 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Let's talk about the collision between machine learning and human resources management?
Let's talk about the collision between machine learning and human resources management?
Let's talk about the collision between machine learning and human resources management?
Preface
In recent years, many major breakthroughs have been made in the field of machine learning, and human resource management service products driven by artificial intelligence technology also have a huge and dynamic market. More and more companies and government agencies are gradually thinking about applying machine learning technology to human resource management, making effective decisions through neural networks, and accurately predicting the results of human resource management.
This article introduces four aspects of applying machine learning to human resource management research, mainly including technical difficulties, introduction to human resources management decision-making systems, system design methods and system security. It is hoped that readers can have a preliminary understanding of related research. .
Technical Difficulties
In 2019, CEOs of 20 large companies in the United States conducted relevant seminars. The results showed that the application of machine learning technology faces unique challenges in the field of human resources management. . Developing valuable HRM decision-making systems presents not only technical challenges, but also barriers to vectoring the inherent complexity of HRM outcomes, as well as difficult-to-address data, ethical, legal constraints and concerns about affected employees or other stakeholders. a selection process that some believe to be controversial. HR management decisions need to avoid selection procedures that are susceptible to legal challenges or that are considered controversial by employees or other stakeholders.
The summary includes the following aspects:
- How to establish and supervise a series of research and development projects to explore the application of machine learning in human resources management;
- How to effectively develop NLP-based decision support systems;
- How to test decision support systems to confirm that they are safe to use in decision-making;
- Once the system is developed and tested, how to successfully System converted to acceptable usage.
Introduction to the human resources management decision-making system
The implementation of the human resources management decision-making system faces the following challenges:
- The system should automate decision-making for human decision-makers Provide input, or otherwise interact with the decision-making process?
- What inputs do human decision-makers require, and how effective are candidate machine learning systems at providing these inputs?
- What are the risks of different types of decision support, given the level of functionality currently available in different candidate systems?
This framework demonstrates the principles of a machine learning system for conceptualizing design and human resource management. The idea behind the framework is that system design is inseparable from the system's highest priority goals. HRM objectives help designers choose from the many possible ways in which machine learning can support the HRM decision-making process. The design of the implementation in turn affects how the system is evaluated. For example, systems that automate decision-making may be evaluated based on their accuracy or other important criteria, and systems that provide inputs must be judged based on the accuracy of the inputs and how they affect the overall decision outcome. If the system fails to meet security standards, the implementation design must be modified until the designer is able to obtain a system that is valuable for human resource management objectives and is capable of meeting security parameters.
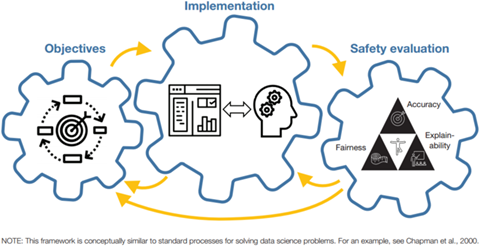 Figure Machine Learning System Framework
Figure Machine Learning System Framework
System Design Methodology
In the early stages of development, there are many design options to integrate machine learning-based Inputs are integrated into decision making. Designs vary in terms of timing (e.g., before or after humans make decisions) and degree of influence (e.g., recommending an option versus directing attention to important features). Five major design implementations of machine learning decision-making systems will be highlighted here:
At decision time, machine learning systems score human resource management records and make decisions automatically without the involvement of human decision-makers .
2. Recommended. Machine learning systems provide recommendations to human decision-makers as additional input.
3. Score. Machine learning systems provide scores to humans as additional input.
4. Summary. Machine learning systems automatically summarize for human decision-makers.
5. Audit. Machine learning systems flag abnormalities for review by human decision-makers as part of the audit process.
The design process begins with determining the priority goals of the machine learning system. Different combinations of goals require different design implementations, as shown in the table.
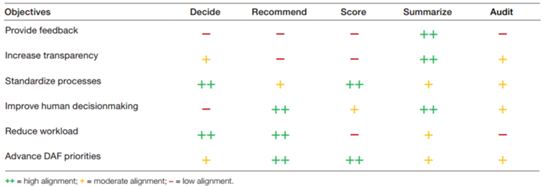 Picture
Picture
These objectives also indicate potential measures of the effectiveness of the evaluation process. For example, if the goal is to reduce workload, the system should reduce the number of human decision-makers or the time they spend recording ratings; if the goal is to improve human decision-making, the system should help improve the quality of decisions by measuring them with evidence. Better contribute to important HR management results.
