The role of overflow in css
The overflow attribute controls how element content beyond the container is displayed. The specific values are: visible: display the overflow content hidden: hide the overflow content scroll: add a scroll bar auto: the browser adds a scroll bar as needed initial: reset to the default value inherit: inherit the parent element attributes

The role of overflow in CSS
The overflow property controls how the browser handles the content of an element that exceeds the boundaries of its container. It determines whether the element is shown, hidden, or scrolled when its content overflows.
Basic syntax:
overflow: [value];
Among them, [value] can be the following values:
1. visible: Display overflow content, no clipping should be applied.
2. hidden: Hide overflowing content so that no content can be seen within the element border.
3. scroll: Add a scroll bar so that users can scroll to view overflowing content.
4. auto: The browser automatically adds scroll bars as needed.
5. initial: Reset the overflow property to the browser default value (usually visible).
6. inherit: Inherit the overflow attribute from the parent element.
Example:
.container {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
overflow: hidden;
}
.content {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}In this example, the container's overflow property is set to hidden, which means that any .content content that exceeds the boundaries of the container will be hidden.
Additional Properties:
The overflow property is also used with other CSS properties to control overflow behavior:
- ##overflow- x: Only controls horizontal overflow (short for overflow).
- overflow-y: Controls only vertical overflow (short for overflow).
- overflow-wrap: Control the wrapping method of text inside the element.
The above is the detailed content of The role of overflow in css. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The price of Bitcoin since its birth 2009-2025 The most complete summary of BTC historical prices
Jan 15, 2025 pm 08:11 PM
The price of Bitcoin since its birth 2009-2025 The most complete summary of BTC historical prices
Jan 15, 2025 pm 08:11 PM
Since its inception in 2009, Bitcoin has become a leader in the cryptocurrency world and its price has experienced huge fluctuations. To provide a comprehensive historical overview, this article compiles Bitcoin price data from 2009 to 2025, covering major market events, changes in market sentiment, and important factors influencing price movements.
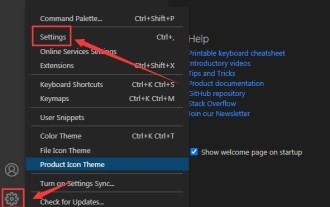 How to set unknown attributes in vscode vscode method to set unknown attributes
May 09, 2024 pm 02:43 PM
How to set unknown attributes in vscode vscode method to set unknown attributes
May 09, 2024 pm 02:43 PM
1. First, open the settings icon in the lower left corner and click the settings option. 2. Then, find the CSS column in the jumped window. 3. Finally, change the drop-down option in the unknownproperties menu to the error button.
 How to isolate styles in components in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
How to isolate styles in components in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Style isolation in Vue components can be achieved in four ways: Use scoped styles to create isolated scopes. Use CSS Modules to generate CSS files with unique class names. Organize class names using BEM conventions to maintain modularity and reusability. In rare cases, it is possible to inject styles directly into the component, but this is not recommended.
 Graphical steps for setting the default properties of CSS in Visual Studio 2019
May 09, 2024 pm 02:01 PM
Graphical steps for setting the default properties of CSS in Visual Studio 2019
May 09, 2024 pm 02:01 PM
1. Open Visual Studio 2019, find its option settings, and click CSS. 2. Here you can see the technical settings of the following attributes. 3. Now you can set text and fill borders here. 4. At this time, you can also set the floating positioning here. 5. At this moment, you can also set the border and background here to complete the operation. 6. Finally, click the OK button here to set the CSS default properties.
 Overview of the historical price of Bitcoin since its birth. Complete collection of historical price trends of Bitcoin.
Jan 15, 2025 pm 08:14 PM
Overview of the historical price of Bitcoin since its birth. Complete collection of historical price trends of Bitcoin.
Jan 15, 2025 pm 08:14 PM
Bitcoin, as a cryptocurrency, has experienced significant market volatility since its inception. This article will provide an overview of the historical price of Bitcoin since its birth to help readers understand its price trends and key moments. By analyzing Bitcoin's historical price data, we can understand the market's assessment of its value, factors affecting its fluctuations, and provide a basis for future investment decisions.
 A list of historical prices since the birth of Bitcoin BTC historical price trend chart (Latest summary)
Feb 11, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
A list of historical prices since the birth of Bitcoin BTC historical price trend chart (Latest summary)
Feb 11, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
Since its creation in 2009, Bitcoin’s price has experienced several major fluctuations, rising to $69,044.77 in November 2021 and falling to $3,191.22 in December 2018. As of December 2024, the latest price has exceeded $100,204.
 How to register for Bitstamp exchange pro? Is it safe? Is it formal?
Aug 13, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
How to register for Bitstamp exchange pro? Is it safe? Is it formal?
Aug 13, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
How to register BitstampPro? Visit the BitstampPro website. Fill in your personal information and email address. Create a password and accept the terms. Verify email address. Is BitstampPro safe? Authentication required. Enforce the use of two-factor authentication. Most assets are stored in cold storage. Use HTTPS to encrypt communication. Conduct regular security audits. Is BitstampPro legitimate? Registered in Luxembourg. Regulated by the Luxembourg Financial Supervisory Committee. Comply with anti-money laundering and know-your-customer regulations.
 The latest price of Bitcoin in 2018-2024 USD
Feb 15, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
The latest price of Bitcoin in 2018-2024 USD
Feb 15, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Real-time Bitcoin USD Price Factors that affect Bitcoin price Indicators for predicting future Bitcoin prices Here are some key information about the price of Bitcoin in 2018-2024:






