 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Stimulate the spatial reasoning ability of large language models: thinking visualization tips
Stimulate the spatial reasoning ability of large language models: thinking visualization tips
Stimulate the spatial reasoning ability of large language models: thinking visualization tips

, allowing us to interact with our environment. It facilitates tasks that require understanding and reasoning about spatial relationships between objects and their motion. Spatial reasoning of language models relies heavily on language to reason about spatial information, and human cognitive abilities far exceed linguistic reasoning. Humans can not only create task-relevant abstract representations from visual perception, but also imagine unseen scenes through the mind's eye. This is a research topic known as#Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive performance in language understanding and various reasoning tasks. However, their role in spatial reasoning, a key aspect of human cognition, remains understudied. Humans have the ability to create mental images of unseen objects and actions through a process known as the mind's eye, making it possible to imagine the unseen world. Inspired by this cognitive ability, researchers proposed "Visualization of Thought (VoT)" . VoT aims to guide the spatial reasoning of LLMs by visualizing their reasoning signs, thereby guiding subsequent reasoning steps. The researchers applied VoT to multi-hop spatial reasoning tasks, including natural language navigation, visual navigation, and visual paving in a two-dimensional grid world. Experimental results show that VoT significantly enhances the spatial reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Notably, VoT outperforms existing multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) on these tasks. Introduction In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance on various language-related tasks. Despite their success in mathematical reasoning, commonsense reasoning, and other reasoning tasks such as symbolic or logical reasoning, their capabilities in spatial reasoning remain underexplored.
Spatial reasoning is a fundamental function of human cognition
mentalimage