Machine learning systems that automatically summarize narrative records can serve as a model for decision support. Most of a person's HR records are divided into two types of free-form text and person attributes. Free-form text such as task lists, descriptions of responsibilities, and summaries of key accomplishments. Personnel attributes are pre-quantified, interpretable, management-useful data, such as years of experience, order of merit, or promotion test scores. While the latter type of information is easier to process and use in models or visualizations, the former type of information is also needed to make fully informed human resource management decisions.
Management processing decisions require thoughtful review of records and a manual review or scoring process by experienced personnel. Of the various design implementations considered to support manual review, "summary" is the most versatile. This is the only design that is moderately or highly consistent with all human resource management goals. Automated summaries are useful for providing feedback, increasing transparency, and improving the accuracy of human decision-making, and they are at least somewhat useful for standardizing and reducing manual workload. At the same time, the summary implementation maintains a high degree of manual control over the decision-making process, so it is more likely than other designs to meet security standards. In fact, the summary highlights the elements of the text that the system deems important and, therefore, is an explanation of the system's decisions. Therefore, summaries can serve as a useful aid in helping managers understand model outputs in other design implementations.
System Security
Human resources management decisions are a vital force that affects the future of the enterprise. Therefore, the principle of “first do no harm” must be adopted when making significant changes to the decision-making process. As investment in machine learning increases, a wealth of research and policy documents aim to provide normative guidance for the responsible and ethical use of machine learning (and artificial intelligence more generally).
For example, existing rules and frameworks to protect member privacy will continue to apply to any development projects. During development and deployment, three principles are particularly relevant for testing systems that require machine learning systems to be accurate, fair, and interpretable:
Accuracy means that a machine learning system or the model it contains is correct with a high probability predict the outcome of interest.
Fairness means that the machine learning system treats subgroups equally.
Explainability means humans can understand the factors and relationships that lead to the results of a machine learning system.
These security standards sometimes conflict with each other. To increase fairness, designers may impose limitations on the system that reduce its accuracy or interpretability. To increase interpretability, system designers may use more interpretable (but less flexible) modeling methods, which may impact accuracy and fairness. Testing must include balancing accuracy, fairness, and interpretability to arrive at a design that meets human resource management objectives as well as legal and ethical constraints.
Regarding fairness, it is important to note that there is no single definition of fairness, and it is often impossible to satisfy competitive types of fairness. Therefore, agencies must choose a definition to move forward with testing. A distinction is made here between procedural fairness, which ensures that an HR management process or algorithm treats members of different subgroups equally, and outcome fairness, which checks whether a model or process outcome is biased.
Finally, explainability is critical to achieving human resource management goals because people may ignore or abuse the system if they don't understand how it contributes to better decision-making. Furthermore, defining explainability is inseparable from the target audience, as different types of users require different levels of explanation. Designers can consider using inherently interpretable models to increase interpretability, and they can also conduct human-in-the-loop testing to assess how well people understand the system's functionality.
Summary Summary
This article mainly introduces the research of machine learning in the field of human resources management from four aspects: technical difficulties, introduction to human resources management decision-making systems, system design methods and system security. We hope it can be helpful to readers who want to have a preliminary understanding of this research.
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about the collision between machine learning and human resources management?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
In the fields of machine learning and data science, model interpretability has always been a focus of researchers and practitioners. With the widespread application of complex models such as deep learning and ensemble methods, understanding the model's decision-making process has become particularly important. Explainable AI|XAI helps build trust and confidence in machine learning models by increasing the transparency of the model. Improving model transparency can be achieved through methods such as the widespread use of multiple complex models, as well as the decision-making processes used to explain the models. These methods include feature importance analysis, model prediction interval estimation, local interpretability algorithms, etc. Feature importance analysis can explain the decision-making process of a model by evaluating the degree of influence of the model on the input features. Model prediction interval estimate
 Transparent! An in-depth analysis of the principles of major machine learning models!
