A brief history of broadband Internet technology
In today's digital age, broadband has become a necessity for each of us and every family. Without it, we would be restless and restless.
So, do you know the technical principles behind broadband? From the earliest 56k "cat" dial-up to the current Gigabit cities and Gigabit homes, what kind of changes has our broadband technology experienced? In today’s article, let’s take a closer look at the “Broadband Story”.█ xDSL and ISDN
Have you seen the following interface? I believe that many friends born in the 70s and 80s must have seen it and are very familiar with it. Yes, this is the interface for "dial-up Internet access" when we first came into contact with the Internet. That was more than 20 years ago, when Xiao Zaojun was still in college. In order to access the Internet, I need to buy a modem card (Modem, commonly known as "cat") and plug it into the computer. Then plug the only phone line in the dormitory into the "cat". Only after the settings are completed can you start dialing.
I believe that many friends born in the 70s and 80s must have seen it and are very familiar with it. Yes, this is the interface for "dial-up Internet access" when we first came into contact with the Internet. That was more than 20 years ago, when Xiao Zaojun was still in college. In order to access the Internet, I need to buy a modem card (Modem, commonly known as "cat") and plug it into the computer. Then plug the only phone line in the dormitory into the "cat". Only after the settings are completed can you start dialing. 
 Yes, you read that right, it’s that slow . At the beginning, our entire dormitory relied on this "trickle" to connect us to the school system to select courses. Please feel for yourself how you felt at that time...With this primitive method, once you dial up to access the Internet, the phone cannot be connected and is in a "busy" state. Moreover, the cost of dial-up Internet access is also very expensive. Just like making a phone call, it is charged by the minute (about 3 cents a minute). The speed is inherently slow, but watching the money flow away can drive you to death. If you feel that the Internet speed in the dormitory is slow, you can also choose to go to the Internet cafe. The earliest Internet cafes also had dial-up Internet access. Later, some Internet cafes began to upgrade. On the door of these Internet cafes, there are often a few big words written - "ISDN dedicated line, high-speed surfing".
Yes, you read that right, it’s that slow . At the beginning, our entire dormitory relied on this "trickle" to connect us to the school system to select courses. Please feel for yourself how you felt at that time...With this primitive method, once you dial up to access the Internet, the phone cannot be connected and is in a "busy" state. Moreover, the cost of dial-up Internet access is also very expensive. Just like making a phone call, it is charged by the minute (about 3 cents a minute). The speed is inherently slow, but watching the money flow away can drive you to death. If you feel that the Internet speed in the dormitory is slow, you can also choose to go to the Internet cafe. The earliest Internet cafes also had dial-up Internet access. Later, some Internet cafes began to upgrade. On the door of these Internet cafes, there are often a few big words written - "ISDN dedicated line, high-speed surfing".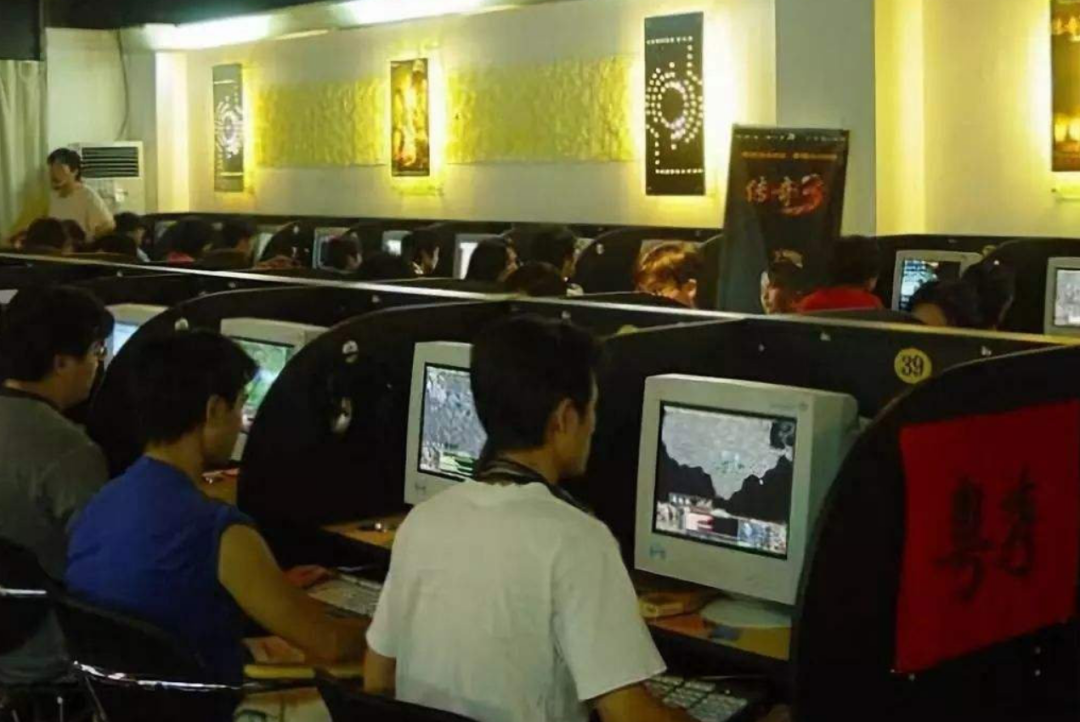 



 Later, on the basis of ADSL, ADSL2 and ADSL2 were upgraded, and the rate could reach 20Mbps for a time. Later, there were a series of technologies such as VDSL and VDSL2. These technologies are often collectively referred to as xDSL technologies.