in the fields of neuroscience, philosophy of mind, and cognitive science. Building on this cognitive function, humans facilitate spatial reasoning through the manipulation of mental images, such as navigation, mental rotation, mental paper folding, and mental simulation. Figure 1 illustrates the human processes involved in navigation tasks. Humans enhance their spatial awareness and guide their decision-making by creating mental images of paths, utilizing various sensory inputs such as navigation instructions or map images. They then simulated path planning through the mind's eye.Figure 1: Humans can enhance their spatial awareness and guide decision-making by creating mental images during spatial reasoning. Likewise, large language models (LLMs) can build internal mental images. The researchers proposed VoT to trigger the "mind's eye" of LLMs by visualizing their thinking at each intermediate step, thereby promoting spatial reasoning. Inspired by this cognitive mechanism, researchers speculate that LLMs have the ability to create and manipulate mental images in the mind's eye for spatial reasoning. As shown in Figure 1, LLMs may potentially process and understand spatial information in various formats. They may be able to visualize internal states and manipulate these mental images through the mind's eye to guide subsequent reasoning steps to enhance spatial reasoning. Therefore, researchers proposed
Visualization of Thought (VoT) prompts to elicit this ability. This method adds a visual-spatial sketchpad to LLMs to visualize their reasoning steps and guide subsequent steps. VoT employs zero demonstration prompts, rather than relying on few demonstrations or using CLIP for text-to-image visualization. This choice stems from the ability of LLMs to obtain a variety of mental images from text-based visual art. 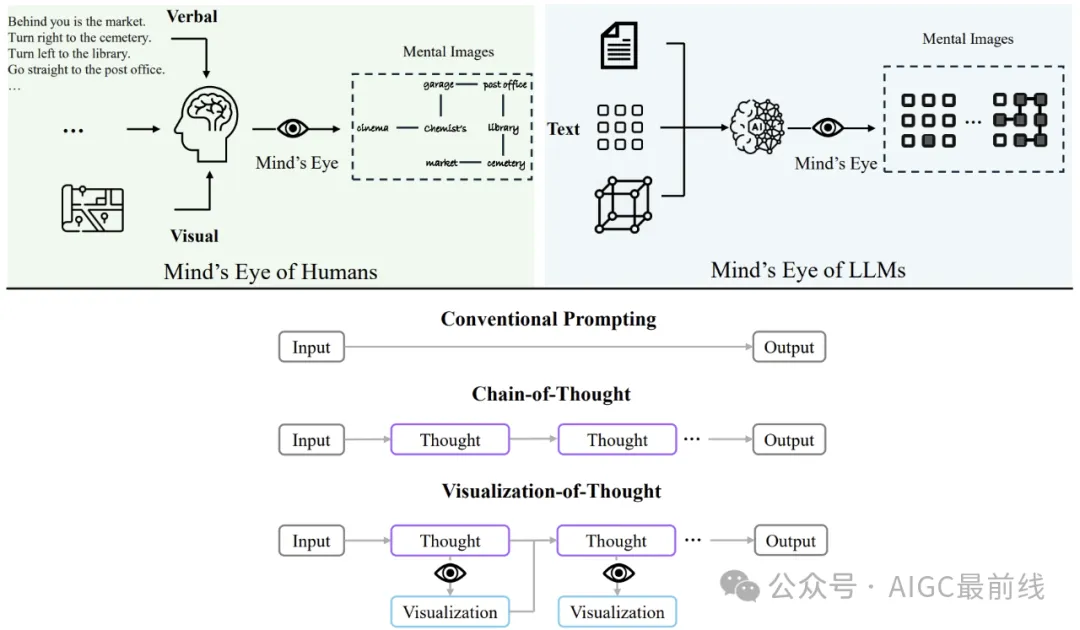
natural language navigation, visual navigation, and visual laying
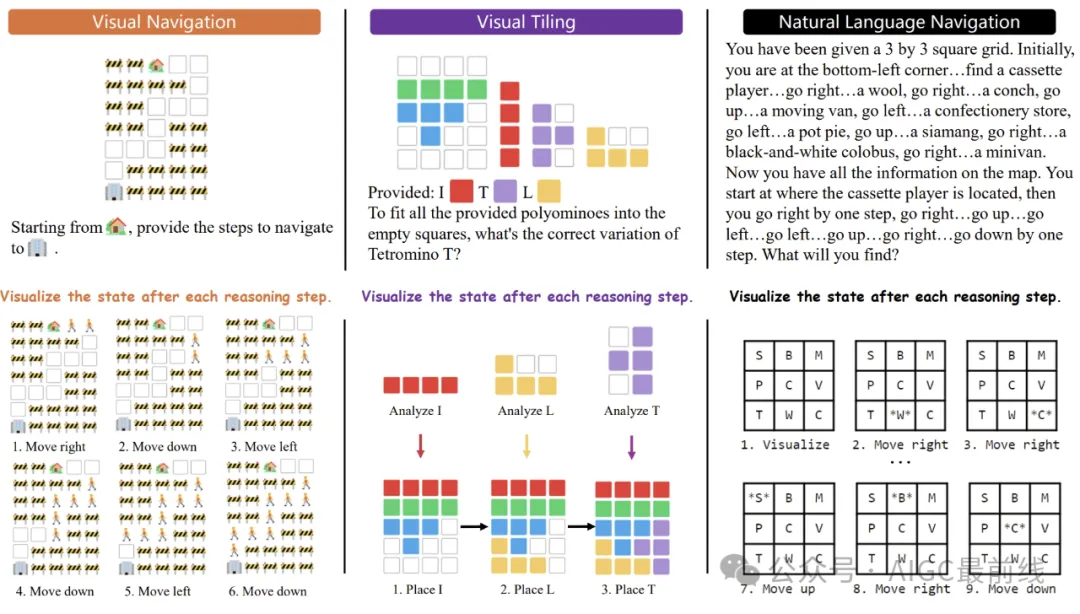
. These tasks require understanding spatial, directional, and geometric shape reasoning. To simulate human-like multisensory perception, the researchers designed 2D grid worlds that use special characters as rich input formats in LLMs' visual navigation and visual laying tasks. Different models (GPT-4, GPT-4V) and prompting techniques were compared on these three tasks. Research results show thatVoT prompts consistently prompt LLMs to visualize their reasoning steps and guide subsequent steps. Therefore, this method achieves significant performance improvements on the corresponding tasks.
