Detailed explanation of Java multi-threading implementation
Java multi-threading enables concurrent programming and improves performance and responsiveness. Threads can be created by inheriting the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface. The thread life cycle includes NEW, RUNNABLE and other states. Synchronization mechanisms such as mutex locks and the synchronized keyword avoid data races. The actual case shows the scenario of multi-threaded file downloading. Parallel downloading is achieved by creating a thread pool and download tasks.

Detailed explanation of Java multi-threading
Introduction
Multi-threading is implemented in Java The basic mechanism of concurrent programming that allows applications to perform multiple tasks simultaneously to improve performance and responsiveness. This article will introduce in detail the concept, implementation and practical cases of Java multithreading.
Thread Basics
A thread is a lightweight process that shares memory and resources with other threads. In Java, threads are represented using the Thread class, which provides methods to start, pause, and stop threads.
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
// 线程执行的任务
}
}Creating threads
Threads can be created in two ways:
- Inherit the
Threadclass : You can create a new class that extends theThreadclass and override therun()method to specify the tasks performed by the thread. - Implements the
Runnableinterface: It is possible to create a new class that implements theRunnableinterface, which is just a class withrun()Method interface. This class can then be passed as a parameter to theThreadconstructor.
// 继承 Thread 类
class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
// 线程执行的任务
}
}
// 实现 Runnable 接口
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// 线程执行的任务
}
}Thread life cycle
A thread can be in one of the following states:
- NEW: The thread has been created but not started yet.
- RUNNABLE: The thread is running.
- BLOCKED: The thread is waiting for a resource.
- WAITING: The thread is waiting for a certain condition.
- TIMED_WAITING: The thread is waiting for a certain condition, up to the specified time.
- TERMINATED: The thread has completed execution.
Thread synchronization
When multiple threads access shared resources, they must be synchronized to avoid data races. Java provides the following synchronization mechanism:
- Mutex lock:Each object has its own built-in mutex lock, which can be used to ensure that only one thread accesses the object at a time Share data.
- synchronized keyword: The
synchronizedkeyword can be added to a method or block of code to ensure that only the thread holding the object's lock can execute the code.
Practical case: Multi-threaded file download
The following code demonstrates how to use multi-threading to download files from multiple URLs:
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLConnection;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MultiThreadedDownloader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] urls = {
"https://example.com/file1.zip",
"https://example.com/file2.zip",
"https://example.com/file3.zip"
};
// 创建一个线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 为每个 URL 创建一个下载任务
for (String url : urls) {
executor.submit(new DownloadTask(url));
}
// 关闭线程池
executor.shutdown();
}
static class DownloadTask implements Runnable {
private String url;
public DownloadTask(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 从 URL 建立连接
URLConnection connection = new URL(url).openConnection();
// 设置下载位置
String fileName = url.substring(url.lastIndexOf('/') + 1);
File file = new File("downloads/" + fileName);
// 创建输出流
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 读取输入流并写入输出流
int read;
while ((read = connection.getInputStream().read()) != -1) {
outputStream.write(read);
}
// 关闭流
outputStream.close();
connection.getInputStream().close();
System.out.println("下载文件 " + fileName + " 完成");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Java multi-threading implementation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power Introduction Java is a powerful programming language used in everything from mobile applications to enterprise-level systems. For beginners, Java's syntax is simple and easy to understand, making it an ideal choice for learning programming. Basic Syntax Java uses a class-based object-oriented programming paradigm. Classes are templates that organize related data and behavior together. Here is a simple Java class example: publicclassPerson{privateStringname;privateintage;
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
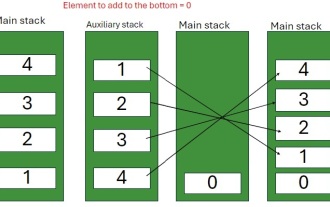 Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
A stack is a data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. In other words, The last element we add to a stack is the first one to be removed. When we add (or push) elements to a stack, they are placed on top; i.e. above all the




