What does robustness mean?
Robustness: the ability to withstand disturbances and errors
Robustness refers to the ability of a system or product to cope with accidents, disturbances and failures without affecting its primary function. It is when a system remains stable, resilient and reliable, even under stress or adverse conditions.
Characteristics of Robustness
- Fault tolerance: The system can continue to operate even if single or multiple faults occur.
- Adaptability: The system is able to adjust its behavior in response to changing circumstances or needs.
- Robustness: The system remains functional under extreme conditions.
- Resilience: The system is able to recover quickly from interruptions or failures.
- Redundancy: The system contains multiple components, which ensures normal operation of the system even if one or more components fail.
Methods to achieve robustness
- Modular design:Decompose the system into independent modules so that it can be easily Isolate the fault.
- Fault handling mechanism: Establish a mechanism to detect and handle faults to prevent them from causing system crashes.
- Redundancy: Use backup components or systems to ensure that the system remains available in the event of component failure.
- Testing and Validation: Identify and address potential weaknesses through a comprehensive testing and validation process.
- Continuous Monitoring: Monitor the system in real time to detect and quickly respond to any anomalies.
Benefits of robustness
- Improve system availability and reliability
- Reduce downtime and data loss
- Reduce costs and risks
- Enhance customer satisfaction and brand reputation
Robustness is critical to ensuring systems can operate reliably in a variety of environments and conditions. By achieving robustness, organizations can improve the efficiency of their operations, increase resiliency and protect critical assets.
The above is the detailed content of What does robustness mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
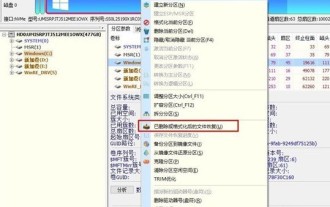 How to recover diskgenius data diskgenius data recovery tutorial
May 08, 2024 pm 02:22 PM
How to recover diskgenius data diskgenius data recovery tutorial
May 08, 2024 pm 02:22 PM
Step 1: You can directly select the partition in the hard disk partition map above the main interface of DiskGenius, right-click, and then select the [Deleted or Formatted File Recovery] menu item in the pop-up shortcut menu (as shown in the picture) . Step 2: The recovery options window pops up, check the three options of [Recover Deleted Files], [Complete Recovery], and [Additional Scan for Known File Types] (as shown in the picture). Step 3: Click the [Select File Type] button on the right and specify the file type you need to recover in the pop-up window (as shown in the picture). Step 4: After setting the recovery options and clicking the [Start] button, the DiskGenius software will start scanning the data in the hard disk or partition. First, a scanning window will pop up (as shown in the figure)
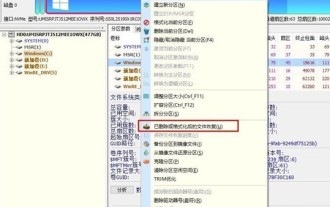 How to recover files with the partition tool diskgenius How to recover files with the partition tool diskgenius
May 08, 2024 pm 02:25 PM
How to recover files with the partition tool diskgenius How to recover files with the partition tool diskgenius
May 08, 2024 pm 02:25 PM
1. You can directly select the partition in the hard disk partition map above the main interface of DiskGenius, right-click, and then select the [Deleted or Formatted File Recovery] menu item in the pop-up shortcut menu, as shown in the figure below. 2. The recovery options window pops up, check the three options of [Recover Deleted Files], [Complete Recovery], and [Additional Scan for Known File Types], as shown in the figure below. 3. Click the [Select File Type] button on the right and specify the file type you need to recover in the pop-up window, as shown in the figure below. 4. After setting the recovery options and clicking the [Start] button, the DiskGenius software will start scanning the data in the hard disk or partition. First, a scanning window will pop up, as shown in the figure below. 5. After the scan is completed,
 How long does the motherboard battery last?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:04 PM
How long does the motherboard battery last?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:04 PM
How often should you replace a computer motherboard battery? Generally speaking, the service life of a motherboard battery is 3-5 years, but it may be shorter or longer. If the computer has problems such as inaccurate clock and incorrect system settings, it may be caused by damage to the motherboard battery. The motherboard battery should be replaced every 2 to 3 years. The motherboard battery is used to record the time of the computer system, that is, to maintain the accuracy of the system clock. When the battery is insufficient, the time will return to the factory date. When CMOS errors occur frequently when starting the computer, and the date and time are incorrect, it is time to replace the battery. The battery life of the motherboard is very long, usually about 5 years. The battery is in a charging state when the computer is turned on, and the BIOS is discharged after the computer is shut down to maintain the associated information in the BIOS (such as
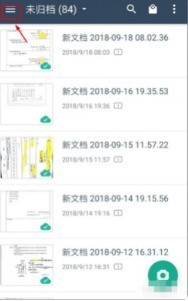 How to recover deleted files with Scanner Almighty King_How to recover deleted files with Scanner Almighty King
May 07, 2024 am 10:22 AM
How to recover deleted files with Scanner Almighty King_How to recover deleted files with Scanner Almighty King
May 07, 2024 am 10:22 AM
1. First open Scanner, click the button in the upper left corner to display the personal interface, as shown in the figure below. 2. Then click Settings and slide the interface to find the help interface button, as shown in the figure below. 3. Then find the help button and click to enter, as shown in the figure below. 4. Then find [I deleted a document by mistake, how do I restore it? 】, click to enter, as shown in the figure below. 5. We can see that there is a URL, follow the instructions to log in to the URL to restore (unsynchronized files cannot be restored, be sure to synchronize important files after scanning), as shown in the figure below. 6. After logging in, you can view your synchronized files and find the files you accidentally deleted, as shown in the figure below.
