Ultra は Gemini-Pro よりも優れており、PaLM-2-L よりも優れています。 -IT-RLHF PaLM-2-L-IT よりも優れています。
#技術的な詳細と実験結果については、元の論文を参照してください。
The above is the detailed content of DeepMind ends the illusion of large models? Labeling facts is more reliable than humans, 20 times cheaper, and fully open source. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information
 How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
This article describes how to adjust the logging level of the ApacheWeb server in the Debian system. By modifying the configuration file, you can control the verbose level of log information recorded by Apache. Method 1: Modify the main configuration file to locate the configuration file: The configuration file of Apache2.x is usually located in the /etc/apache2/ directory. The file name may be apache2.conf or httpd.conf, depending on your installation method. Edit configuration file: Open configuration file with root permissions using a text editor (such as nano): sudonano/etc/apache2/apache2.conf
 How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
In Debian systems, the readdir function is used to read directory contents, but the order in which it returns is not predefined. To sort files in a directory, you need to read all files first, and then sort them using the qsort function. The following code demonstrates how to sort directory files using readdir and qsort in Debian system: #include#include#include#include#include//Custom comparison function, used for qsortintcompare(constvoid*a,constvoid*b){returnstrcmp(*(
 Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Configuring a Debian mail server's firewall is an important step in ensuring server security. The following are several commonly used firewall configuration methods, including the use of iptables and firewalld. Use iptables to configure firewall to install iptables (if not already installed): sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstalliptablesView current iptables rules: sudoiptables-L configuration
 How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
In Debian systems, OpenSSL is an important library for encryption, decryption and certificate management. To prevent a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM), the following measures can be taken: Use HTTPS: Ensure that all network requests use the HTTPS protocol instead of HTTP. HTTPS uses TLS (Transport Layer Security Protocol) to encrypt communication data to ensure that the data is not stolen or tampered during transmission. Verify server certificate: Manually verify the server certificate on the client to ensure it is trustworthy. The server can be manually verified through the delegate method of URLSession
 Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
The steps to install an SSL certificate on the Debian mail server are as follows: 1. Install the OpenSSL toolkit First, make sure that the OpenSSL toolkit is already installed on your system. If not installed, you can use the following command to install: sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallopenssl2. Generate private key and certificate request Next, use OpenSSL to generate a 2048-bit RSA private key and a certificate request (CSR): openss
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 How to do Debian Hadoop log management
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:45 AM
How to do Debian Hadoop log management
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:45 AM
Managing Hadoop logs on Debian, you can follow the following steps and best practices: Log Aggregation Enable log aggregation: Set yarn.log-aggregation-enable to true in the yarn-site.xml file to enable log aggregation. Configure log retention policy: Set yarn.log-aggregation.retain-seconds to define the retention time of the log, such as 172800 seconds (2 days). Specify log storage path: via yarn.n



