 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Javascript aop (aspect-oriented programming) around analysis_javascript skills
Javascript aop (aspect-oriented programming) around analysis_javascript skills
Javascript aop (aspect-oriented programming) around analysis_javascript skills
Aop is also called aspect-oriented programming, in which "notification" is the specific implementation of aspects, which is divided into before (pre-notification), after (post-notification), and around (surround notification). Students who have used spring must be familiar with it. Very familiar, but in js, AOP is a seriously ignored technical point. However, using aop can effectively improve js code logic. For example, in front-end frameworks dojo and yui3, AOP is promoted to an internal mechanism of custom events, which can be seen everywhere in the source code. Thanks to this abstraction, Dojo's custom events are extremely powerful and flexible. The implementation of aop in dojo is in the dojo/aspect module. There are three main methods: before, after, and around. This article will lead you step by step to implement the around method. Subsequent articles will provide an in-depth analysis of the structural system of the dojo/aspect module.
To implement surround notification in js, the simplest and most thought-provoking way is to use callback
advice = function(originalFunc){
console.log("before function");
originalFunc();
console.log("after function");
}
var obj = {
foo: function(){
console.log('foo');
}
}
advice(obj.foo)Result:
before function
foo
after function
Haha, it’s too simple. Can you go back to sleep? . . .
But, isn’t it a bit too rough? . . . The promised surroundings. . . . At least the next call to obj.foo should have this result, instead of a dry "foo"; for this we need to make some changes and use closures
advice = function(originalFunc){
return function() {
console.log("before function");
originalFunc();
console.log("after function");
}
}
var obj = {
foo: function(){
console.log(this.name);
},
name: "obj"
}
obj.foo = advice(obj.foo)
obj.foo()Output:
before function
after function
It seems that the surround effect has been achieved, but where has the promised name gone? . . .
In the closure returned by advice, we also need to deal with scope issues
advice = function(originalFunc){
return function() {
console.log("before function");
originalFunc();
console.log("after function");
}
}
var obj = {
foo: function(){
console.log(this.name);
},
name: "obj"
}
keepContext = function() {
return obj['foo'].call(obj);
}
obj.foo = advice(keepContext);It seems that the scope problem is solved by using call. Let’s run it and see:
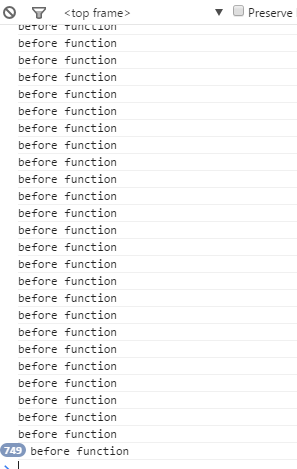
Damn it, is this the legendary endless loop? . . .
It seems that we still need to make some changes and use an intermediate variable to eliminate the infinite loop
advice = function(originalFunc){
return function() {
console.log("before function");
originalFunc();
console.log("after function");
}
}
var obj = {
foo: function(){
console.log(this.name);
},
name: "obj"
}
var exist = obj.foo;
keepContext = function() {
return exist.call(obj);
}
obj.foo = advice(keepContext);
obj.foo();Output:
before function
obj
after function
Haha, the world suddenly became a beautiful place. . . .
But does this bunch of code seem too low? Should we come up with some high-level abstractions? Well, I think so too
function around(obj, prop, advice){
var exist = obj[prop];
var advised = advice(function(){
return exist.call(obj, arguments);
});
obj[prop] = advised;
}
advice = function(originalFunc){
return function() {
console.log("before function");
originalFunc();
console.log("after function");
}
}
var obj = {
foo: function(){
console.log(this.name);
},
name: "obj"
}
around(obj, 'foo', advice);
obj.foo();The around method decouples the processing process from the specific object; as long as advice is written in the following format, the around effect can be achieved
advice = function(originalFunc){
return function() {
//before
originalFunc();
//after
}
}Haha, you are so tall and cool in an instant, so cool. . . .
Then the question comes: What should I do if I accidentally call the around method one more time? . . . Forehead. . . . This is a question. Should we let around return a handle with a remove method to eliminate the binding, just like binding/removing events.
What remove means is that the next time the function is executed, it will no longer execute the corresponding around method, but only run the originalFunc method
function around(obj, prop, advice){
var exist = obj[prop];
var previous = function(){
return exist.call(obj, arguments);
};
var advised = advice(previous);
obj[prop] = advised;
return {
remove: function(){
obj[prop] = exist;
advice = null;
previous = null;
exist = null;
obj = null;
}
}
}
var count = 1;
advice = function(originalFunc){
var current = count++;
return function() {
console.log("before function " + current);
originalFunc(arguments);
console.log("after function " + current);
}
}
var obj = {
foo: function(arg){
console.log(this.name + " and " + arg);
},
name: "obj"
}
h1 = around(obj, 'foo', advice);
h2 = around(obj, 'foo', advice);
obj.foo();
h1.remove();
obj.foo();
h2.remove();
obj.foo();Output:
before function 2 before function 1 obj and [object Arguments] after function 1 after function 2 obj and undefined before function 1
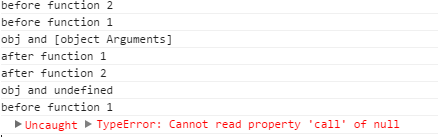
This. . Not only does it turn out to be a bit messy. . . Also reported an error. . . . Yes, it's bearable, but my uncle can't bear it. My uncle can't bear it, but my sister-in-law can't bear it!
Ah, closure. . . Please give me strength!
function around(obj, prop, advice){
var exist = obj[prop];
var previous = function(){
return exist.apply(obj, arguments);
};
var advised = advice(previous);
obj[prop] = function(){
//当调用remove后,advised为空
//利用闭包的作用域链中可以访问到advised跟previous变量,根据advised是否为空可以来决定调用谁
return advised ? advised.apply(obj, arguments) : previous.apply(obj, arguments);
};
return {
remove: function(){
//利用闭包的作用域链,在remove时将advised置空,这样执行过程中不会进入本次around
//这几个不能删
//obj[prop] = exist;
advised = null;
advice = null;
//previous = null;
//exist = null;
//obj = null;
}
}
}
var count = 1;
advice = function(originalFunc){
var current = count++;
return function() {
console.log("before function " + current);
originalFunc.apply(this, arguments);
console.log("after function " + current);
}
}
var obj = {
foo: function(arg){
console.log(this.name + " and " + arg);
},
name: "obj"
}
h1 = around(obj, 'foo', advice);
h2 = around(obj, 'foo', advice);
obj.foo('hello world');
h1.remove();
obj.foo('hello world');
h2.remove();
obj.foo('hello world');Output:
before function 2 before function 1 obj and hello world after function 1 after function 2 before function 2 obj and hello world after function 2 obj and hello world
After the fight, call it a day!
The first time I stayed up all night to blog, I was also drunk. At two o'clock, I heard the fuck me next door. At four o'clock, I heard the crow of crows. There was also an unknown bird chirping. At five o'clock, there were a lot of people. Birds chirp. . . .
Reference article:
Use AOP to improve javascript code
AOP (aspect-oriented programming) and OOP (object-oriented programming) of yui3

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1391
1391
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data



