The role of order by in sql
The ORDER BY clause in SQL sorts the rows in the result set to display the data in a specific order. It sorts one or more columns in ascending or descending order, and supports advanced usage such as multi-column sorting, null value handling, and more.

The role of ORDER BY in SQL
In SQL, the ORDER BY clause is used to compare the results in the result set. Rows are sorted. It allows you to sort your data in ascending or descending order based on one or more columns.
Main functions:
- #Organize the result set:Sort the rows returned from the query to display the data in a specific order .
- Group by specific columns: Group rows into a set of columns with the same value before sorting each group.
Syntax:
<code>SELECT ... FROM ... WHERE ... ORDER BY column_name1 [ASC | DESC], column_name2 [ASC | DESC], ...;</code>
- column_name: The name of the column to be sorted.
- ASC: Sort in ascending order (smallest to largest).
- DESC: Sort in descending order (largest to smallest).
Example:
Let us consider a table containing people information:
<code>CREATE TABLE persons ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255), age INT );</code>
To sort the people in the table in ascending order by name, We can use the following query:
<code>SELECT * FROM persons ORDER BY name ASC;</code>
This will return rows sorted by name from A to Z.
Advanced usage:
The ORDER BY clause also supports some advanced usage:
- Multiple column sorting: Sort multiple columns at once, such as ascending name and descending age.
- Null value processing: Specify whether the null value is ranked first or last.
- NULLS FIRST/LAST: Sort NULL values to the front or last of the result set.
By using the ORDER BY clause, you can organize and arrange your data efficiently, simplifying query and report generation.
The above is the detailed content of The role of order by in sql. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to check traffic on Apple mobile phone
May 09, 2024 pm 06:00 PM
How to check traffic on Apple mobile phone
May 09, 2024 pm 06:00 PM
How to check data usage on Apple 1. The specific steps to check data usage on Apple mobile phone are as follows: Open the settings of the phone. Click the Cellular button. Scroll down on the cellular network page to see the specific data usage of each application. Click Apply to also set allowed networks. 2. Turn on the phone, find the settings option on the phone desktop, and click to enter. In the settings interface, find "Cellular Network" in the taskbar below and click to enter. In the cellular network interface, find the "Usage" option on the page and click to enter. 3. Another way is to check the traffic by yourself through the mobile phone, but the mobile phone can only see the total usage and will not display the remaining traffic: turn on the iPhone, find the "Settings" option and open it. Select "Bee"
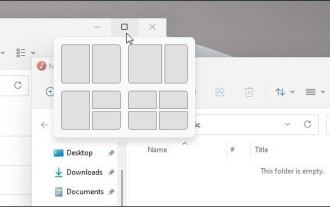 How to disable snapshot layout in Windows 11_ Tips for not using snapshot layout in win11
May 08, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
How to disable snapshot layout in Windows 11_ Tips for not using snapshot layout in win11
May 08, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Win11 system announced the new [Snapshot Layout], which provides users with various window layout options through the [Maximize] button, so that users can choose from multiple layout templates to display two, three or four on the screen. open applications. This is an improvement over dragging multiple windows to the sides of the screen and then adjusting everything manually. [SnapGroups] will save the collection of apps the user is using and their layout, allowing the user to easily return to that setting when they have to stop and deal with other things. If someone is using a monitor that the user must unplug, when re-docking, the previously used snapshot layout will also be restored. To use snapshot layout, we can use the keyboard shortcut WindowsKey+Z to start
 How to sort the list page alphabetically in vscode How to sort the list page alphabetically in vscode
May 09, 2024 am 09:40 AM
How to sort the list page alphabetically in vscode How to sort the list page alphabetically in vscode
May 09, 2024 am 09:40 AM
1. First, after opening the vscode interface, click the settings icon button in the lower left corner of the page 2. Then, click the Settings option in the drop-down page column 3. Then, find the Explorer option in the jumped window 4. Finally, on the right side of the page Click the OpenEditorsnaming option, select the alphabetical button from the drop-down page and save the settings to complete the alphabetical sorting
 How to use merge in java
May 09, 2024 am 06:03 AM
How to use merge in java
May 09, 2024 am 06:03 AM
The merge() method in Java Collections merges two sorted ordered collections to generate a new sorted collection, maintaining the original order. Syntax: public static <T> List<T> merge(SortedMap<T, Double> a, SortedMap<T, Double> b). It accepts two sorted collections and returns a new collection containing all elements in sorted order. Note: The values of duplicate keys will be merged according to the merge function, and the original collection will not be modified.
 What are the advanced C++ performance optimization techniques?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
What are the advanced C++ performance optimization techniques?
May 08, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
Performance optimization techniques in C++ include: Profiling to identify bottlenecks and improve array layout performance. Memory management uses smart pointers and memory pools to improve allocation and release efficiency. Concurrency leverages multi-threading and atomic operations to increase throughput of large applications. Data locality optimizes storage layout and access patterns and enhances data cache access speed. Code generation and compiler optimization applies compiler optimization techniques, such as inlining and loop unrolling, to generate optimized code for specific platforms and algorithms.
 What are the top ten virtual currency trading platforms? Ranking of the top ten virtual currency trading platforms in the world
Feb 20, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
What are the top ten virtual currency trading platforms? Ranking of the top ten virtual currency trading platforms in the world
Feb 20, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
With the popularity of cryptocurrencies, virtual currency trading platforms have emerged. The top ten virtual currency trading platforms in the world are ranked as follows according to transaction volume and market share: Binance, Coinbase, FTX, KuCoin, Crypto.com, Kraken, Huobi, Gate.io, Bitfinex, Gemini. These platforms offer a wide range of services, ranging from a wide range of cryptocurrency choices to derivatives trading, suitable for traders of varying levels.
 How to modify the desktop icon layout in win11? Introduction to modification methods
May 09, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
How to modify the desktop icon layout in win11? Introduction to modification methods
May 09, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
Windows 11 system can modify the desktop layout, so how to do it specifically? Let’s take a look below! To modify the desktop icon layout in Windows 11, you can follow the following steps: 1. Right-click a blank space on the desktop and select "Icon Layout". 2. In the icon layout menu, you can choose different layout options, including automatic arrangement of icons, grid layout, free arrangement of icons and hidden icons. 3. After selecting the appropriate layout option, your desktop icons will automatically be arranged according to the selected layout. Note: In Windows 11, desktop icons have relatively few setting options and are less customizable than previous Windows versions. If you need more advanced desktop customization settings, consider using
 How to adjust Sesame Open Exchange into Chinese
Mar 04, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
How to adjust Sesame Open Exchange into Chinese
Mar 04, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
How to adjust Sesame Open Exchange to Chinese? This tutorial covers detailed steps on computers and Android mobile phones, from preliminary preparation to operational processes, and then to solving common problems, helping you easily switch the Sesame Open Exchange interface to Chinese and quickly get started with the trading platform.






