 web3.0
web3.0
 Detailed explanation of Artela: parallel EVM+ driver, exploring the infinite scalability and large-scale application implementation of blockchain
Detailed explanation of Artela: parallel EVM+ driver, exploring the infinite scalability and large-scale application implementation of blockchain
Detailed explanation of Artela: parallel EVM+ driver, exploring the infinite scalability and large-scale application implementation of blockchain
Author: YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core
Foreword:
EVM is an advanced model specifically designed to promote the further development of the Ethereum Virtual Machine to better Adapt to the rapidly changing crypto landscape. In this model, as the innovation and productivity of Web2 are gradually integrated into Web3, practical technologies such as artificial intelligence, DePIN and DeFi security are also rapidly integrated into cryptographic applications. EVM provides a brand-new solution that not only promotes the development of large-scale applications, but also accelerates the integration of cryptocurrency and mainstream applications by seamlessly integrating EVM assets, protocols, and infrastructure. It enhances the scalability of the blockchain by implementing native extensions on the EVM WASM chain, and further optimizes the processing capabilities of the blockchain by supporting parallel EVM execution.
According to Techandtips123, parallel EVM is like the division of labor when organizing a party. Suppose you need to prepare for a move and have everyone perform their duties: A transports the bulky luggage, B transports the valuables, C is responsible for moving the items, and D is responsible for the sanitary layout of the new location. This division of labor allows the entire work to be completed by four people, greatly saving time and improving efficiency.
The concept of parallel EVM is similar, by allocating computing tasks to multiple execution units. In the Ethereum network, many participants process different transactions simultaneously, and each transaction acts like an independent task, such as transferring money or generating new tokens. Each participant works independently on a task on the EVM, just like an independent computer program running on the blockchain. Once completed, the results of these tasks are aggregated back into the network and form the final block. When a single executor cannot handle a large number of transactions independently, the speed decreases and the difficulty of use increases. Parallel EVM was introduced to solve this problem. By allowing multiple executors to process different transactions at the same time, the network is able to process more transactions faster, reducing congestion and related costs.
The idea of introducing new “layers”:

图源:Artela — From EVM+ to EVM++
Vitalik Buterin noted: “L2 is for extensions and L3 is for customization features such as privacy protection. In this vision, no one is trying to provide 'scalability squared'; instead, there is one layer in the stack to help applications scale, and another layer to meet the custom functionality needs of different use cases."
In Vitalik's vision for Ethereum, "layers" that address non-scaling needs clearly play an important role. His perspective underscores the need for blockchain networks to support “custom functionality.” For Ethereum, the way to meet this need may be to build a new layer, while Artela adds "native extensions" on top of the base layer.
As far as blockchain is concerned, functionality refers to the ability to support various applications. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), as a runtime engine that supports smart contracts, is the mainstream model for creating DApps to implement functions. EVM was originally proposed by Ethereum and has now been adopted by many smart contract chains, often called EVM-enabled chains or EVM-equivalent chains. However, current EVMs have proven to be limited in supporting the extended functionality of DApps. The key challenge is how to expand the functional boundaries in the EVM chain. In practice, there are two directions for improvement:
Replacing EVM with a better virtual machine;
Strengthening EVM through supplementary extensions.
The first method circumvents the limitations of EVM, but requires giving up EVM-based smart contracts. MoveVM and FuelVM are examples of this implementation. While more advanced virtual machines may be needed in the future, it will take quite some time for them to reach the same level of maturity and popularity as EVMs.
The second approach is to introduce a new stack that enhances EVM by "extending" it. The purpose of this is to push the functional limits of the EVM beyond its original specification while maintaining EVM equivalence. This approach is to enhance DApp functionality on top of existing EVM infrastructure. Exploring EVM enhancements opens the door to exciting possibilities and continued innovation in DApp functionality, leading to significant emerging innovations.
Artela:
EVM in the Artela Network
Artela’s mission is to create a base layer blockchain network to meet the growing demand for large-scale decentralized applications need. Artela’s innovative design allows developers to create native extensions on top of the blockchain’s base layer in a modular fashion, increasing the programmability of the blockchain. This approach will help developers implement custom functionality in a lightweight and dynamic way, opening the door to faster innovation and more possibilities.
