How to clone git
To clone a Git repository, follow these steps: Get the URL of the remote repository. Use the git clone [remote repository URL] command. Verify that the cloning was successful (ls -al). Set up a remote branch (git remote add origin [remote repository URL]). Fetch remote branch updates (git fetch origin).

How to use Git Clone
Git Clone is one of the most commonly used Git commands that allows you to create a remote A local copy of the Git repository. Here are the steps to clone a Git repository:
1. Get the URL of the remote repository
First, you need to get the URL of the remote Git repository you want to clone. This URL is typically found on a repository hosting platform such as GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
2. Use the git clone command
In the directory where you wish to create a local copy, run the following command:
<code>git clone [远程存储库 URL]</code>
For example, to clone the name For the remote repository of "my-repo", you can run:
<code>git clone https://github.com/my-username/my-repo</code>
3. Verify the clone
When the cloning is complete, Git will create a local file containing the remote repository Directory of library contents. To verify that the cloning was successful, you can run the following command:
<code>ls -al</code>
This will list all files and directories in the current directory, including the newly cloned repository.
4. Set remote branches
Clone does not set remote branches by default. To set up a remote branch, you can run the following command:
<code>git remote add origin [远程存储库 URL]</code>
This will create a remote branch named "origin", pointing to the original repository.
5. Fetch the remote branch
Finally, you can fetch updates from the remote branch using the following command:
<code>git fetch origin</code>
This will fetch the remote branch and download them to your local copy.
Note:
- You can specify the depth (number of history records) of the clone using the
--depthoption. - Clone is a quick and easy way to create a copy of a remote repository.
- Make sure you have the necessary permissions to clone the remote repository.
The above is the detailed content of How to clone git. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
There are many ways to install DeepSeek, including: compile from source (for experienced developers) using precompiled packages (for Windows users) using Docker containers (for most convenient, no need to worry about compatibility) No matter which method you choose, Please read the official documents carefully and prepare them fully to avoid unnecessary trouble.
 Summary of FAQs for DeepSeek usage
Feb 19, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
Summary of FAQs for DeepSeek usage
Feb 19, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
DeepSeekAI Tool User Guide and FAQ DeepSeek is a powerful AI intelligent tool. This article will answer some common usage questions to help you get started quickly. FAQ: The difference between different access methods: There is no difference in function between web version, App version and API calls, and App is just a wrapper for web version. The local deployment uses a distillation model, which is slightly inferior to the full version of DeepSeek-R1, but the 32-bit model theoretically has 90% full version capability. What is a tavern? SillyTavern is a front-end interface that requires calling the AI model through API or Ollama. What is breaking limit
 What are the AI tools?
Nov 29, 2024 am 11:11 AM
What are the AI tools?
Nov 29, 2024 am 11:11 AM
AI tools include: Doubao, ChatGPT, Gemini, BlenderBot, etc.
 What are the Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds? Common Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds Inventory
Mar 05, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
What are the Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds? Common Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds Inventory
Mar 05, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
Grayscale Investment: The channel for institutional investors to enter the cryptocurrency market. Grayscale Investment Company provides digital currency investment services to institutions and investors. It allows investors to indirectly participate in cryptocurrency investment through the form of trust funds. The company has launched several crypto trusts, which has attracted widespread market attention, but the impact of these funds on token prices varies significantly. This article will introduce in detail some of Grayscale's major crypto trust funds. Grayscale Major Crypto Trust Funds Available at a glance Grayscale Investment (founded by DigitalCurrencyGroup in 2013) manages a variety of crypto asset trust funds, providing institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals with compliant investment channels. Its main funds include: Zcash (ZEC), SOL,
 Delphi Digital: How to change the new AI economy by parsing the new ElizaOS v2 architecture?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 07:00 PM
Delphi Digital: How to change the new AI economy by parsing the new ElizaOS v2 architecture?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 07:00 PM
ElizaOSv2: Empowering AI and leading the new economy of Web3. AI is evolving from auxiliary tools to independent entities. ElizaOSv2 plays a key role in it, which gives AI the ability to manage funds and operate Web3 businesses. This article will dive into the key innovations of ElizaOSv2 and how it shapes an AI-driven future economy. AI Automation: Going to independently operate ElizaOS was originally an AI framework focusing on Web3 automation. v1 version allows AI to interact with smart contracts and blockchain data, while v2 version achieves significant performance improvements. Instead of just executing simple instructions, AI can independently manage workflows, operate business and develop financial strategies. Architecture upgrade: Enhanced A
 As top market makers enter the crypto market, what impact will Castle Securities have on the industry?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
As top market makers enter the crypto market, what impact will Castle Securities have on the industry?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
The entry of top market maker Castle Securities into Bitcoin market maker is a symbol of the maturity of the Bitcoin market and a key step for traditional financial forces to compete for future asset pricing power. At the same time, for retail investors, it may mean the gradual weakening of their voice. On February 25, according to Bloomberg, Citadel Securities is seeking to become a liquidity provider for cryptocurrencies. The company aims to join the list of market makers on various exchanges, including exchanges operated by CoinbaseGlobal, BinanceHoldings and Crypto.com, people familiar with the matter said. Once approved by the exchange, the company initially planned to set up a market maker team outside the United States. This move is not only a sign
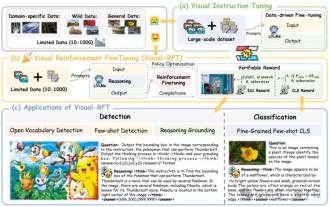 Significantly surpassing SFT, the secret behind o1/DeepSeek-R1 can also be used in multimodal large models
Mar 12, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Significantly surpassing SFT, the secret behind o1/DeepSeek-R1 can also be used in multimodal large models
Mar 12, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Researchers from Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai AILab and the Chinese University of Hong Kong have launched the Visual-RFT (Visual Enhancement Fine Tuning) open source project, which requires only a small amount of data to significantly improve the performance of visual language big model (LVLM). Visual-RFT cleverly combines DeepSeek-R1's rule-based reinforcement learning approach with OpenAI's reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) paradigm, successfully extending this approach from the text field to the visual field. By designing corresponding rule rewards for tasks such as visual subcategorization and object detection, Visual-RFT overcomes the limitations of the DeepSeek-R1 method being limited to text, mathematical reasoning and other fields, providing a new way for LVLM training. Vis
 Bitwise: Businesses Buy Bitcoin A Neglected Big Trend
Mar 05, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Bitwise: Businesses Buy Bitcoin A Neglected Big Trend
Mar 05, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Weekly Observation: Businesses Hoarding Bitcoin – A Brewing Change I often point out some overlooked market trends in weekly memos. MicroStrategy's move is a stark example. Many people may say, "MicroStrategy and MichaelSaylor are already well-known, what are you going to pay attention to?" This is true, but many investors regard it as a special case and ignore the deeper market forces behind it. This view is one-sided. In-depth research on the adoption of Bitcoin as a reserve asset in recent months shows that this is not an isolated case, but a major trend that is emerging. I predict that in the next 12-18 months, hundreds of companies will follow suit and buy large quantities of Bitcoin