Apr 12, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
Transparent! An in-depth analysis of the principles of major machine learning models!
Apr 12, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
In layman’s terms, a machine learning model is a mathematical function that maps input data to a predicted output. More specifically, a machine learning model is a mathematical function that adjusts model parameters by learning from training data to minimize the error between the predicted output and the true label. There are many models in machine learning, such as logistic regression models, decision tree models, support vector machine models, etc. Each model has its applicable data types and problem types. At the same time, there are many commonalities between different models, or there is a hidden path for model evolution. Taking the connectionist perceptron as an example, by increasing the number of hidden layers of the perceptron, we can transform it into a deep neural network. If a kernel function is added to the perceptron, it can be converted into an SVM. this one
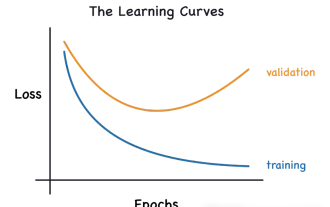 Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
This article will introduce how to effectively identify overfitting and underfitting in machine learning models through learning curves. Underfitting and overfitting 1. Overfitting If a model is overtrained on the data so that it learns noise from it, then the model is said to be overfitting. An overfitted model learns every example so perfectly that it will misclassify an unseen/new example. For an overfitted model, we will get a perfect/near-perfect training set score and a terrible validation set/test score. Slightly modified: "Cause of overfitting: Use a complex model to solve a simple problem and extract noise from the data. Because a small data set as a training set may not represent the correct representation of all data." 2. Underfitting Heru
 The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
In the 1950s, artificial intelligence (AI) was born. That's when researchers discovered that machines could perform human-like tasks, such as thinking. Later, in the 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense funded artificial intelligence and established laboratories for further development. Researchers are finding applications for artificial intelligence in many areas, such as space exploration and survival in extreme environments. Space exploration is the study of the universe, which covers the entire universe beyond the earth. Space is classified as an extreme environment because its conditions are different from those on Earth. To survive in space, many factors must be considered and precautions must be taken. Scientists and researchers believe that exploring space and understanding the current state of everything can help understand how the universe works and prepare for potential environmental crises
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Explainable AI: Explaining complex AI/ML models
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:08 PM
Explainable AI: Explaining complex AI/ML models
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:08 PM
Translator | Reviewed by Li Rui | Chonglou Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models are becoming increasingly complex today, and the output produced by these models is a black box – unable to be explained to stakeholders. Explainable AI (XAI) aims to solve this problem by enabling stakeholders to understand how these models work, ensuring they understand how these models actually make decisions, and ensuring transparency in AI systems, Trust and accountability to address this issue. This article explores various explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) techniques to illustrate their underlying principles. Several reasons why explainable AI is crucial Trust and transparency: For AI systems to be widely accepted and trusted, users need to understand how decisions are made
 Outlook on future trends of Golang technology in machine learning
May 08, 2024 am 10:15 AM
Outlook on future trends of Golang technology in machine learning
May 08, 2024 am 10:15 AM
The application potential of Go language in the field of machine learning is huge. Its advantages are: Concurrency: It supports parallel programming and is suitable for computationally intensive operations in machine learning tasks. Efficiency: The garbage collector and language features ensure that the code is efficient, even when processing large data sets. Ease of use: The syntax is concise, making it easy to learn and write machine learning applications.
 Is Flash Attention stable? Meta and Harvard found that their model weight deviations fluctuated by orders of magnitude
May 30, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
Is Flash Attention stable? Meta and Harvard found that their model weight deviations fluctuated by orders of magnitude
May 30, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
MetaFAIR teamed up with Harvard to provide a new research framework for optimizing the data bias generated when large-scale machine learning is performed. It is known that the training of large language models often takes months and uses hundreds or even thousands of GPUs. Taking the LLaMA270B model as an example, its training requires a total of 1,720,320 GPU hours. Training large models presents unique systemic challenges due to the scale and complexity of these workloads. Recently, many institutions have reported instability in the training process when training SOTA generative AI models. They usually appear in the form of loss spikes. For example, Google's PaLM model experienced up to 20 loss spikes during the training process. Numerical bias is the root cause of this training inaccuracy,





