 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Shanghai Jiao Tong University's new framework unlocks CLIP long text capabilities, grasps the details of multi-modal generation, and significantly improves image retrieval capabilities
Shanghai Jiao Tong University's new framework unlocks CLIP long text capabilities, grasps the details of multi-modal generation, and significantly improves image retrieval capabilities
Shanghai Jiao Tong University's new framework unlocks CLIP long text capabilities, grasps the details of multi-modal generation, and significantly improves image retrieval capabilities
CLIP long text capability is unlocked, and the performance of image retrieval tasks is significantly improved!
Some key details can also be captured. Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Shanghai AI Laboratory proposed a new framework Long-CLIP.
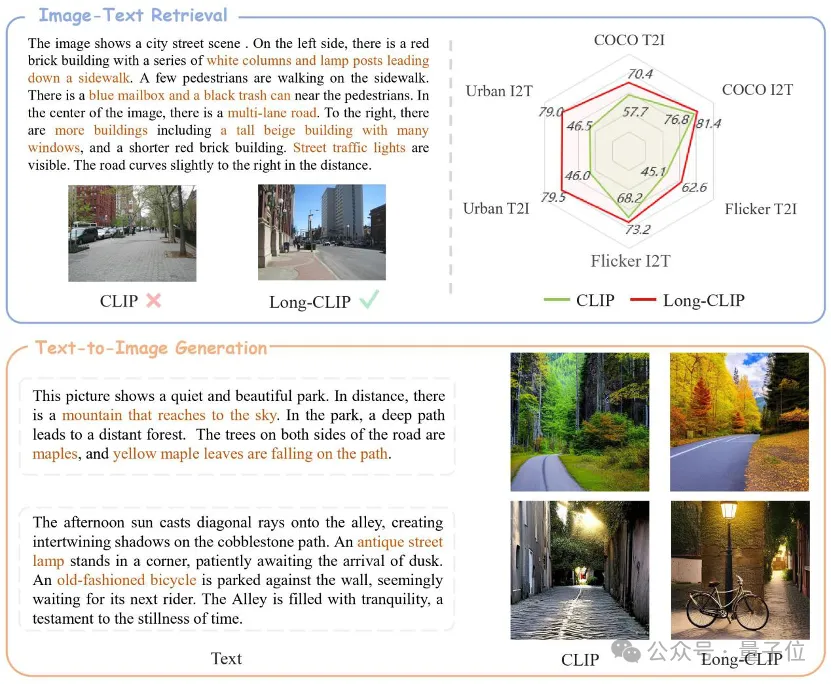
△The brown text is the key detail that distinguishes the two images
Long-CLIP is based on maintaining the original feature space of CLIP, in the downstream such as image generation Plug and play in the task to achieve fine-grained image generation of long text.
Long text-image retrieval increased by 20%, short text-image retrieval increased by 6%.
Unlocking CLIP long text capabilities
CLIP aligns visual and text modalities and has powerful zero-shot generalization capabilities. Therefore, CLIP is widely used in various multi-modal tasks, such as image classification, text image retrieval, image generation, etc.
But a major drawback of CLIP is the lack of long text capabilities.
First of all, due to the use of absolute position encoding, the text input length of CLIP is limited to 677 tokens. Not only that, experiments have proven that the real effective length of CLIP is even less than 20 tokens, which is far from enough to represent fine-grained information. However, to overcome this limitation, researchers have proposed a solution. By introducing specific tags in the text input, the model can focus on the important parts. The position and number of these tokens in the input are determined in advance and will not exceed 20 tokens. In this way, CLIP is able to
Long text missing on the text side also limits the capabilities of the visual side when processing text input. Since it only contains short text, CLIP's visual encoder will only extract the most important components of an image, while ignoring various details. This is very detrimental to fine-grained tasks such as cross-modal retrieval.
At the same time, the lack of long text also makes CLIP adopt a simple modeling method similar to bag-of-feature (BOF), which does not have complex capabilities such as causal reasoning.
In response to this problem, researchers proposed the Long-CLIP model.

Specifically proposed two major strategies: Knowledge-Preserving Stretching of Positional Embedding (Knowledge-Preserving Stretching of Positional Embedding) and fine-tuning strategy of adding core component alignment (Primary Component Matching).
Knowledge-preserving positional encoding expansion
A simple method to extend the input length and enhance long text capabilities is to first interpolate the positional encoding at a fixed ratio λ1 , and then fine-tune it with long text.
Researchers found that the training degree of different position encodings of CLIP is different. Since the training text is likely to be mainly short text, the lower position coding is more fully trained and can accurately represent the absolute position, while the higher position coding can only represent its approximate relative position. Therefore, the cost of interpolating codes at different positions is different.
Based on the above observations, the researcher retained the first 20 position codes, and for the remaining 57 position codes, interpolated with a larger ratio λ2 , the calculation formula It can be expressed as: 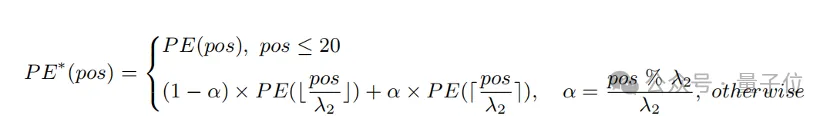
Experiments show that compared with direct interpolation, this strategy can significantly improve the performance on various tasks while supporting a longer total length.
