The historical evolution and development prospects of Java generics
Java generics were introduced in Java 5 and are used to store objects type-safely. It allows element types to be specified in the collection definition, thereby eliminating conversion errors, improving code reuse and performance. Java 7 introduced type inference and Java 8 introduced the Stream API. Future trends include generic methods, generic class evolution, and new generic collections. Generics are widely used, such as the filterByAge() method, which can filter specific age elements of different types of objects.

The historical evolution and development prospects of Java generics
Introduction
Java Generics are a mechanism for type-safetying code that have revolutionized Java programming since their introduction in Java 5. This article will delve into the historical evolution of Java generics and look at its future prospects.
Java before Generics
Before Java 5, developers had to use collections with objects or primitive types. This has some limitations, such as:
- Casting: The elements in the collection need to be explicitly converted to the required type.
- Type checking: Unable to enforce the type of elements in a collection.
- Code redundancy: A lot of repetitive code needs to be written to handle different types of collections.
Generics in Java 5
Generics are the solution to these limitations. By using generics, developers can specify the type of elements when defining a collection, for example:
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
The <String> here is called a type parameter, which specifies the names The list will only contain elements of type String.
Benefits and Impact
The introduction of generics has brought many benefits to Java, including:
- Type safety: Enforce the type of elements in the collection and eliminate conversion errors.
- Code reuse: Reduces duplicate code and improves code readability and maintainability.
- Performance improvements: Generic collections are faster than reflection operations due to type erasure (removing type parameters at runtime).
Generics enhancements in Java 7 and 8
In Java 7, generics have been further enhanced to include type inference, which eliminates the need for specification The need for type parameters:
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>()
Java 8 introduces new collection interfaces, such as Stream, which uses generics to support chained operations of the stream API.
Future Outlook
As Java continues to develop, generics will continue to play an important role in the future. Some potential developments include:
- Generic methods: Allow generic methods to accept generic parameters.
- Evolution of generic classes: Improved implementation of generic classes through TypeVars and erasure.
- New generic collections: Provides more generic collections specialized for specific scenarios.
Practical Case
To show generics in action, here is an example:
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public static <T extends Person> List<T> filterByAge(List<T> persons, int age) {
List<T> filtered = new ArrayList<>();
for (T person : persons) {
if (person.getAge() == age) {
filtered.add(person);
}
}
return filtered;
}
}This example shows how generics Reuse code for different types of objects. filterByAge() The method accepts a generic list as parameter and returns a new list of elements that match the given age.
The above is the detailed content of The historical evolution and development prospects of Java generics. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Is sum a keyword in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
Is sum a keyword in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
The sum keyword does not exist in C language, it is a normal identifier and can be used as a variable or function name. But to avoid misunderstandings, it is recommended to avoid using it for identifiers of mathematical-related codes. More descriptive names such as array_sum or calculate_sum can be used to improve code readability.
 What is the difference between `var` and `type` keyword definition structure in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
What is the difference between `var` and `type` keyword definition structure in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
Two ways to define structures in Go language: the difference between var and type keywords. When defining structures, Go language often sees two different ways of writing: First...
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
 Can Python parameter annotations use strings?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Can Python parameter annotations use strings?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Alternative usage of Python parameter annotations In Python programming, parameter annotations are a very useful function that can help developers better understand and use functions...
 How to modify node content in XML
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to modify node content in XML
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
XML node content modification skills: 1. Use the ElementTree module to locate nodes (findall(), find()); 2. Modify text attributes; 3. Use XPath expressions to accurately locate them; 4. Consider encoding, namespace and exception handling; 5. Pay attention to performance optimization (avoid repeated traversals)
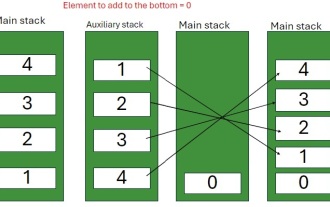 Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
A stack is a data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. In other words, The last element we add to a stack is the first one to be removed. When we add (or push) elements to a stack, they are placed on top; i.e. above all the