Later, on the basis of ADSL, ADSL2 and ADSL2 were upgraded, and the rate could reach 20Mbps for a time. Later, there were a series of technologies such as VDSL and VDSL2. These technologies are often collectively referred to as xDSL technologies. 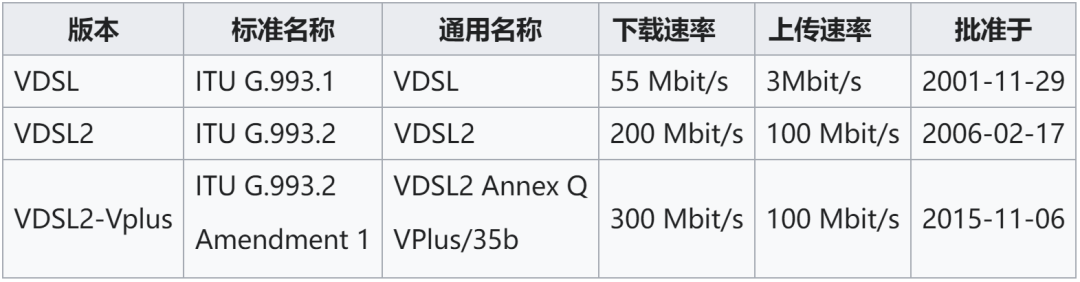 Until now, xDSL technology is still used in some places abroad. Based on G.Fast evolved from VDSL2, the maximum theoretical speed can reach 1Gbps. We mentioned earlier that some domestic Internet cafes use ISDN technology. In fact, the life cycle of this ISDN technology is relatively short. ADSL technology has developed before it has been developed. At that time, some Internet cafes upgraded to ADSL, and some changed to other dedicated lines, such as DDN (Digital Data Network, Digital Data Network), but that is a story later. In addition to ADSL, there are also radio and television broadband (cable access) and other Internet access methods around us. Radio and Television Broadband, I believe everyone who has used it will be impressed . In fact, it is a way to provide broadband access through the coaxial cable of cable television (CATV).
Until now, xDSL technology is still used in some places abroad. Based on G.Fast evolved from VDSL2, the maximum theoretical speed can reach 1Gbps. We mentioned earlier that some domestic Internet cafes use ISDN technology. In fact, the life cycle of this ISDN technology is relatively short. ADSL technology has developed before it has been developed. At that time, some Internet cafes upgraded to ADSL, and some changed to other dedicated lines, such as DDN (Digital Data Network, Digital Data Network), but that is a story later. In addition to ADSL, there are also radio and television broadband (cable access) and other Internet access methods around us. Radio and Television Broadband, I believe everyone who has used it will be impressed . In fact, it is a way to provide broadband access through the coaxial cable of cable television (CATV). 
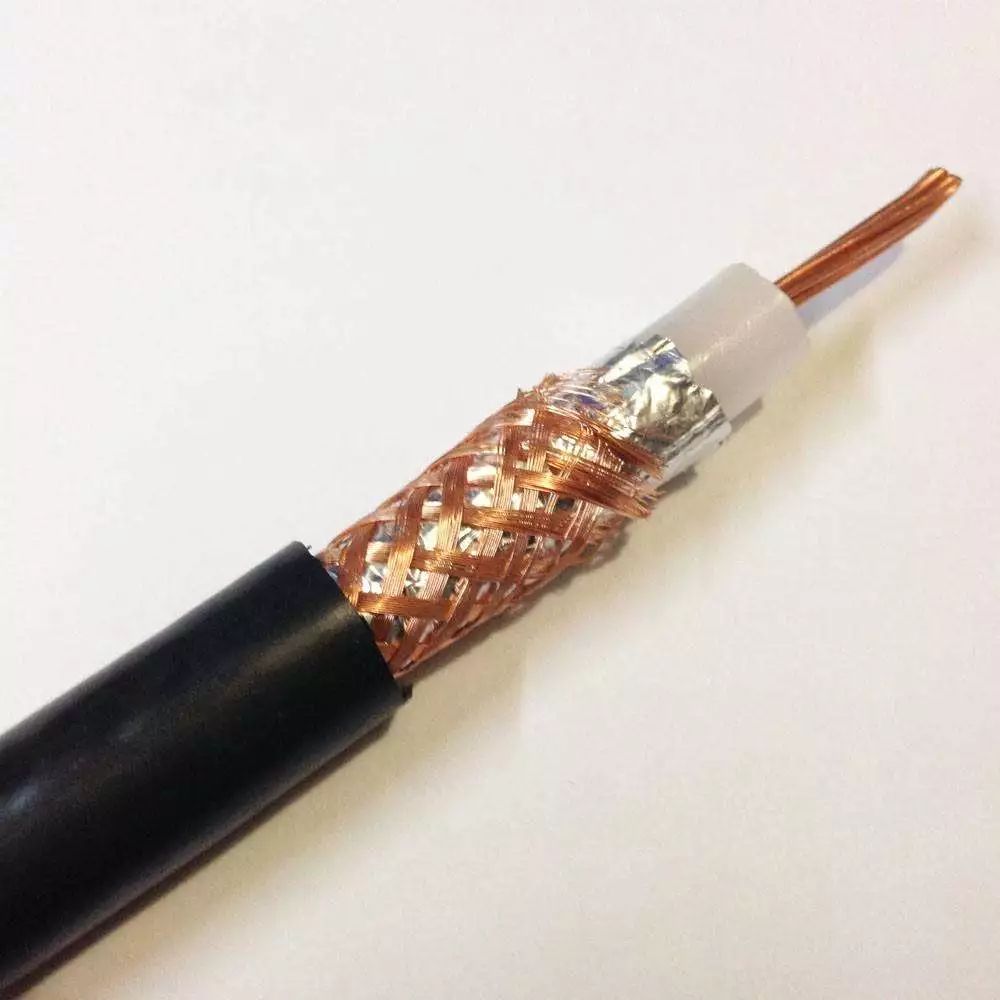

█ EPON and GPON
ADSL brings a significant improvement in the network experience. While we were immersed in this improvement, a new and more awesome technology came to us. This technology is, of course, fiber optic broadband. ADSL and ISDN are both based on metal cables and copper media. In the 1960s, the British-Chinese scientist Kao Kun published a paper proposing the theoretical basis for using optical fibers (optical fibers) for data communications. Not long after, the American company Corning actually pulled out the world's first optical fiber with attenuation that met the requirements, and this magical invention was introduced to the world.