Add fine-tuning of core attribute alignment
Merely introducing long-text fine-tuning will lead the model into another misunderstanding, that is, including all details equally. To address this problem, researchers introduced the strategy of core attribute alignment in fine-tuning.
Specifically, researchers use the principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm to extract core attributes from fine-grained image features, filter the remaining attributes and reconstruct coarse-grained image features, and combine them with generalized of short text. This strategy requires that the model not only contains more details (fine-grained alignment), but also identifies and models the most core attributes (core component extraction and coarse-grained alignment).
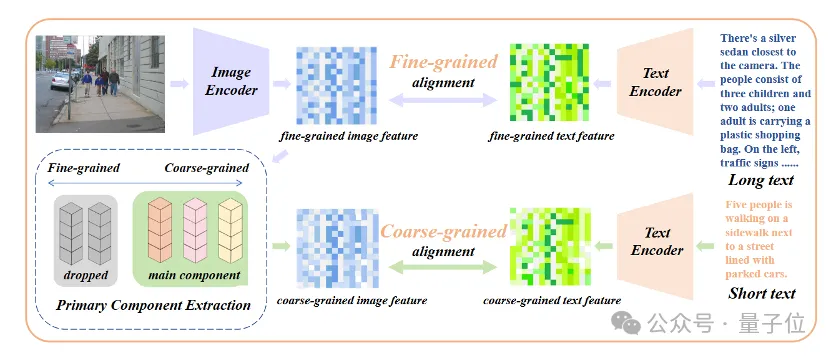
△Add the fine-tuning process of core attribute alignment
Plug and play in various multi-modal tasks
In pictures and texts In fields such as retrieval and image generation, Long-CLIP can replace CLIP plug-and-play.
For example, in image and text retrieval, Long-CLIP can capture more fine-grained information in image and text modes, thereby enhancing the ability to distinguish similar images and text, and greatly improving the performance of image and text retrieval.
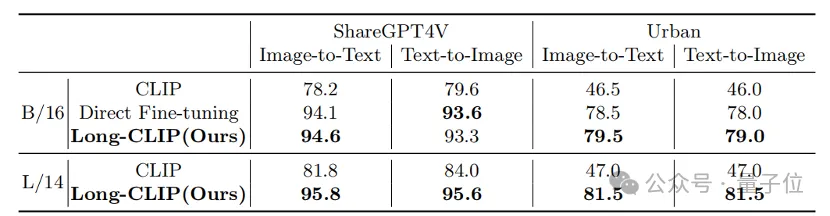
Whether it is in traditional short text retrieval (COCO, Flickr30k) or long text retrieval tasks, Long-CLIP has significantly improved the recall rate.
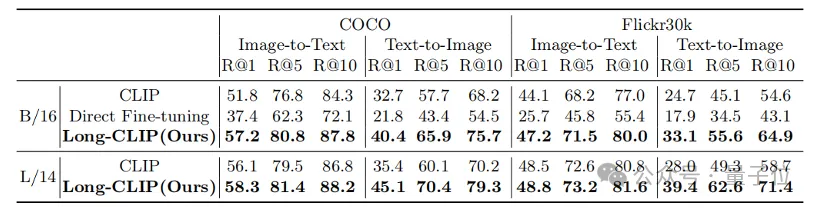
△Short text-image retrieval experimental results


Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.15378
Code link: https://github.com/beichenzbc/Long-CLIP
The above is the detailed content of Shanghai Jiao Tong University's new framework unlocks CLIP long text capabilities, grasps the details of multi-modal generation, and significantly improves image retrieval capabilities. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Installing MySQL on CentOS involves the following steps: Adding the appropriate MySQL yum source. Execute the yum install mysql-server command to install the MySQL server. Use the mysql_secure_installation command to make security settings, such as setting the root user password. Customize the MySQL configuration file as needed. Tune MySQL parameters and optimize databases for performance.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to choose a GitLab database in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:39 PM
How to choose a GitLab database in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:39 PM
When installing and configuring GitLab on a CentOS system, the choice of database is crucial. GitLab is compatible with multiple databases, but PostgreSQL and MySQL (or MariaDB) are most commonly used. This article analyzes database selection factors and provides detailed installation and configuration steps. Database Selection Guide When choosing a database, you need to consider the following factors: PostgreSQL: GitLab's default database is powerful, has high scalability, supports complex queries and transaction processing, and is suitable for large application scenarios. MySQL/MariaDB: a popular relational database widely used in Web applications, with stable and reliable performance. MongoDB:NoSQL database, specializes in
 How to view GitLab logs under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
How to view GitLab logs under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
A complete guide to viewing GitLab logs under CentOS system This article will guide you how to view various GitLab logs in CentOS system, including main logs, exception logs, and other related logs. Please note that the log file path may vary depending on the GitLab version and installation method. If the following path does not exist, please check the GitLab installation directory and configuration files. 1. View the main GitLab log Use the following command to view the main log file of the GitLabRails application: Command: sudocat/var/log/gitlab/gitlab-rails/production.log This command will display product



