 web3.0
web3.0
 What does automated market maker mean? How do automated market makers (AMMs) make money?
What does automated market maker mean? How do automated market makers (AMMs) make money?
What does automated market maker mean? How do automated market makers (AMMs) make money?
Automated market makers are a type of decentralized exchange that rely on algorithms to determine the price of digital assets and use pairs of exchangeable assets. These protocols are actually based on smart contracts that automatically set and provide the trading price between two digital assets. Therefore, these assets will be automatically exchanged between them based on algorithms, rather than based on order books as in traditional finance. Therefore, the entities participating in this exchange only interact with this smart contract and not with each other. Automated market makers are still important in DeFi. Many investors may still not know how this automatic market maker makes money? Let me analyze it for you below.
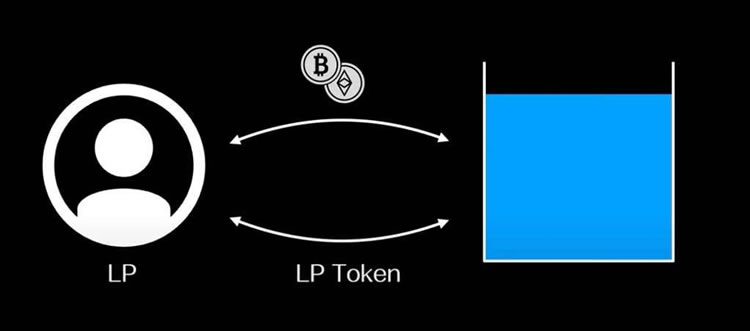
What does automatic market maker mean?
An automated market maker (AMM) is a mechanism used in decentralized exchanges (DEX) that automatically calculates transaction prices between assets through algorithms.
This mechanism allows automated transactions of crypto-assets and other digital assets without permission. The decentralized nature means that there is no third-party intermediary involved, reducing transaction costs and improving transaction efficiency. Automated market makers operate by setting up liquidity pools that store a certain amount of an asset and are used to match orders from buyers and sellers, with algorithms determining prices based on the amount of assets in the pool and trading demand. This decentralized market-making model solves some problems of traditional exchanges, such as transaction slippage and transaction efficiency, but it also brings some new challenges, such as how to ensure the accuracy and security of the algorithm.
How do automatic market makers make money?
Most market makers in the market are large economic players. Market makers maintain market liquidity and make profits by buying and selling securities based on open market quotes. In addition to profits from the bid-ask spread, market makers also receive an additional source of revenue from commissions on liquidity provided by the exchange.
1. Bid-Ask Spread
For investors who want to trade quickly and in large quantities, the trading party is likely to be a market maker. Investors must pay a little more to buy or sell at a lower price to ensure a smooth transaction. At this time, the price between buying and selling becomes the profit of the market maker. Of course, this profit is very small and cannot be earned by anyone except the market maker. In addition to this, market makers need to be able to ensure that they can still hold profits in the event of a price dip or two, for example, by providing exemptions from market maker fees or even subsidizing their fees.
2. Liquidity Commission of the Exchange
The exchange needs trading volume to make trading popular and the exchange to earn fees from it. Therefore, the exchange needs the participation of external market makers to ensure that the various financial instruments on its exchange have sufficient liquidity. There are many different forms of participation, often with fee waivers. After reaching a certain trading volume, the exchange will provide more fee reductions and additional commissions. Conversely, if a market maker does not reach a certain trading volume specified by the exchange, it will be notorious for terminating its interest in the relationship.
What about automated market makers?
Now that you know what a market maker does, you may be eager to explore an automated market maker account explained in detail. Decentralized exchanges focus on eliminating all intermediary processes associated with crypto trading. DEX does not provide any support for the hosting infrastructure or order matching system.
Therefore, DEX users can enjoy a considerable degree of autonomy and initiate transactions directly through their non-custodial wallets. However, the most interesting aspect of decentralized exchanges is the replacement of order matching systems and order book models with autonomous protocols called autonomous market makers, or AMMs.
In the most basic sense, an AMM or Automated Market Maker is basically a protocol, algorithm or formula that helps in pricing assets. Rather than employing an order book model like traditional exchanges, automated market maker algorithms help price assets. Additionally, you should also note that the formula for AMM may vary for each protocol.
For example, Uniswap’s automatic market maker formula is “x*y=k”. In this formula, “x” represents the amount of a specific token in the liquidity pool, while “y” represents the amount of another token in the liquidity pool. The “k” in Uniswap’s automated market maker formula represents a fixed constant in the equation. The fixed constant "k" clearly indicates that the total liquidity in the pool should always remain constant.
Interestingly, you can find different automated market maker algorithms in another AMM, depending on its specific target use case. On the other hand, all AMMs have one significant similarity between them, namely the fact that they use algorithms to determine asset prices. AMMs can help decentralize the process of getting good prices on crypto assets, allowing any individual to create their own market on the blockchain network. Some famous examples of AMM crypto exchanges include Curve, Uniswap, and Balancer.