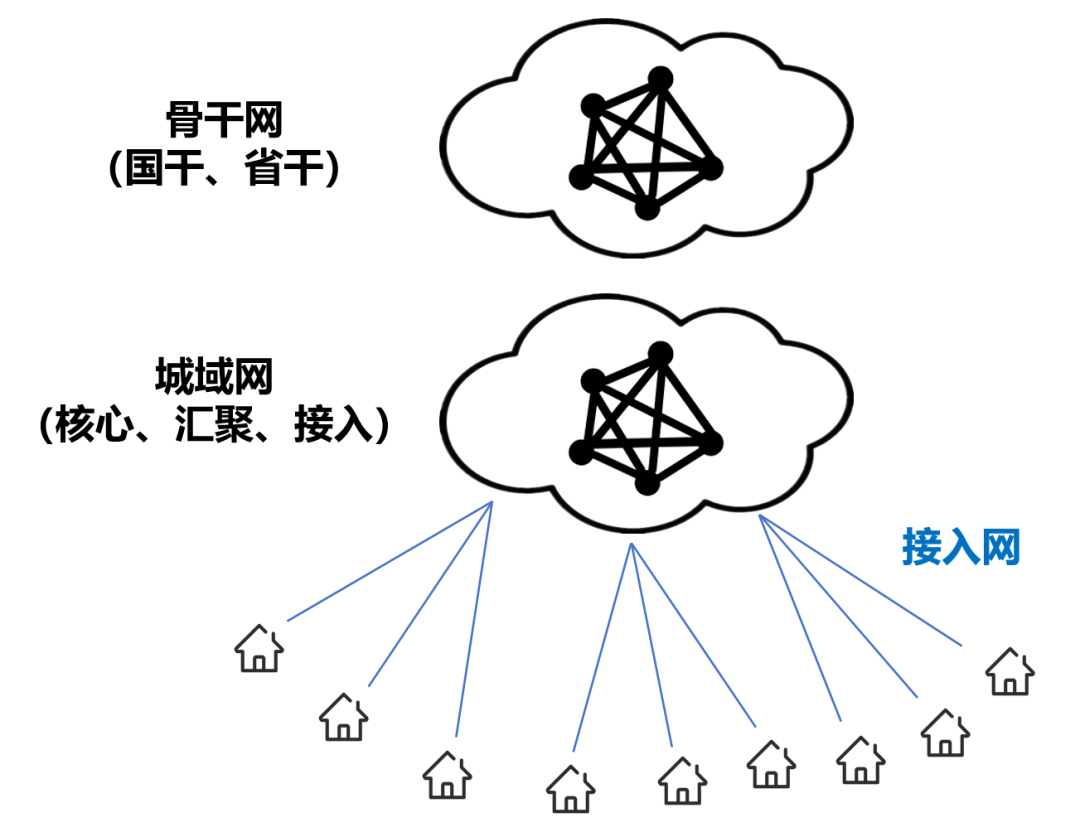 The early optical communication technology was relatively weak (PDH/SDH stage), and the optical fiber transmission signal had a large attenuation. Therefore, all active optical networks (Active Optical Network, AON) are developed, which require the introduction of external energy (power supply) to strengthen (relay) the light. The equipment is more complex and the cost is higher. Later, the technology gradually matured, light could be transmitted farther, and Passive Optical Network (PON) began to appear.
The early optical communication technology was relatively weak (PDH/SDH stage), and the optical fiber transmission signal had a large attenuation. Therefore, all active optical networks (Active Optical Network, AON) are developed, which require the introduction of external energy (power supply) to strengthen (relay) the light. The equipment is more complex and the cost is higher. Later, the technology gradually matured, light could be transmitted farther, and Passive Optical Network (PON) began to appear. 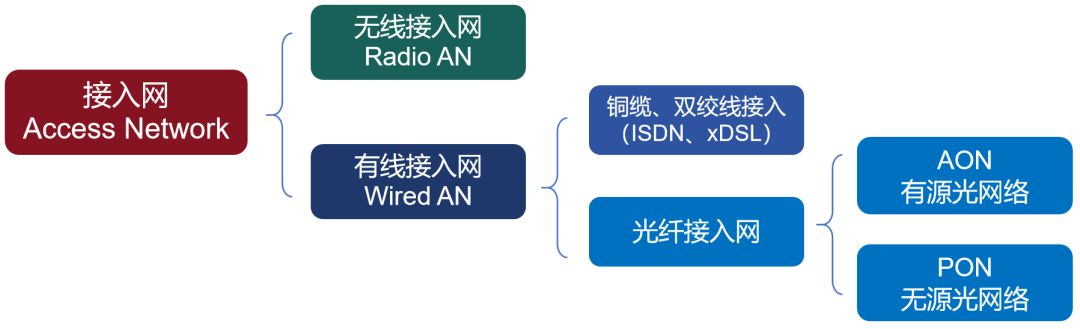 Passive optical network is divided into OLT, ODN, ONT/ONU. OLT (Optical Line Terminal) is the office-side equipment, and ONT/ONU (Optical Network Unit/Terminal) is the user-side equipment (such as optical modem).
Passive optical network is divided into OLT, ODN, ONT/ONU. OLT (Optical Line Terminal) is the office-side equipment, and ONT/ONU (Optical Network Unit/Terminal) is the user-side equipment (such as optical modem).  ODN is an optical distribution network (Optical Distribution Network), which can be understood as the trunk of PON. The passivity of PON mainly refers to this part of passivity, which will greatly reduce construction and maintenance costs. In the early stages of PON (the late 1980s), manufacturers basically introduced narrowband PON technology. The speed of this technology is very low, no more than 2Mbps. Moreover, because manufacturers are working on their own, there has been no unified norms and standards. In 1995, seven network operators including BELLSOUTH, BT, and France Telecom jointly initiated the establishment of the Full Service Access Network Alliance (FSAN), hoping to propose a unified optical access network equipment standard. Soon after, in 1997, based on the recommendations of FSAN, ITU-T (Telecommunications Standards Bureau of the International Telecommunications Union) launched the APON technology system, which is the G.983.1 standard. APON is ATM PON. ATM is not an automatic teller machine, it is the abbreviation of Asynchronous Transfer Mode. The essence of ATM is a transmission protocol. The older generation of communicators must be familiar with ATM. It was once a competitor of the IP protocol and was once very popular. In 2001, FSAN and ITU-T upgraded and revised the APON specification, and changed the name to BPON (Broadband PON, broadband passive optical network). The reason for changing the name was that they did not want APON to be misunderstood as only providing ATM services. In order to further improve the rate standard of PON, in 2002, FSAN launched a new work to standardize PON networks above 1Gbps. In March 2003, based on FSAN's recommendations, ITU-T promulgated the G.984 standard, which is GPON (Gigabit-capable PON, Gigabit Passive Optical Network).