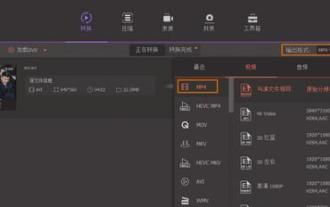 The easiest way to convert mobile phone videos to MP4 (quick tips for converting mobile phone videos to MP4 format)
May 08, 2024 pm 08:43 PM
The easiest way to convert mobile phone videos to MP4 (quick tips for converting mobile phone videos to MP4 format)
May 08, 2024 pm 08:43 PM
But sometimes it is necessary to convert it to MP4 format to play on other devices. People shoot more and more mobile phone videos with the popularity of smartphones. To help users quickly convert mobile phone videos to MP4 format, this article will introduce the simplest method. 1. Use professional video conversion tools to convert mobile phone videos to MP4 format, such as FFmpeg, etc., such as HandBrake. Can meet the needs of different users, these tools provide rich conversion options. 2. Mobile phone application conversion tools such as iConv also provide video conversion functions. Users only need to import mobile phone videos into the application and choose to output them in MP4 format. Some mobile phone applications such as VideoConverte
 How to set disk high temperature alarm with CrystalDiskInfo hard disk detection tool_How to set disk high temperature alarm with CrystalDiskInfo hard disk detection tool
May 07, 2024 am 10:01 AM
How to set disk high temperature alarm with CrystalDiskInfo hard disk detection tool_How to set disk high temperature alarm with CrystalDiskInfo hard disk detection tool
May 07, 2024 am 10:01 AM
Step 1: Open CrystalDiskInfo and enter the main interface. After entering, switch the disk for which you want to set the alarm. Step 2: Then click on the currently displayed temperature location. Step 3: After clicking, the temperature alarm setting function will pop up. The default is 60℃. Step 4: You can drag the scroll bar to set the temperature, and then click the Apply button. Step 5: If there are multiple disks, you can click the drop-down box above to select other hard disks for settings.
 How to solve the problem that the excel table cannot be opened
May 08, 2024 pm 08:36 PM
How to solve the problem that the excel table cannot be opened
May 08, 2024 pm 08:36 PM
Steps to solve an Excel table that cannot be opened: Check whether the file type is correct; repair the file or choose another application to open; disable add-ins; change file associations; reset Excel default settings; try other methods (such as reinstalling Excel).
 How to forcefully restore your phone to factory settings (detailed steps will teach you how to quickly restore your phone to its original state)
May 06, 2024 pm 09:46 PM
How to forcefully restore your phone to factory settings (detailed steps will teach you how to quickly restore your phone to its original state)
May 06, 2024 pm 09:46 PM
Mobile phones have become an essential part of people's lives with the advancement of technology. Such as software conflicts, the need to restore factory settings, system crashes, etc. Sometimes there are some problems with the phone, however. This article will introduce in detail how to forcefully restore the phone to factory settings. Check backup and storage of important data: Make sure you have backed up important data before performing a forced factory reset, and ensure the availability of backup files to avoid data loss. 2. Turn off the phone and enter recovery mode: Until the recovery mode option appears on the screen, press and hold the power key and volume down key on the phone (different phone models may vary). 3. Use the volume keys to navigate: Use the volume keys to scroll up and down to select different options in recovery mode. Find "wip





