How to read sqlserver logs
SQL Server logs contain valuable information about database server activity that can help diagnose problems and ensure the smooth operation of the database. The logs can be viewed in the following ways: Using SQL Server Configuration Manager (SSMS) Using the NOTEPAD.EXE or TYPE command from the command prompt Log file types include: Error log Slow query log Query log Log information type: Timestamp Severity Event type Detailed Message troubleshooting steps: Check the error log for error and warning messages Identify long queries in the slow query log and optimize them Review query patterns and execution times in the query log

How to view SQL Server logs
SQL Server logs contain important information about database server activity and errors. Reviewing these logs is critical to diagnosing problems and ensuring the smooth operation of the database.
How to view the log:
1. SQL Server Configuration Manager (SSMS)
- Open SSMS and connect to the SQL Server instance.
- In Object Explorer, expand the Administration folder and select SQL Server Logs.
- Right-click on the desired log and select "View Log File".
2. Command Prompt
- Open the command prompt and navigate to the SQL Server log path (usually %ProgramFiles%\Microsoft SQL Server \MSSQL15.SQL2019\MSSQL\Log).
- Enter one of the following commands:
<code>NOTEPAD.EXE <log_file_name> TYPE <log_file_name></code>
Log file type:
1. Error log: Record Information about errors and warnings.
2. Slow query log: Record queries that take a long time to execute.
3. Query log: Records information about executed queries.
Information type:
The log file contains the following types of information:
- Time stamp: The event occurred time.
- Severity: Error, warning, or information.
- Event type: For example, login, query, or error.
- Detailed Message: More information about the incident.
Troubleshooting:
To troubleshoot SQL Server issues, review the following sections:
1. Errors Logs: Look for error and warning messages to understand the source of the problem.
2. Slow query log: Identify queries that take a long time to execute and optimize them to improve performance.
3. Query logs: Review query patterns and execution times to find potential problems.
Regularly viewing and analyzing SQL Server logs is critical to monitoring database activity, troubleshooting problems, and ensuring optimal performance of your database.
The above is the detailed content of How to read sqlserver logs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to import mdf file into sqlserver
Apr 08, 2024 am 11:41 AM
How to import mdf file into sqlserver
Apr 08, 2024 am 11:41 AM
The import steps are as follows: Copy the MDF file to SQL Server's data directory (usually C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL\DATA). In SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), open the database and select Attach. Click the Add button and select the MDF file. Confirm the database name and click the OK button.
 How to solve the problem that the object named already exists in the sqlserver database
Apr 05, 2024 pm 09:42 PM
How to solve the problem that the object named already exists in the sqlserver database
Apr 05, 2024 pm 09:42 PM
For objects with the same name that already exist in the SQL Server database, the following steps need to be taken: Confirm the object type (table, view, stored procedure). IF NOT EXISTS can be used to skip creation if the object is empty. If the object has data, use a different name or modify the structure. Use DROP to delete existing objects (use caution, backup recommended). Check for schema changes to make sure there are no references to deleted or renamed objects.
 What to do if the sqlserver service cannot be started
Apr 05, 2024 pm 10:00 PM
What to do if the sqlserver service cannot be started
Apr 05, 2024 pm 10:00 PM
When the SQL Server service fails to start, here are some steps to resolve: Check the error log to determine the root cause. Make sure the service account has permission to start the service. Check whether dependency services are running. Disable antivirus software. Repair SQL Server installation. If the repair does not work, reinstall SQL Server.
 How to check sqlserver port number
Apr 05, 2024 pm 09:57 PM
How to check sqlserver port number
Apr 05, 2024 pm 09:57 PM
To view the SQL Server port number: Open SSMS and connect to the server. Find the server name in Object Explorer, right-click it and select Properties. In the Connection tab, view the TCP Port field.
 How to recover accidentally deleted database in sqlserver
Apr 05, 2024 pm 10:39 PM
How to recover accidentally deleted database in sqlserver
Apr 05, 2024 pm 10:39 PM
If you accidentally delete a SQL Server database, you can take the following steps to recover: stop database activity; back up log files; check database logs; recovery options: restore from backup; restore from transaction log; use DBCC CHECKDB; use third-party tools. Please back up your database regularly and enable transaction logging to prevent data loss.
 Where is the sqlserver database?
Apr 05, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Where is the sqlserver database?
Apr 05, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
SQL Server database files are usually stored in the following default location: Windows: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL\DATALinux: /var/opt/mssql/data The database file location can be customized by modifying the database file path setting.
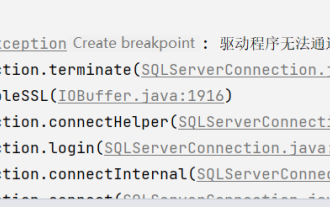 How to solve Java connection SqlServer error
May 01, 2023 am 09:22 AM
How to solve Java connection SqlServer error
May 01, 2023 am 09:22 AM
The problem was found that this time I was using the SqlServer database, which I had not used before, but the problem was not serious. After I connected the SqlServer according to the steps in the requirements document, I started the SpringBoot project and found an error, as follows: At first I thought it was a SqlServer connection. There was a problem, so I went to check the database and found that everything was normal. I first asked my colleagues if they had such a problem, and found that they did not, so I started my best part, facing Baidu. programming. The specific error message I started to solve was this, so I started Baidu error reporting: ERRORc.a.d.p.DruidDataSource$CreateCo
 How to delete sqlserver if the installation fails?
Apr 05, 2024 pm 11:27 PM
How to delete sqlserver if the installation fails?
Apr 05, 2024 pm 11:27 PM
If the SQL Server installation fails, you can clean it up by following these steps: Uninstall SQL Server Delete registry keys Delete files and folders Restart the computer