ODN is an optical distribution network (Optical Distribution Network), which can be understood as the trunk of PON. The passivity of PON mainly refers to this part of passivity, which will greatly reduce construction and maintenance costs. In the early stages of PON (the late 1980s), manufacturers basically introduced narrowband PON technology. The speed of this technology is very low, no more than 2Mbps. Moreover, because manufacturers are working on their own, there has been no unified norms and standards. In 1995, seven network operators including BELLSOUTH, BT, and France Telecom jointly initiated the establishment of the Full Service Access Network Alliance (FSAN), hoping to propose a unified optical access network equipment standard. Soon after, in 1997, based on the recommendations of FSAN, ITU-T (Telecommunications Standards Bureau of the International Telecommunications Union) launched the APON technology system, which is the G.983.1 standard. APON is ATM PON. ATM is not an automatic teller machine, it is the abbreviation of Asynchronous Transfer Mode. The essence of ATM is a transmission protocol. The older generation of communicators must be familiar with ATM. It was once a competitor of the IP protocol and was once very popular. In 2001, FSAN and ITU-T upgraded and revised the APON specification, and changed the name to BPON (Broadband PON, broadband passive optical network). The reason for changing the name was that they did not want APON to be misunderstood as only providing ATM services. In order to further improve the rate standard of PON, in 2002, FSAN launched a new work to standardize PON networks above 1Gbps. In March 2003, based on FSAN's recommendations, ITU-T promulgated the G.984 standard, which is GPON (Gigabit-capable PON, Gigabit Passive Optical Network). 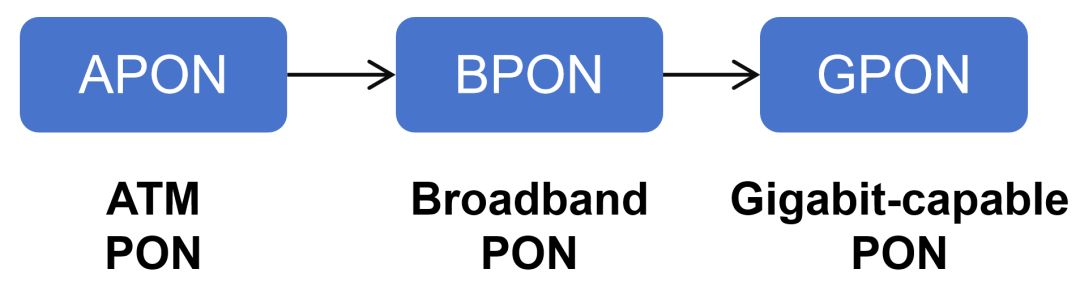 While FSAN and ITU-T were working in full swing, another standardization organization was not idle and began to tinker with PON technology. It is the equally famous IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers). IEEE is the developer and backer of Ethernet standards. After the IEEE released the Gigabit Ethernet standard in 1998, it was thinking about developing a PON standard based on Ethernet. In 2000, IEEE established the EFM working group and officially launched related standardization work. The full name of the EFM working group is interesting, called Ethernet for the First Mile, and it belongs to the IEEE 802.3 group that develops Ethernet standards. In April 2004, the EFM working group was completed and officially launched the IEEE 802.3ah standard, which is EPON (Ethernet PON, PON based on Ethernet Ethernet).
While FSAN and ITU-T were working in full swing, another standardization organization was not idle and began to tinker with PON technology. It is the equally famous IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers). IEEE is the developer and backer of Ethernet standards. After the IEEE released the Gigabit Ethernet standard in 1998, it was thinking about developing a PON standard based on Ethernet. In 2000, IEEE established the EFM working group and officially launched related standardization work. The full name of the EFM working group is interesting, called Ethernet for the First Mile, and it belongs to the IEEE 802.3 group that develops Ethernet standards. In April 2004, the EFM working group was completed and officially launched the IEEE 802.3ah standard, which is EPON (Ethernet PON, PON based on Ethernet Ethernet). 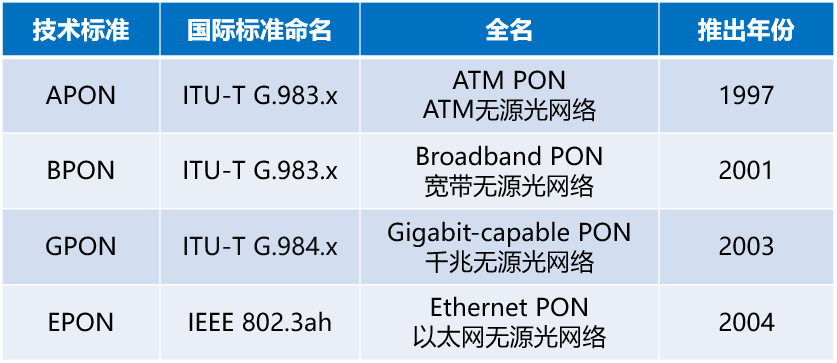 Later, as time passed, ATM gradually lost ground in the competition with IP. APON (BPON) has also been abandoned by operators due to cost, efficiency and other reasons, and has withdrawn from the stage of history. Therefore, I won’t introduce much about APON (BPON), and you don’t need to know too much about it. Anyway, everyone remembers that the mainstream industry at that time was EPON and GPON. They are different technical systems launched by different standards organizations. There is no upgrading, evolution or substitution relationship between the two, and they can be regarded as parallel developments. There is a lot of information online about the specific technical differences between the two, so you can study it separately. In short, EPON and GPON each have their own advantages and disadvantages. Simply put, GPON has larger bandwidth, can carry more users, and is more efficient, but it is also more complex to implement, so the cost is higher. Judging from the domestic market share, EPON was widely adopted by China Telecom at that time, while GPON was more popular with China Unicom and China Mobile. Overseas, most countries and regions use GPON except Japan and a few countries that use EPON. If you have any impressions, around 2010, telecommunications technicians began to come to your home to replace equipment and no longer used telephone lines to access the Internet. Instead, it is a network cable connected to the weak current box. The inner core of the network cable is often separated. There are 8 wire cores, 2 of which are connected to the RJ11 port to connect to the phone; the other 6 wires are connected to the computer to access the Internet.