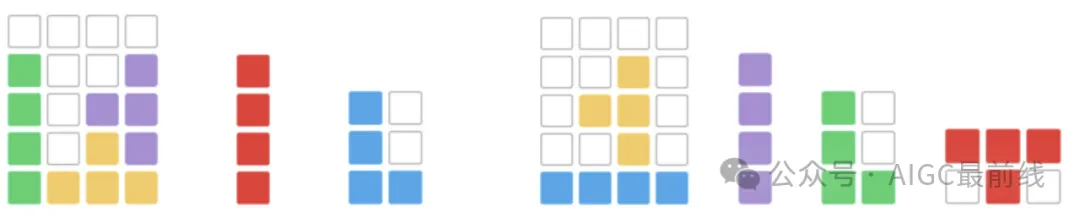
Figure 2: Examples of navigation maps in different settings, with a house emoji representing the starting point and an office emoji representing the destination. Spatial reasoning refers to the ability to understand and reason about the spatial relationships between objects, their movements and interactions. This skill is important for a wide range of real-world applications, such as navigation, robotics, and autonomous driving. These areas require action planning based on visual perception and a detailed understanding of spatial dimensions. Although several tasks and datasets have been developed to explore spatial semantics embedded in text, research efforts have generally focused on how spatial terms are linguistically structured. Recently, significant achievements and impressive results have been achieved on these benchmarks by converting spatial terms into logical forms and employing logical programming. This means that performing well on these tasks does not necessarily mean that large language models (LLMs) truly understand spatial information, nor does it provide an accurate measure of their spatial awareness. Spatial awareness involves understanding spatial relationships, directions, distances, and geometry, which are essential for planning actions in the physical world. To assess LLMs' spatial awareness and spatial reasoning abilities, the researchers selected a number of tasks that test navigation and geometric reasoning skills, including natural language navigation, visual navigation, and visual paving. Natural language navigation involves browsing the underlying spatial structure through a random walk, aiming to identify previously visited locations. The concept was inspired by previous research on human cognition, using an approach similar to a random walk along a graph structure. This process requires an understanding of loop closure, which is critical for spatial navigation. The visual navigation task presents LLMs with a synthetic 2D grid world and challenges them to exploit visual cues Navigate. The model must generate navigation instructions to move in four directions (left, right, up, and down) from a starting point to a destination while avoiding obstacles. This involves two subtasks: route planning and next step prediction, which require multi-hop spatial reasoning, of which the former is more complex. Visual tiling is a classic spatial reasoning challenge. Extending this concept to test LLMs' ability to understand, organize, and reason about shapes within a limited area enhances the assessment of spatial reasoning skills. The task involves a rectangle with unfilled cells and various domino blocks, such as the I-domino block consisting of four aligned squares. The model must choose the appropriate domino block variation, such as choosing the direction of the I-domino block, to solve the question-and-answer puzzle. Figure 3: Example of visual laying with masked domino blocks. The image does not show the rotated and mirrored variations of the domino blocks. Given the way humans process spatial information in tasks such as navigation, mental images, such as maps, are often created to enhance spaces Awareness or simulated movement to guide decision-making. The research goal is to evoke the spatial awareness of LLMs and enable reasoning based on actual situations by visualizing their intermediate reasoning steps. Researchers introduce a Visualization of Thinking (VoT) prompt: "Visualize the state after each reasoning step." This new spatial reasoning paradigm aims to generate reasoning signs and visualization results in an interleaved manner. Figure 4: Examples of VoT prompts in three tasks that LLM generates inference signs and visualizations to track in a staggered manner state that changes over time. Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.03622.pdfSpatial Reasoning
Natural Language Navigation

Visual Navigation

Visual tiling

ThinkingVisual Tips


The above is the detailed content of Stimulate the spatial reasoning ability of large language models: thinking visualization tips. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Step-by-step guide to using Groq Llama 3 70B locally
Jun 10, 2024 am 09:16 AM
Step-by-step guide to using Groq Llama 3 70B locally
Jun 10, 2024 am 09:16 AM
Translator | Bugatti Review | Chonglou This article describes how to use the GroqLPU inference engine to generate ultra-fast responses in JanAI and VSCode. Everyone is working on building better large language models (LLMs), such as Groq focusing on the infrastructure side of AI. Rapid response from these large models is key to ensuring that these large models respond more quickly. This tutorial will introduce the GroqLPU parsing engine and how to access it locally on your laptop using the API and JanAI. This article will also integrate it into VSCode to help us generate code, refactor code, enter documentation and generate test units. This article will create our own artificial intelligence programming assistant for free. Introduction to GroqLPU inference engine Groq
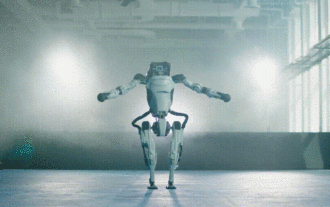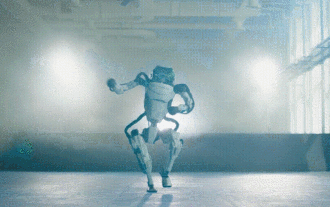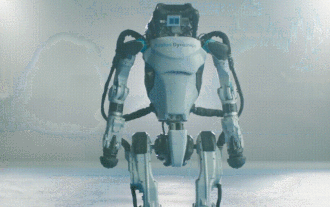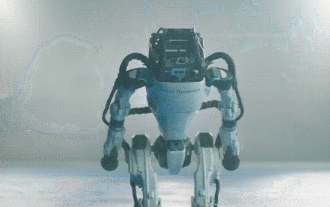 Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Boston Dynamics Atlas officially enters the era of electric robots! Yesterday, the hydraulic Atlas just "tearfully" withdrew from the stage of history. Today, Boston Dynamics announced that the electric Atlas is on the job. It seems that in the field of commercial humanoid robots, Boston Dynamics is determined to compete with Tesla. After the new video was released, it had already been viewed by more than one million people in just ten hours. The old people leave and new roles appear. This is a historical necessity. There is no doubt that this year is the explosive year of humanoid robots. Netizens commented: The advancement of robots has made this year's opening ceremony look like a human, and the degree of freedom is far greater than that of humans. But is this really not a horror movie? At the beginning of the video, Atlas is lying calmly on the ground, seemingly on his back. What follows is jaw-dropping