Artela has an extension layer that allows the addition of local user-defined extension modules called Aspects, improving programmability while ensuring compatibility with existing EVM smart contracts. Aspect allows developers to inject additional logic throughout the transaction lifecycle outside of smart contracts to handle transactions and related blocks.
Artela 已经建立了一个高度可扩展的 EVM+ 网络,利用Aspect编程(见扩展链接1)与EVM兼容的网络上引入了WASM虚拟机,这些虚拟机可以相互操作,实现链上扩展程序的动态添加和执行。EVM+ 使开发人员能够构建高性能协议、模块化 DApp,并针对特定场景定制底层功能。
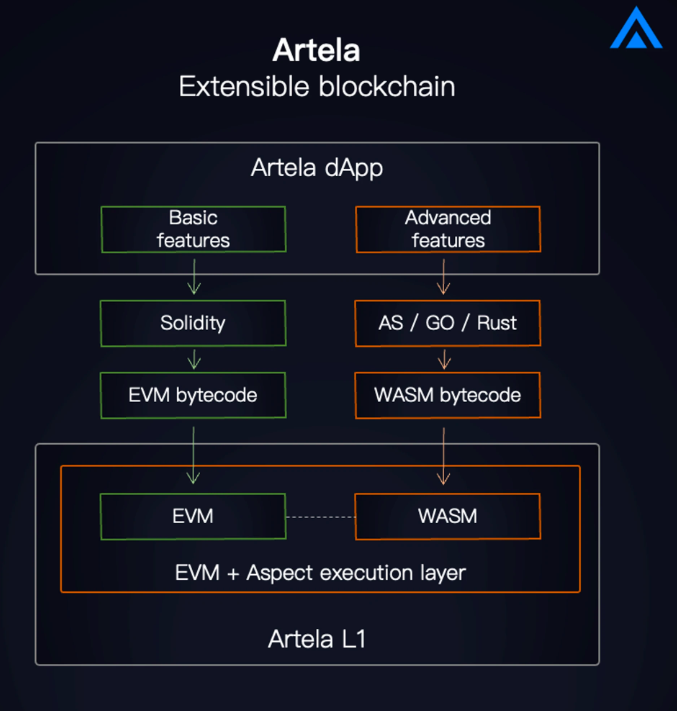
图源:Artela官方
在 DevNet 和 Public Testnet 期间,Artela与社区的开发人员共同开发,探索 EVM+ 网络的潜力,并由此产生了富有想象力的使用案例:
利用 WASM 作为链上协处理器,促进人工智能代理算法和其他高性能模块直接在区块链上执行,同时确保与 EVM 系统的无缝互操作性;
参与自主世界的链上人工智能代理,实现可与用户互动的真正可编程链上 NPC;
可选择实时执行的链上安全模块,允许 DeFi 协议即时识别和恢复可疑交易。
一个既能完全实现链上协议、人工智能和安全 DeFi,又能保持与 EVM 世界的兼容性和互操作性的新时代即将到来。
从 EVM+ 到 EVM++
Artela 的愿景是建立一个无限可扩展的网络,EVM+ 不是最终目标而是一个起点。Artela 的下一步是 EVM++,这是一个平行的 EVM+ 网络,可以充分释放可扩展区块链的潜力。EVM+ 释放了 EVM 的可扩展性,旨在适应新的加密世界,在这个世界里,Web2 的生产力和创新,以及人工智能、DePIN 和金融科技等实用技术,正在迅速融入 DApps。EVM++ 释放了 EVM 的可扩展性,使这个极具创造力的网络能够进一步促进 DApps 的大规模应用,并加速加密货币与主流应用的整合。
EVM++并行弹性 EVM 网络
Artela 的并行 EVM++ 将分两个阶段实施。
第一阶段涉及在 EVM+ 下并行执行事务。Artela 的网络不仅实现了基本的并行 EVM,还解决了 EVM+ Aspect 下并行执行的难题,这是一个在 WASM 虚拟机上运行的扩展程序,可在事务的生命周期内调用。
在第二阶段,Artela 将利用并行功能,并将其与弹性计算相结合,实现弹性区块空间,这是一种动态机制,允许 DApp 将并行执行的优势最大化。
并行EVM简述
Artela 的水平可扩展架构围绕并行执行而设计,通过弹性计算确保网络节点计算能力的可扩展性,最终实现弹性块空间。
并行执行:Artela 上的事务可以并行执行。Artela 网络根据事务依赖性冲突分析,对并行执行的事务进行分组;
弹性计算:验证器节点支持横向扩展,网络会根据当前的网络负载或订阅情况自动调整验证器的计算节点。扩展过程由弹性协议协调,确保共识网络中有足够的弹性计算节点;
弹性区块空间:基于弹性计算,除了扩展公共区块空间外,有独立区块空间需求的大型 DApp 还可以在网络中申请专用弹性区块空间。