Later, as time passed, ATM gradually lost ground in the competition with IP. APON (BPON) has also been abandoned by operators due to cost, efficiency and other reasons, and has withdrawn from the stage of history. Therefore, I won’t introduce much about APON (BPON), and you don’t need to know too much about it. Anyway, everyone remembers that the mainstream industry at that time was EPON and GPON. They are different technical systems launched by different standards organizations. There is no upgrading, evolution or substitution relationship between the two, and they can be regarded as parallel developments. There is a lot of information online about the specific technical differences between the two, so you can study it separately. In short, EPON and GPON each have their own advantages and disadvantages. Simply put, GPON has larger bandwidth, can carry more users, and is more efficient, but it is also more complex to implement, so the cost is higher. Judging from the domestic market share, EPON was widely adopted by China Telecom at that time, while GPON was more popular with China Unicom and China Mobile. Overseas, most countries and regions use GPON except Japan and a few countries that use EPON. If you have any impressions, around 2010, telecommunications technicians began to come to your home to replace equipment and no longer used telephone lines to access the Internet. Instead, it is a network cable connected to the weak current box. The inner core of the network cable is often separated. There are 8 wire cores, 2 of which are connected to the RJ11 port to connect to the phone; the other 6 wires are connected to the computer to access the Internet. 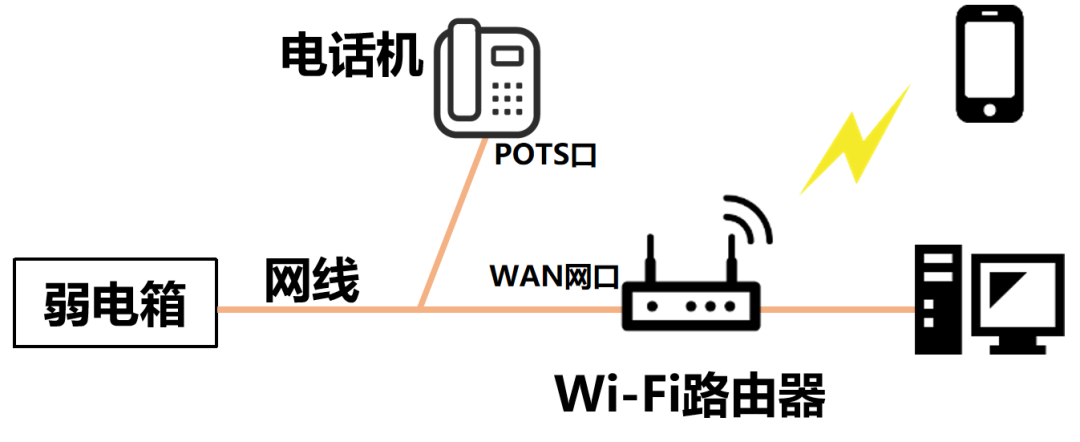 At that time, Wi-Fi wireless routers gradually began to appear, and network cables could be connected to the wireless routers, allowing more desktop computers and laptops to access the Internet. After the emergence of smart phones around 2008, mobile phones can also access the Internet through Wi-Fi. Our internet access has taken another leap forward. With the emergence of 3G/4G at that time, the prosperous mobile Internet era officially began. The network cable connected to the weak current box mentioned just now basically belongs to FTTB (Fiber to the Building) or FTTC (Fiber to the Curb) technology. Taking FTTB as an example, the optical fiber from the operator is connected to the ONU in the weak power room of the building, and then converted into LAN and connected to the user's home.
At that time, Wi-Fi wireless routers gradually began to appear, and network cables could be connected to the wireless routers, allowing more desktop computers and laptops to access the Internet. After the emergence of smart phones around 2008, mobile phones can also access the Internet through Wi-Fi. Our internet access has taken another leap forward. With the emergence of 3G/4G at that time, the prosperous mobile Internet era officially began. The network cable connected to the weak current box mentioned just now basically belongs to FTTB (Fiber to the Building) or FTTC (Fiber to the Curb) technology. Taking FTTB as an example, the optical fiber from the operator is connected to the ONU in the weak power room of the building, and then converted into LAN and connected to the user's home. 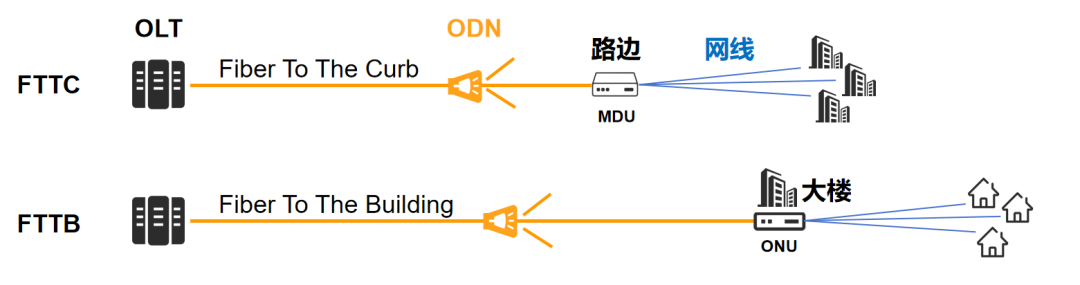 During that period, there was another characteristic of the times: After the third round of restructuring of domestic telecom operators in 2008, China Mobile acquired China Tietong and began to build on Tietong’s foundation. , vigorously enter the home broadband market. Later, China Unicom also joined the fray. This directly led to fierce competition in the home broadband market, and broadband costs began to drop significantly. Within a few years, FTTB began to become FTTH. It is no longer the network cable that enters the home, but the optical fiber.