 The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
In the 1950s, artificial intelligence (AI) was born. That's when researchers discovered that machines could perform human-like tasks, such as thinking. Later, in the 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense funded artificial intelligence and established laboratories for further development. Researchers are finding applications for artificial intelligence in many areas, such as space exploration and survival in extreme environments. Space exploration is the study of the universe, which covers the entire universe beyond the earth. Space is classified as an extreme environment because its conditions are different from those on Earth. To survive in space, many factors must be considered and precautions must be taken. Scientists and researchers believe that exploring space and understanding the current state of everything can help understand how the universe works and prepare for potential environmental crises
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 Large models are also very powerful in time series prediction! The Chinese team activates new capabilities of LLM and achieves SOTA beyond traditional models
Apr 11, 2024 am 09:43 AM
Large models are also very powerful in time series prediction! The Chinese team activates new capabilities of LLM and achieves SOTA beyond traditional models
Apr 11, 2024 am 09:43 AM
The potential of large language models is stimulated - high-precision time series prediction can be achieved without training large language models, surpassing all traditional time series models. Monash University, Ant and IBM Research jointly developed a general framework that successfully promoted the ability of large language models to process sequence data across modalities. The framework has become an important technological innovation. Time series prediction is beneficial to decision-making in typical complex systems such as cities, energy, transportation, and remote sensing. Since then, large models are expected to revolutionize time series/spatiotemporal data mining. The general large language model reprogramming framework research team proposed a general framework to easily use large language models for general time series prediction without any training. Two key technologies are mainly proposed: timing input reprogramming; prompt prefixing. Time-
 Deploy large language models locally in OpenHarmony
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:02 AM
Deploy large language models locally in OpenHarmony
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:02 AM
This article will open source the results of "Local Deployment of Large Language Models in OpenHarmony" demonstrated at the 2nd OpenHarmony Technology Conference. Open source address: https://gitee.com/openharmony-sig/tpc_c_cplusplus/blob/master/thirdparty/InferLLM/docs/ hap_integrate.md. The implementation ideas and steps are to transplant the lightweight LLM model inference framework InferLLM to the OpenHarmony standard system, and compile a binary product that can run on OpenHarmony. InferLLM is a simple and efficient L
 Ten humanoid robots shaping the future
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Ten humanoid robots shaping the future
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
The following 10 humanoid robots are shaping our future: 1. ASIMO: Developed by Honda, ASIMO is one of the most well-known humanoid robots. Standing 4 feet tall and weighing 119 pounds, ASIMO is equipped with advanced sensors and artificial intelligence capabilities that allow it to navigate complex environments and interact with humans. ASIMO's versatility makes it suitable for a variety of tasks, from assisting people with disabilities to delivering presentations at events. 2. Pepper: Created by Softbank Robotics, Pepper aims to be a social companion for humans. With its expressive face and ability to recognize emotions, Pepper can participate in conversations, help in retail settings, and even provide educational support. Pepper's
 Promoting the digital upgrading of the industry, Qianjiang Robot builds an intelligent manufacturing ecosystem
Sep 24, 2023 am 10:13 AM
Promoting the digital upgrading of the industry, Qianjiang Robot builds an intelligent manufacturing ecosystem
Sep 24, 2023 am 10:13 AM
Automation, intelligence, and digital intelligence are the development directions of traditional manufacturing. As one of the key equipment for automated production lines, intelligent logistics, human-machine collaboration, and customized production, robots play a key role in the change from traditional manufacturing to intelligent manufacturing. Aistar Qianjiang Robot has covered four major business segments: core components of industrial robots, complete robots, industrial software, and intelligent manufacturing system integration. At the 23rd China International Industrial Expo held from September 19th to 23rd, Aistar Qianjiang Robot Jiang Robot joins hands with a number of affiliated companies to focus on industrial automation, industrial robots and intelligent manufacturing, providing users with high-end, intelligent, and unmanned industrial complete solutions. Chen Helin, Chairman of ASD Co., Ltd. and Director of Zhejiang Qianjiang Robot Co., Ltd. said,