“弹性区块空间”
弹性区块空间指的是可动态扩展的区块空间,为具有高交易吞吐量需求的 DApp 提供具有协议保证的专用区块空间。默认情况下,区块的公共区块空间容量有限。当 DApp 申请独立区块空间时,区块将增加额外空间,该空间只容纳与 DApp 智能合约相关的交易。当区块空间扩大时,验证者需要增加弹性执行节点,以扩大相应的处理能力。
弹性区块空间是区块链的一种扩展机制,可在保持互操作性的同时实现无限扩展。分片区块链、应用链网络、Layer2 等可扩展网络也能提供独立的区块空间,但隔离和区块生成是不同步的。弹性区块空间允许具有独立区块空间的 DApp 通过同一区块中的原子交易进行同步交互,避免了异步跨链通信的需要。
当 Artela 网络中的 DApp 需要高度可扩展性时,它可以订阅弹性区块空间来处理吞吐量的增加。弹性区块空间和本地扩展为 Artela 中的 DApp 提供了可扩展性和定制功能。
Artela 利用本地扩展增强 DApp 功能
通过利用Aspect 编程,开发人员能够创建本地扩展(见扩展链接2),在所有区块链基础层之上将自定义功能纳入 DApp,并与现有的 EVM 智能合约相结合,以增强 DApp 的功能。
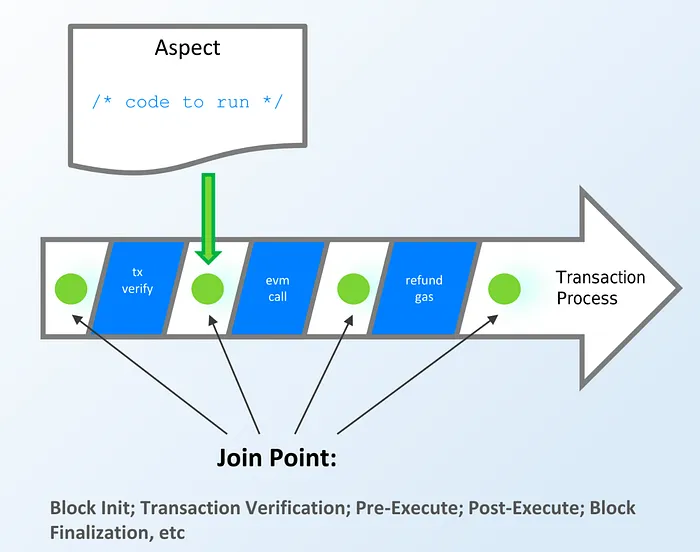
图源作者:Joshua Esin
1.增强可扩展性:
在 Artela 中,Aspect 编程的优势之一在于其无与伦比的可扩展性。传统的智能合约在修改或扩展功能时往往会受到限制。Artela 的 Aspect 编程通过提供模块化和可扩展的框架克服了这一障碍。开发人员可以无缝扩展现有合约的功能,而无需修改其核心逻辑。这种可扩展性为更加敏捷和可扩展的 dApp 开发铺平了道路。
2.提高安全性:
在不断发展的区块链安全领域,Artela 的 Aspect Programming 引入了一种模式转变。与传统的白盒安全措施不同,Aspect 编程提供了一个补充性的黑盒安全解决方案。实时监控、主动风险缓解和运行时行为分析有助于建立一个强大的安全框架,防止漏洞并确保协议的连续性。
3.链上意图求解器:
Artela 的 Aspect Programming 引入了链上意图求解器的革命性概念。传统上用户需要指定详细的函数调用来执行事务,有了链上意图解算器,用户可以用人类可读的语言表达所需的结果,从而获得更直观、更可定制的体验。例如,用户可以将其意图指定为 "用 X ETH 兑换 Y USDC",从而无需调用复杂的函数。
4.准时制(JIT)操作:
JIT 操作是广泛应用于各种场景的强大概念,通过 Artela 的 Aspect Programming这一概念获得了灵活性。在区块生命周期内执行链上逻辑并将其与原子交易中的智能合约相结合,为 JIT 清算、JIT LP 管理和 MEV 捕捉 AMM 策略提供了可能性。
5.本地事件驱动行动:
Artela 中的原生事件驱动操作使用户能够订阅实时链上事件,触发原子任务。这一功能有助于保持链上和链下状态的一致性,实现异步跨链消息通知,并增强区块链自动化。
6.全链游戏:
Artela 的 Aspect Programming 将其影响力扩展到游戏领域,为开发人员提供了增强游戏内资产可编程性的工具。有了 Artela,游戏设备 NFT 可以通过可编程性进行升级,从而在游戏生态系统中开创多功能用户体验的新时代。
7.OnChain MicroServices:
Artela 能够在区块链网络上创建公共链上服务,促进不同用户和组织的集体维护和治理。这种模式促进了资源共享、协同创新,减少了发展障碍,有助于去中心化金融生态系统的发展。
