Best practices for access modifiers of Java functions
Best practice for access modifiers for Java functions: Use the most restrictive modifier, which defaults to private. Inner classes use the private modifier. Protected methods use the protected modifier, allowing access by subclasses. All properties in the immutable class are set to private and accessed through getter methods. Public APIs use the public modifier to make them accessible to external classes.

Best Practices for Access Modifiers of Java Functions
Access modifiers control the access of code outside a class or package to methods, Property access rights. Following appropriate best practices improves code encapsulation, security, and promotes code maintainability.
Access permission modifiers
There are 4 access permission modifiers in Java:
- public: Class Or accessible outside the package
- protected: Accessible within the same package or subclass
- default (no explicit modifier): Same Accessible within the package
- private: Accessible only within the class
Best Practice
-
Use the most restrictive access modifier: Methods and properties should be made
privateby default and raised only when necessary. -
Inner classes: For inner classes, use the
privateaccess modifier to restrict external access. -
Protected methods: Using the
protectedaccess modifier allows subclass methods to access parent class protected methods. -
Immutable classes: For immutable classes (classes whose state cannot be modified), all properties should be
privateand passedgettermethods access. -
Public API: Public API should use the
publicaccess modifier so that it can be accessed by external classes.
Practical case
Consider a Person class, which has a getFirstName() method:
public class Person {
private String firstName;
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
}Since the firstName attribute is only used internally by the class, make it private. The getFirstName() method uses the public access modifier so that it is accessible to external classes.
Conclusion
Following these best practices can significantly improve the accessibility, security, and maintainability of your Java code. By explicitly restricting access levels, you protect sensitive data, reduce coupling, and promote more robust, maintainable applications.
The above is the detailed content of Best practices for access modifiers of Java functions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
 How to evaluate the destructive power of the website after discovering suspicious Trojan files?
Apr 01, 2025 am 08:39 AM
How to evaluate the destructive power of the website after discovering suspicious Trojan files?
Apr 01, 2025 am 08:39 AM
When a suspicious Trojan file is found on the website, how to evaluate its destructive power? Recently, a suspicious Trojan file was found while performing a security scan on the website. ...
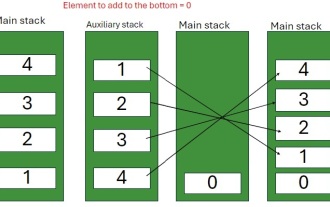 Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
A stack is a data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. In other words, The last element we add to a stack is the first one to be removed. When we add (or push) elements to a stack, they are placed on top; i.e. above all the
 What are the Zookeeper security policies under the Debian system?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:45 AM
What are the Zookeeper security policies under the Debian system?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:45 AM
This article outlines the strategies for enhancing ZooKeeper security in Debian systems. These policies cover multiple aspects such as data protection, access control and overall system protection. Core Security Measures: Data Encryption: Ensuring the confidentiality of ZooKeeper data is crucial. This can be achieved in the following ways: Client encryption: Encryption on the client before the data is sent to the ZooKeeper server. Server-side encryption: The ZooKeeper server is responsible for encrypting and decrypting data. Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL): Use the TLS/SSL protocol to encrypt all communications between the client and the server to prevent data from being stolen during transmission.




