How to adjust the position of components in bootstrap
Bootstrap provides a variety of ways to adjust the position of components: Offset class: Horizontally offset components. Auxiliary class: adjust component alignment. Grid system: Controls the number of columns the component occupies in the grid. Inline elements: Create floating layouts. Absolute positioning: Moves a component out of its regular flow and positions it anywhere on the page.

Bootstrap Adjusting Component Position
Bootstrap provides a variety of ways to adjust the position of components to create flexible and Responsive layout.
Offset Class
To offset a component horizontally, you can use the .offset-* class. For example, .offset-md-2 will offset the component 2 columns to the right on medium screens.
Auxiliary classes
There are several auxiliary classes in Bootstrap that can be used to adjust the position of components, including:
-
.pull -leftand.pull-right: Align the component to the left or right. -
.text-center: Center-align the component. -
.text-justify: Align both ends of the component.
Grid System
Bootstrap’s grid system allows you to create complex layouts and precisely control the placement of components. By using the .col-* classes you can specify the number of columns the component occupies in the raster.
Inline Elements
Bootstrap's inline element classes (such as .inline-block) allow you to create floating layouts. This can be achieved by setting the component as an inline element and positioning it using margins or padding.
Absolute Positioning
Absolute positioning is a more advanced method that allows you to move a component out of its regular flow and position it anywhere on the page Location. This can be achieved by using the .position-absolute class and the top, bottom, left and right properties .
Examples
Here are some examples of using Bootstrap to adjust the position of components:
-
.col-md-6.offset -md-3: Creates a text block 6 columns wide and offset 3 columns to the right on medium screens. -
.text-center.pull-left: Creates a center-aligned title that floats to the left of the page. -
.inline-block.ml-2: Creates a block of inline elements and pads it 2 units to the left. -
.position-absolute.top-0.right-0: Create a popup window positioned absolutely in the upper right corner of the page.
The above is the detailed content of How to adjust the position of components in bootstrap. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to introduce bootstrap into Eclipse
Apr 05, 2024 am 02:30 AM
How to introduce bootstrap into Eclipse
Apr 05, 2024 am 02:30 AM
Introduce Bootstrap in Eclipse in five steps: Download the Bootstrap file and unzip it. Import the Bootstrap folder into the project. Add Bootstrap dependency. Load Bootstrap CSS and JS in HTML files. Start using Bootstrap to enhance your user interface.
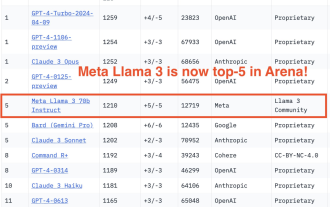 750,000 rounds of one-on-one battle between large models, GPT-4 won the championship, and Llama 3 ranked fifth
Apr 23, 2024 pm 03:28 PM
750,000 rounds of one-on-one battle between large models, GPT-4 won the championship, and Llama 3 ranked fifth
Apr 23, 2024 pm 03:28 PM
Regarding Llama3, new test results have been released - the large model evaluation community LMSYS released a large model ranking list. Llama3 ranked fifth, and tied for first place with GPT-4 in the English category. The picture is different from other benchmarks. This list is based on one-on-one battles between models, and the evaluators from all over the network make their own propositions and scores. In the end, Llama3 ranked fifth on the list, followed by three different versions of GPT-4 and Claude3 Super Cup Opus. In the English single list, Llama3 overtook Claude and tied with GPT-4. Regarding this result, Meta’s chief scientist LeCun was very happy and forwarded the tweet and
 How to introduce idea into bootstrap
Apr 05, 2024 am 02:33 AM
How to introduce idea into bootstrap
Apr 05, 2024 am 02:33 AM
Steps to introduce Bootstrap in IntelliJ IDEA: Create a new project and select "Web Application". Add "Bootstrap" Maven dependency. Create an HTML file and add Bootstrap references. Replace with the actual path to the Bootstrap CSS file. Run the HTML file to use Bootstrap styles. Tip: Use a CDN to import Bootstrap or customize HTML file templates.
 How to use bootstrap to test mediation effects
Apr 05, 2024 am 03:57 AM
How to use bootstrap to test mediation effects
Apr 05, 2024 am 03:57 AM
The Bootstrap test uses resampling technology to evaluate the reliability of the statistical test and is used to prove the significance of the mediation effect: first, calculate the confidence interval of the direct effect, indirect effect and mediation effect; secondly, calculate the significance of the mediation type according to the Baron and Kenny or Sobel method. significance; and finally estimate the confidence interval for the natural indirect effect.
 How to read the results of bootstrap mediation test
Apr 05, 2024 am 03:30 AM
How to read the results of bootstrap mediation test
Apr 05, 2024 am 03:30 AM
The Bootstrap mediation test evaluates the mediation effect by resampling the data multiple times: Indirect effect confidence interval: indicates the estimated range of the mediation effect. If the interval does not contain zero, the effect is significant. p-value: Evaluates the probability that the confidence interval does not contain zero, with values less than 0.05 indicating significant. Sample size: The number of data samples used for analysis. Bootstrap subsampling times: the number of repeated samplings (500-2000 times). If the confidence interval does not contain zero and the p-value is less than 0.05, the mediation effect is significant, indicating that the mediating variable explains the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
 What is the difference between bootstrap and springboot
Apr 05, 2024 am 04:00 AM
What is the difference between bootstrap and springboot
Apr 05, 2024 am 04:00 AM
The main difference between Bootstrap and Spring Boot is: Bootstrap is a lightweight CSS framework for website styling, while Spring Boot is a powerful, out-of-the-box backend framework for Java web application development. Bootstrap is based on CSS and HTML, while Spring Boot is based on Java and the Spring framework. Bootstrap focuses on creating the look and feel of a website, while Spring Boot focuses on back-end functionality. Spring Boot can be integrated with Bootstrap to create fully functional, beautiful
 How to export the results of bootstrap test mediation effect stata command
Apr 05, 2024 am 03:39 AM
How to export the results of bootstrap test mediation effect stata command
Apr 05, 2024 am 03:39 AM
Export the results of the Bootstrap mediation effect test in Stata: Save the results: bootstrap post Create variable list: local vars: coef se ci Export the results (CSV): export delimited results.csv, varlist(`vars') replace comma nolabel
 How to read the results of bootstrap analysis
Apr 05, 2024 am 03:36 AM
How to read the results of bootstrap analysis
Apr 05, 2024 am 03:36 AM
Bootstrap analysis is a statistical resampling technique that provides the following information about statistical inference: Confidence interval: the possible range of an estimate. p-value: The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis. Bootstrapping distribution: How an estimator varies across samples. Skewness and standard deviation: the asymmetry and dispersion of a distribution. Data point impact: The impact of a specific data point on an estimator. Robustness: The stability of an estimator to extreme values.