During that period, there was another characteristic of the times: After the third round of restructuring of domestic telecom operators in 2008, China Mobile acquired China Tietong and began to build on Tietong’s foundation. , vigorously enter the home broadband market. Later, China Unicom also joined the fray. This directly led to fierce competition in the home broadband market, and broadband costs began to drop significantly. Within a few years, FTTB began to become FTTH. It is no longer the network cable that enters the home, but the optical fiber. 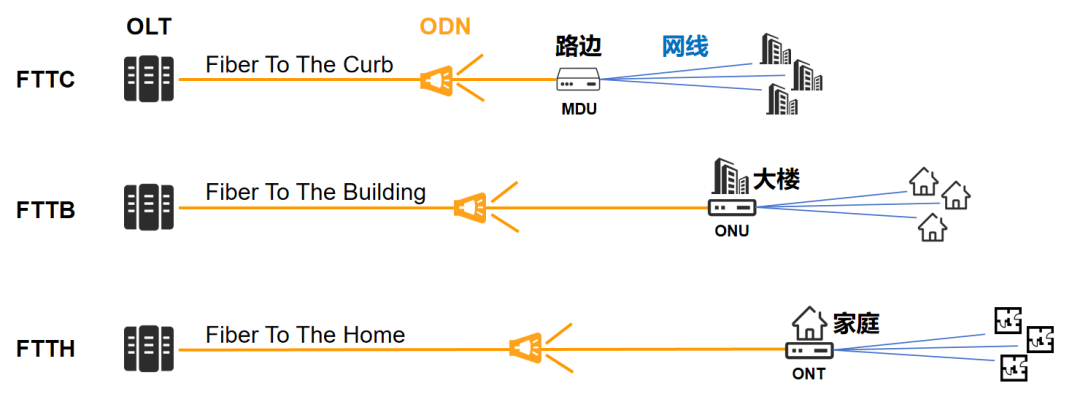 We have an optical modem. The optical fiber is plugged into the optical modem (ONT). The network is exclusive, and the speed becomes faster and more stable.
We have an optical modem. The optical fiber is plugged into the optical modem (ONT). The network is exclusive, and the speed becomes faster and more stable. 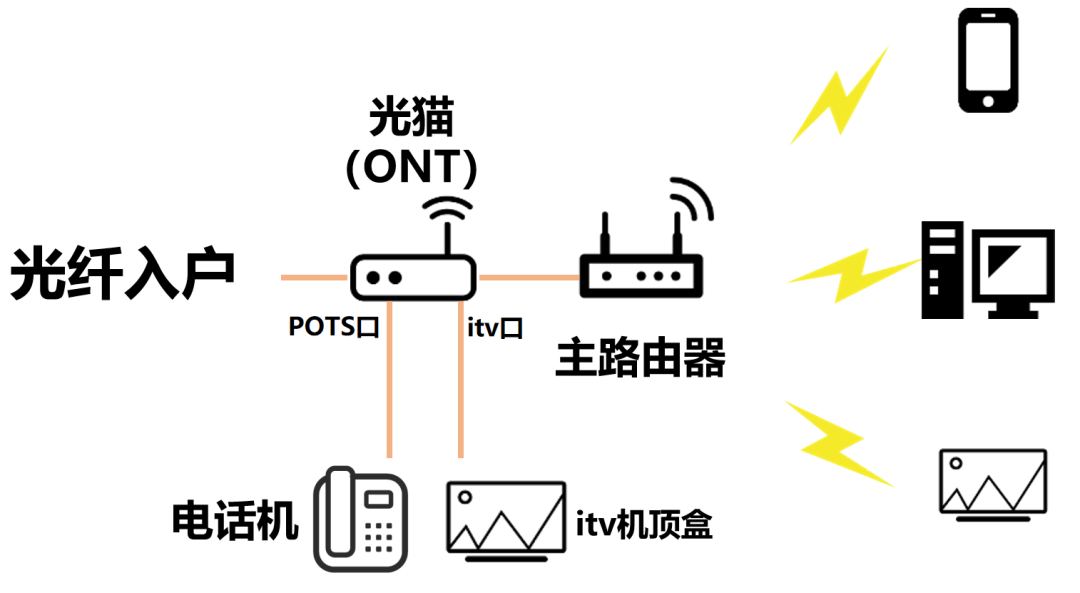
█ 10G PON and 10G EPON
EPON and GPON are both PONs at the 1Gbps level. Note that this 1Gbps is not the rate on the user side. EPON and GPON can only provide users with a rate of 100Mbps. Obviously, with the development of the times, this rate cannot meet the needs of home and enterprise users. As a result, PON began to evolve to the 10Gbps level. In 2006, IEEE began to establish a project to formulate a 10Gbit/s rate EPON system standard, which was later IEEE 802.3av, 10G-EPON. In this standard, 10G EPON is divided into 2 types: one is asymmetric mode, that is, the downlink rate is 10Gbps, and the uplink rate is 1Gbps; the other is symmetric mode, that is, the uplink and downlink rates are both 10Gbps. ITU-T’s GPON is also evolving. In 2008, the ITU launched research on the next generation GPON standard. In 2010, the XG-PON standard was born, which is the ITU-T G.987 series. At the beginning, there were two modes of XG-PON. One was the asymmetric mode XG-PON1, with a downlink rate of 10Gbps and an uplink rate of 2.5Gbps; the other was a symmetric mode XG-PON2, with both uplink and downlink rates. to 10Gbps. Later, around 2013, it was recommended to cancel the XG-PON2 symmetry solution because it was difficult to implement. XG-PON1 was directly renamed to XG-PON. Later, in 2015, the symmetric scheme was restarted and adopted a new name, called XGS-PON (S stands for symmetric, symmetric). In 2017, ITU officially adopted the G.9807 XGS-PON international standard. Now, the industry will collectively refer to XG-PON and XGS-PON as XG (S)-PON.