Custom collection classes in Java collection framework
In the Java collection framework, we can create custom collection classes to meet specific needs. These collection classes can be created by extending the Collection interface or its sub-interfaces and need to implement all required methods, such as adding and removing elements. Custom collection classes provide fine-grained control over collection behavior, enhancing code maintainability and reusability.

Custom collection class in Java collection framework
In Java collection framework, we can create our own custom collection class as needed. Custom collection classes allow us to define collections that meet specific requirements and behaviors.
Steps
To create a custom collection class, perform the following steps:
-
Create the base class: Extend
CollectionInterface or its sub-interface (e.g.List,Set). -
Implement required methods: Implement all required methods defined in the interface (such as
add(),remove(),contains()). - Provide a builder: (Optional) Provide a builder to simplify the creation of the collection.
Practical case: car dealer collection
The following is an example of a car dealer collection, which inherits from the List interface:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
We can use this custom collection to manage cars in car dealerships:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
Output:
1 2 |
|
Advantages
The advantages of using a custom collection class include:
- Allows us to define collections that meet specific requirements.
- Provides finer control over collection operations.
- Promote code maintainability and reusability.
The above is the detailed content of Custom collection classes in Java collection framework. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to quickly set up a custom avatar in Netflix
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
How to quickly set up a custom avatar in Netflix
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
An avatar on Netflix is a visual representation of your streaming identity. Users can go beyond the default avatar to express their personality. Continue reading this article to learn how to set a custom profile picture in the Netflix app. How to quickly set a custom avatar in Netflix In Netflix, there is no built-in feature to set a profile picture. However, you can do this by installing the Netflix extension on your browser. First, install a custom profile picture for the Netflix extension on your browser. You can buy it in the Chrome store. After installing the extension, open Netflix on your browser and log into your account. Navigate to your profile in the upper right corner and click
 How to customize background image in Win11
Jun 30, 2023 pm 08:45 PM
How to customize background image in Win11
Jun 30, 2023 pm 08:45 PM
How to customize background image in Win11? In the newly released win11 system, there are many custom functions, but many friends do not know how to use these functions. Some friends think that the background image is relatively monotonous and want to customize the background image, but don’t know how to customize the background image. If you don’t know how to define the background image, the editor has compiled the steps to customize the background image in Win11 below. If you are interested If so, take a look below! Steps for customizing background images in Win11: 1. Click the win button on the desktop and click Settings in the pop-up menu, as shown in the figure. 2. Enter the settings menu and click Personalization, as shown in the figure. 3. Enter Personalization and click on Background, as shown in the picture. 4. Enter background settings and click to browse pictures
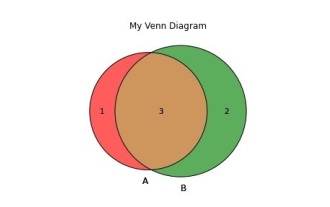 How to create and customize Venn diagrams in Python?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 02:37 PM
How to create and customize Venn diagrams in Python?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 02:37 PM
A Venn diagram is a diagram used to represent relationships between sets. To create a Venn diagram we will use matplotlib. Matplotlib is a commonly used data visualization library in Python for creating interactive charts and graphs. It is also used to create interactive images and charts. Matplotlib provides many functions to customize charts and graphs. In this tutorial, we will illustrate three examples to customize Venn diagrams. The Chinese translation of Example is: Example This is a simple example of creating the intersection of two Venn diagrams; first, we imported the necessary libraries and imported venns. Then we create the dataset as a Python set, after that we use the "venn2()" function to create
 How to customize shortcut key settings in Eclipse
Jan 28, 2024 am 10:01 AM
How to customize shortcut key settings in Eclipse
Jan 28, 2024 am 10:01 AM
How to customize shortcut key settings in Eclipse? As a developer, mastering shortcut keys is one of the keys to improving efficiency when coding in Eclipse. As a powerful integrated development environment, Eclipse not only provides many default shortcut keys, but also allows users to customize them according to their own preferences. This article will introduce how to customize shortcut key settings in Eclipse and give specific code examples. Open Eclipse First, open Eclipse and enter
 How to enable and customize crossfades in Apple Music on iPhone with iOS 17
Jun 28, 2023 pm 12:14 PM
How to enable and customize crossfades in Apple Music on iPhone with iOS 17
Jun 28, 2023 pm 12:14 PM
The iOS 17 update for iPhone brings some big changes to Apple Music. This includes collaborating with other users on playlists, initiating music playback from different devices when using CarPlay, and more. One of these new features is the ability to use crossfades in Apple Music. This will allow you to transition seamlessly between tracks, which is a great feature when listening to multiple tracks. Crossfading helps improve the overall listening experience, ensuring you don't get startled or dropped out of the experience when the track changes. So if you want to make the most of this new feature, here's how to use it on your iPhone. How to Enable and Customize Crossfade for Apple Music You Need the Latest
 How to implement custom middleware in CodeIgniter
Jul 29, 2023 am 10:53 AM
How to implement custom middleware in CodeIgniter
Jul 29, 2023 am 10:53 AM
How to implement custom middleware in CodeIgniter Introduction: In modern web development, middleware plays a vital role in applications. They can be used to perform some shared processing logic before or after the request reaches the controller. CodeIgniter, as a popular PHP framework, also supports the use of middleware. This article will introduce how to implement custom middleware in CodeIgniter and provide a simple code example. Middleware overview: Middleware is a kind of request
 Why is it difficult to implement collection-like functions in Go language?
Mar 24, 2024 am 11:57 AM
Why is it difficult to implement collection-like functions in Go language?
Mar 24, 2024 am 11:57 AM
It is difficult to implement collection-like functions in the Go language, which is a problem that troubles many developers. Compared with other programming languages such as Python or Java, the Go language does not have built-in collection types, such as set, map, etc., which brings some challenges to developers when implementing collection functions. First, let's take a look at why it is difficult to implement collection-like functionality directly in the Go language. In the Go language, the most commonly used data structures are slice and map. They can complete collection-like functions, but
 The operation process of edius custom screen layout
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
The operation process of edius custom screen layout
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
1. The picture below is the default screen layout of edius. The default EDIUS window layout is a horizontal layout. Therefore, in a single-monitor environment, many windows overlap and the preview window is in single-window mode. 2. You can enable [Dual Window Mode] through the [View] menu bar to make the preview window display the playback window and recording window at the same time. 3. You can restore the default screen layout through [View menu bar>Window Layout>General]. In addition, you can also customize the layout that suits you and save it as a commonly used screen layout: drag the window to a layout that suits you, then click [View > Window Layout > Save Current Layout > New], and in the pop-up [Save Current Layout] Layout] enter the layout name in the small window and click OK