去中心化网络的内置 "功能层":提升区块链能力。
Artela 的编程模型为区块链网络引入了一个内置的 "功能层",无需第三方网络或复杂的链外系统。该功能层扩展了基础层的本机功能,包括安全保护、保管员功能、自动化、链外同步。该功能层的集成标志着去中心化网络在协议开发和用户体验方面的飞跃。
结语:
Web3 的基础技术是公共区块链,它首先由中本聪的比特币网络推向世界,后来由以太坊等智能合约平台大大扩展了其功能。有些人认为区块链是去中心化的数据网络,即分布式账本技术。实际上它远不止数据层面这么简单。
区块链更像是一台计算机而不是账本或数据库,如今我们面临的挑战是如何设计出更好的计算机。Artela 区块链是在 Cosmos SDK 的基础上构建的并在引擎层面做了许多改进,其次Artela 与 EVM 兼容,创新是引入了 Aspect Programming(特征编程),以实现链上扩展。除了 EVM,Artela 还添加了第二个基于 WASM 的虚拟机,以支持多种编程语言(汇编脚本、rust、C、C++),并能访问更多的链上资源,因此EVM 适用于通用智能合约,而Aspect VM 适用于特定应用扩展。
扩展链接:
(1)https://docs.artela.network/main/Aspect-Programming/Aspect (Aspect官方解释)
(2)https://docs.artela.network/Core-Concepts/Chain-Native-Pattern (利用Aspect编程本地扩展)
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Artela: parallel EVM+ driver, exploring the infinite scalability and large-scale application implementation of blockchain. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 gate.io registration tutorial
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
gate.io registration tutorial
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
This article provides a detailed Gate.io registration tutorial, covering every step from accessing the official website to completing registration, including filling in registration information, verifying, reading user agreements, etc. The article also emphasizes security measures after successful registration, such as setting up secondary verification and completing real-name authentication, and gives tips from beginners to help users safely start their digital asset trading journey.