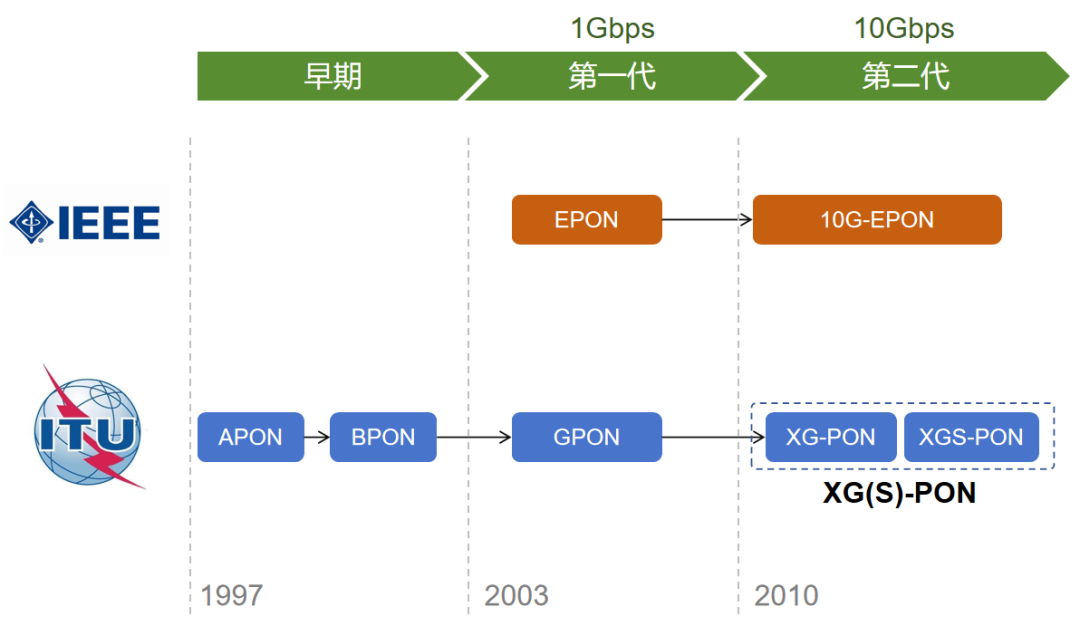 XG (S)-PON and 10G-EPON are both 10Gbps level. On the user side, the rate achieved is 1Gbps, or gigabit. The Gigabit cities and Gigabit homes that many places in China have been promoting in recent years are mainly based on these two technologies. Everyone should have noticed that starting from 2018, the broadband at our homes has gradually increased from 100M to 200M, 500M, and 1000M. Telecommunications technicians will contact you every three days and come to your door to replace equipment "for free". Operators also often hold activities, offering various 199 yuan and 299 yuan packages to upgrade home broadband.
XG (S)-PON and 10G-EPON are both 10Gbps level. On the user side, the rate achieved is 1Gbps, or gigabit. The Gigabit cities and Gigabit homes that many places in China have been promoting in recent years are mainly based on these two technologies. Everyone should have noticed that starting from 2018, the broadband at our homes has gradually increased from 100M to 200M, 500M, and 1000M. Telecommunications technicians will contact you every three days and come to your door to replace equipment "for free". Operators also often hold activities, offering various 199 yuan and 299 yuan packages to upgrade home broadband. 
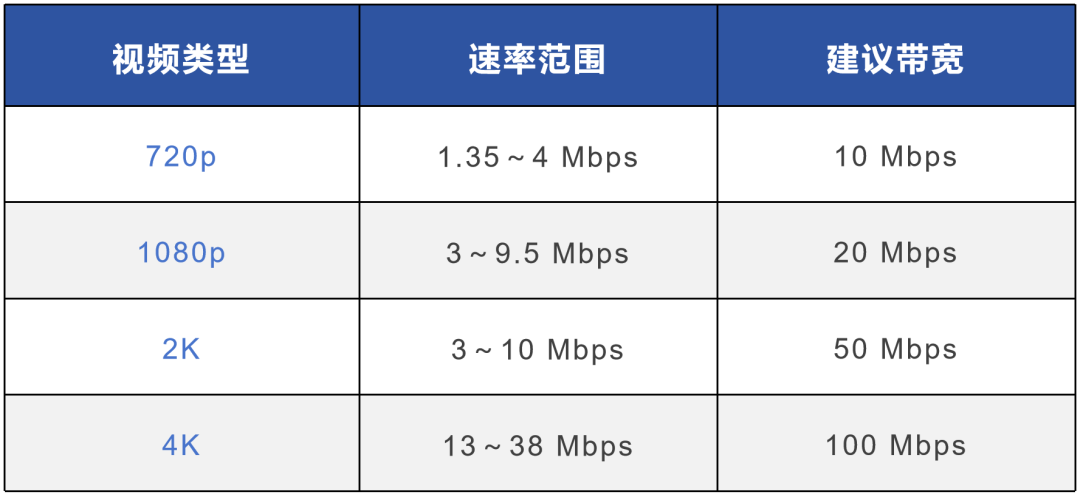 In contrast, the quality experience of Wi-Fi is a bottleneck. It often happens that even with 100M broadband at home, the mobile phone still "turns in circles". Based on this, the solution proposed by the operator is "whole house gigabit", which is FTTR, fiber optic entering the room. Pull fiber optics to every room and then use Wi-Fi to improve the experience.
In contrast, the quality experience of Wi-Fi is a bottleneck. It often happens that even with 100M broadband at home, the mobile phone still "turns in circles". Based on this, the solution proposed by the operator is "whole house gigabit", which is FTTR, fiber optic entering the room. Pull fiber optics to every room and then use Wi-Fi to improve the experience. 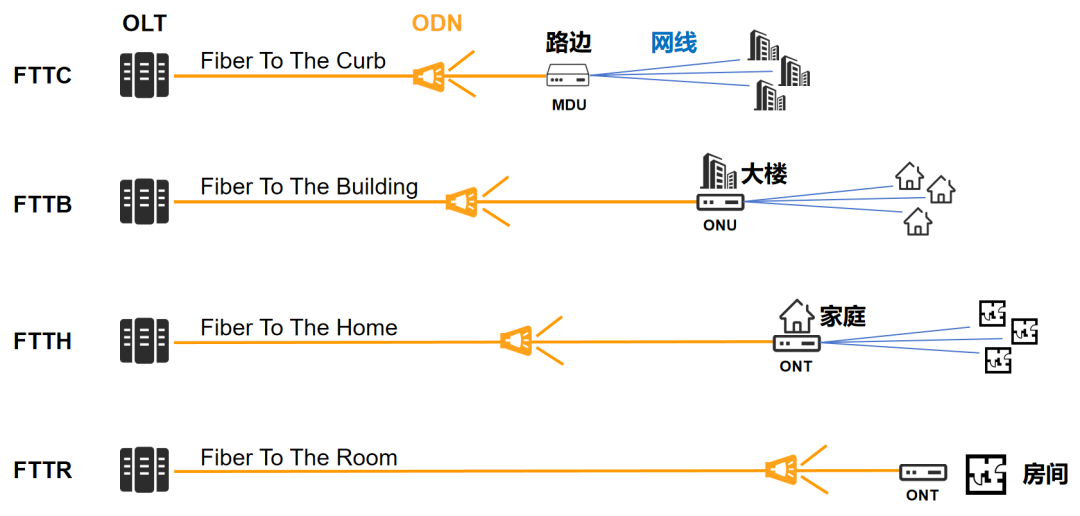

The above is the detailed content of A brief history of broadband Internet technology. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
There are many ways to install DeepSeek, including: compile from source (for experienced developers) using precompiled packages (for Windows users) using Docker containers (for most convenient, no need to worry about compatibility) No matter which method you choose, Please read the official documents carefully and prepare them fully to avoid unnecessary trouble.