I hope investors can understand how automatic market makers make money through the above article. The main way AMM works is to emphasize the primary reason why attracting liquidity is important. A higher level of liquidity in the pool ensures limited potential for slippage on large orders. Therefore, improved liquidity may play a key role in driving increased trading volumes on the platform. It is also important to note that slippage issues can vary significantly depending on the AMM protocol. Automated market maker formulas help determine prices. This formula shows how much the ratio between tokens in a liquidity pool changes after a specific trade. If the ratio changes dramatically, you have to worry about slippage being too high.
The above is the detailed content of What does automated market maker mean? How do automated market makers (AMMs) make money?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What is Ouyi for? What is Ouyi
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
What is Ouyi for? What is Ouyi
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
OKX is a global digital asset trading platform. Its main functions include: 1. Buying and selling digital assets (spot trading), 2. Trading between digital assets, 3. Providing market conditions and data, 4. Providing diversified trading products (such as derivatives), 5. Providing asset value-added services, 6. Convenient asset management.
 okx Ouyi Exchange web version enter link click to enter
Mar 31, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
okx Ouyi Exchange web version enter link click to enter
Mar 31, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
1. Enter the web version of okx Euyi Exchange ☜☜☜☜☜☜ Click to save 2. Click the link of okx Euyi Exchange app ☜☜☜☜ Click to save 3. After entering the official website, the clear interface provides a login and registration portal. Users can choose to log in to an existing account or register a new account according to their own situation. Whether it is viewing real-time market conditions, conducting transactions, or managing assets, the OKX web version provides a simple and smooth operating experience, suitable for beginners and veterans. Visit OKX official website now for easy experience
 gate.io latest registration tutorial for beginners
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:12 PM
gate.io latest registration tutorial for beginners
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:12 PM
This article provides newbies with detailed Gate.io registration tutorials, guiding them to gradually complete the registration process, including accessing the official website, filling in information, identity verification, etc., and emphasizes the security settings after registration. In addition, the article also mentioned other exchanges such as Binance, Ouyi and Sesame Open Door. It is recommended that novices choose the right platform according to their own needs, and remind readers that digital asset investment is risky and should invest rationally.
 The latest registration tutorial for gate.io web version
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
The latest registration tutorial for gate.io web version
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
This article provides a detailed Gate.io web version latest registration tutorial to help users easily get started with digital asset trading. The tutorial covers every step from accessing the official website to completing registration, and emphasizes security settings after registration. The article also briefly introduces other trading platforms such as Binance, Ouyi and Sesame Open Door. It is recommended that users choose the right platform according to their own needs and pay attention to investment risks.
 How to roll positions in digital currency? What are the digital currency rolling platforms?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
How to roll positions in digital currency? What are the digital currency rolling platforms?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Digital currency rolling positions is an investment strategy that uses lending to amplify trading leverage to increase returns. This article explains the digital currency rolling process in detail, including key steps such as selecting trading platforms that support rolling (such as Binance, OKEx, gate.io, Huobi, Bybit, etc.), opening a leverage account, setting a leverage multiple, borrowing funds for trading, and real-time monitoring of the market and adjusting positions or adding margin to avoid liquidation. However, rolling position trading is extremely risky, and investors need to operate with caution and formulate complete risk management strategies. To learn more about digital currency rolling tips, please continue reading.
 ok official portal web version ok exchange official web version login portal
Mar 31, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
ok official portal web version ok exchange official web version login portal
Mar 31, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
This article details how to use the official web version of OK exchange to log in. Users only need to search for "OK Exchange Official Web Version" in their browser, click the login button in the upper right corner after entering the official website, and enter the user name and password to log in. Registered users can easily manage assets, conduct transactions, deposit and withdraw funds, etc. The official website interface is simple and easy to use, and provides complete customer service support to ensure that users have a smooth digital asset trading experience. What are you waiting for? Visit the official website of OK Exchange now to start your digital asset journey!
 How to calculate the transaction fee of gate.io trading platform?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
How to calculate the transaction fee of gate.io trading platform?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
The handling fees of the Gate.io trading platform vary according to factors such as transaction type, transaction pair, and user VIP level. The default fee rate for spot trading is 0.15% (VIP0 level, Maker and Taker), but the VIP level will be adjusted based on the user's 30-day trading volume and GT position. The higher the level, the lower the fee rate will be. It supports GT platform coin deduction, and you can enjoy a minimum discount of 55% off. The default rate for contract transactions is Maker 0.02%, Taker 0.05% (VIP0 level), which is also affected by VIP level, and different contract types and leverages
 What are the recommended websites for virtual currency app software?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
What are the recommended websites for virtual currency app software?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
This article recommends ten well-known virtual currency-related APP recommendation websites, including Binance Academy, OKX Learn, CoinGecko, CryptoSlate, CoinDesk, Investopedia, CoinMarketCap, Huobi University, Coinbase Learn and CryptoCompare. These websites not only provide information such as virtual currency market data, price trend analysis, etc., but also provide rich learning resources, including basic blockchain knowledge, trading strategies, and tutorials and reviews of various trading platform APPs, helping users better understand and make use of them