 okx Ouyi Exchange web version enter link click to enter
Mar 31, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
okx Ouyi Exchange web version enter link click to enter
Mar 31, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
1. Enter the web version of okx Euyi Exchange ☜☜☜☜☜☜ Click to save 2. Click the link of okx Euyi Exchange app ☜☜☜☜ Click to save 3. After entering the official website, the clear interface provides a login and registration portal. Users can choose to log in to an existing account or register a new account according to their own situation. Whether it is viewing real-time market conditions, conducting transactions, or managing assets, the OKX web version provides a simple and smooth operating experience, suitable for beginners and veterans. Visit OKX official website now for easy experience
 ok official portal web version ok exchange official web version login portal
Mar 31, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
ok official portal web version ok exchange official web version login portal
Mar 31, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
This article details how to use the official web version of OK exchange to log in. Users only need to search for "OK Exchange Official Web Version" in their browser, click the login button in the upper right corner after entering the official website, and enter the user name and password to log in. Registered users can easily manage assets, conduct transactions, deposit and withdraw funds, etc. The official website interface is simple and easy to use, and provides complete customer service support to ensure that users have a smooth digital asset trading experience. What are you waiting for? Visit the official website of OK Exchange now to start your digital asset journey!
 What are the recommended websites for virtual currency app software?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
What are the recommended websites for virtual currency app software?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
This article recommends ten well-known virtual currency-related APP recommendation websites, including Binance Academy, OKX Learn, CoinGecko, CryptoSlate, CoinDesk, Investopedia, CoinMarketCap, Huobi University, Coinbase Learn and CryptoCompare. These websites not only provide information such as virtual currency market data, price trend analysis, etc., but also provide rich learning resources, including basic blockchain knowledge, trading strategies, and tutorials and reviews of various trading platform APPs, helping users better understand and make use of them
 Top 10 of the formal Web3 trading platform APP rankings (authoritatively released in 2025)
Mar 31, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Top 10 of the formal Web3 trading platform APP rankings (authoritatively released in 2025)
Mar 31, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Based on market data and common evaluation criteria, this article lists the top ten formal Web3 trading platform APPs in 2025. The list covers well-known platforms such as Binance, OKX, Gate.io, Huobi (now known as HTX), Crypto.com, Coinbase, Kraken, Gemini, BitMEX and Bybit. These platforms have their own advantages in user scale, transaction volume, security, compliance, product innovation, etc. For example, Binance is known for its huge user base and rich product services, while Coinbase focuses on security and compliance. Choosing a suitable platform requires comprehensive consideration based on your own needs and risk tolerance.
 How to roll positions in digital currency? What are the digital currency rolling platforms?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
How to roll positions in digital currency? What are the digital currency rolling platforms?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Digital currency rolling positions is an investment strategy that uses lending to amplify trading leverage to increase returns. This article explains the digital currency rolling process in detail, including key steps such as selecting trading platforms that support rolling (such as Binance, OKEx, gate.io, Huobi, Bybit, etc.), opening a leverage account, setting a leverage multiple, borrowing funds for trading, and real-time monitoring of the market and adjusting positions or adding margin to avoid liquidation. However, rolling position trading is extremely risky, and investors need to operate with caution and formulate complete risk management strategies. To learn more about digital currency rolling tips, please continue reading.
 On which platform is web3 transaction?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
On which platform is web3 transaction?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
This article lists the top ten well-known Web3 trading platforms, including Binance, OKX, Gate.io, Kraken, Bybit, Coinbase, KuCoin, Bitget, Gemini and Bitstamp. The article compares the characteristics of each platform in detail, such as the number of currencies, trading types (spot, futures, options, NFT, etc.), handling fees, security, compliance, user groups, etc., aiming to help investors choose the most suitable trading platform. Whether it is high-frequency traders, contract trading enthusiasts, or investors who focus on compliance and security, they can find reference information from it.
 How to calculate the transaction fee of gate.io trading platform?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
How to calculate the transaction fee of gate.io trading platform?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
The handling fees of the Gate.io trading platform vary according to factors such as transaction type, transaction pair, and user VIP level. The default fee rate for spot trading is 0.15% (VIP0 level, Maker and Taker), but the VIP level will be adjusted based on the user's 30-day trading volume and GT position. The higher the level, the lower the fee rate will be. It supports GT platform coin deduction, and you can enjoy a minimum discount of 55% off. The default rate for contract transactions is Maker 0.02%, Taker 0.05% (VIP0 level), which is also affected by VIP level, and different contract types and leverages




