Home
 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Javascript gets document coordinates and viewport coordinates_javascript skills
Javascript gets document coordinates and viewport coordinates_javascript skills
 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Javascript gets document coordinates and viewport coordinates_javascript skills
Javascript gets document coordinates and viewport coordinates_javascript skills
Javascript gets document coordinates and viewport coordinates_javascript skills
javascript
The position of an element is measured in pixels, with the X coordinate increasing to the right and the Y coordinate increasing going down, however, there are two different points as the origin of the coordinate system: the X and Y coordinates of an element can be relative At the upper left corner of the document or relative to the upper left corner of the viewport in which the document is displayed.
In rated windows and tabs, the "viewport" is only the part of the browser that actually displays the document's content: it does not include the browser's "shell" (such as menus, toolbars, and tabs).
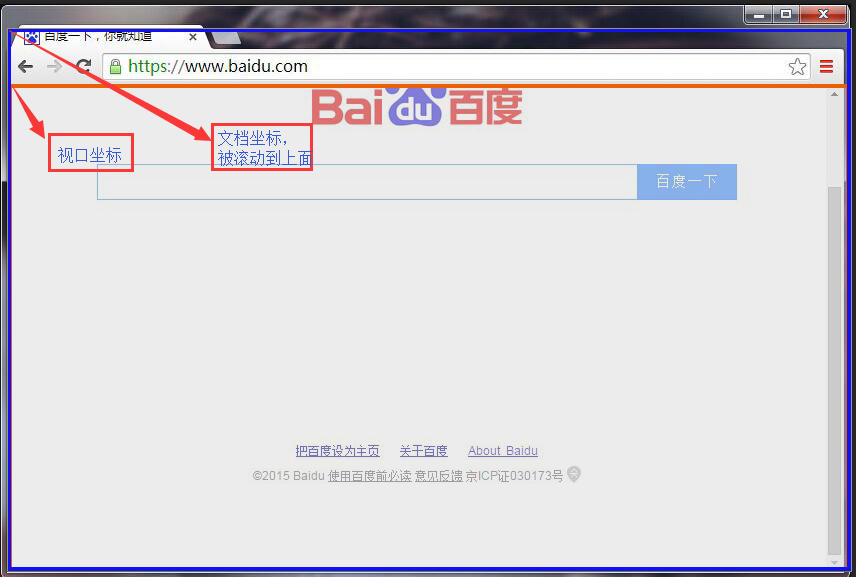
For the document displayed in the frame, the