 Summary of FAQs for DeepSeek usage
Feb 19, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
Summary of FAQs for DeepSeek usage
Feb 19, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
DeepSeekAI Tool User Guide and FAQ DeepSeek is a powerful AI intelligent tool. This article will answer some common usage questions to help you get started quickly. FAQ: The difference between different access methods: There is no difference in function between web version, App version and API calls, and App is just a wrapper for web version. The local deployment uses a distillation model, which is slightly inferior to the full version of DeepSeek-R1, but the 32-bit model theoretically has 90% full version capability. What is a tavern? SillyTavern is a front-end interface that requires calling the AI model through API or Ollama. What is breaking limit
 What are the AI tools?
Nov 29, 2024 am 11:11 AM
What are the AI tools?
Nov 29, 2024 am 11:11 AM
AI tools include: Doubao, ChatGPT, Gemini, BlenderBot, etc.
 What are the Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds? Common Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds Inventory
Mar 05, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
What are the Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds? Common Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds Inventory
Mar 05, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
Grayscale Investment: The channel for institutional investors to enter the cryptocurrency market. Grayscale Investment Company provides digital currency investment services to institutions and investors. It allows investors to indirectly participate in cryptocurrency investment through the form of trust funds. The company has launched several crypto trusts, which has attracted widespread market attention, but the impact of these funds on token prices varies significantly. This article will introduce in detail some of Grayscale's major crypto trust funds. Grayscale Major Crypto Trust Funds Available at a glance Grayscale Investment (founded by DigitalCurrencyGroup in 2013) manages a variety of crypto asset trust funds, providing institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals with compliant investment channels. Its main funds include: Zcash (ZEC), SOL,
 Delphi Digital: How to change the new AI economy by parsing the new ElizaOS v2 architecture?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 07:00 PM
Delphi Digital: How to change the new AI economy by parsing the new ElizaOS v2 architecture?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 07:00 PM
ElizaOSv2: Empowering AI and leading the new economy of Web3. AI is evolving from auxiliary tools to independent entities. ElizaOSv2 plays a key role in it, which gives AI the ability to manage funds and operate Web3 businesses. This article will dive into the key innovations of ElizaOSv2 and how it shapes an AI-driven future economy. AI Automation: Going to independently operate ElizaOS was originally an AI framework focusing on Web3 automation. v1 version allows AI to interact with smart contracts and blockchain data, while v2 version achieves significant performance improvements. Instead of just executing simple instructions, AI can independently manage workflows, operate business and develop financial strategies. Architecture upgrade: Enhanced A
 As top market makers enter the crypto market, what impact will Castle Securities have on the industry?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
As top market makers enter the crypto market, what impact will Castle Securities have on the industry?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
The entry of top market maker Castle Securities into Bitcoin market maker is a symbol of the maturity of the Bitcoin market and a key step for traditional financial forces to compete for future asset pricing power. At the same time, for retail investors, it may mean the gradual weakening of their voice. On February 25, according to Bloomberg, Citadel Securities is seeking to become a liquidity provider for cryptocurrencies. The company aims to join the list of market makers on various exchanges, including exchanges operated by CoinbaseGlobal, BinanceHoldings and Crypto.com, people familiar with the matter said. Once approved by the exchange, the company initially planned to set up a market maker team outside the United States. This move is not only a sign
 Significantly surpassing SFT, the secret behind o1/DeepSeek-R1 can also be used in multimodal large models
Mar 12, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Significantly surpassing SFT, the secret behind o1/DeepSeek-R1 can also be used in multimodal large models
Mar 12, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Researchers from Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai AILab and the Chinese University of Hong Kong have launched the Visual-RFT (Visual Enhancement Fine Tuning) open source project, which requires only a small amount of data to significantly improve the performance of visual language big model (LVLM). Visual-RFT cleverly combines DeepSeek-R1's rule-based reinforcement learning approach with OpenAI's reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) paradigm, successfully extending this approach from the text field to the visual field. By designing corresponding rule rewards for tasks such as visual subcategorization and object detection, Visual-RFT overcomes the limitations of the DeepSeek-R1 method being limited to text, mathematical reasoning and other fields, providing a new way for LVLM training. Vis
 Bitwise: Businesses Buy Bitcoin A Neglected Big Trend
Mar 05, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Bitwise: Businesses Buy Bitcoin A Neglected Big Trend
Mar 05, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Weekly Observation: Businesses Hoarding Bitcoin – A Brewing Change I often point out some overlooked market trends in weekly memos. MicroStrategy's move is a stark example. Many people may say, "MicroStrategy and MichaelSaylor are already well-known, what are you going to pay attention to?" This is true, but many investors regard it as a special case and ignore the deeper market forces behind it. This view is one-sided. In-depth research on the adoption of Bitcoin as a reserve asset in recent months shows that this is not an isolated case, but a major trend that is emerging. I predict that in the next 12-18 months, hundreds of companies will follow suit and buy large quantities of Bitcoin






