One article to clarify what is the Impossible Triangle of Blockchain?
Currently, sharding, Layer 2 and cross-chain bridges are being used as breakthroughs to try to solve the dilemma caused by the impossible triangle of blockchain.
What is the Impossible Triangle of Blockchain?
The Blockchain Impossible Triangle, also known as the Blockchain Trilemma and Blockchain Trilemma, refers to the design and implementation of the Blockchain. The dilemma faced by the three key elements - decentralization, security and scalability.
These three elements are in conflict with each other. According to current technology, it is difficult for us to implement all three elements simultaneously in one system.
Simply put, with the current technical status, no blockchain can be decentralized, secure and fast at the same time. Achieve at most one or two of these.
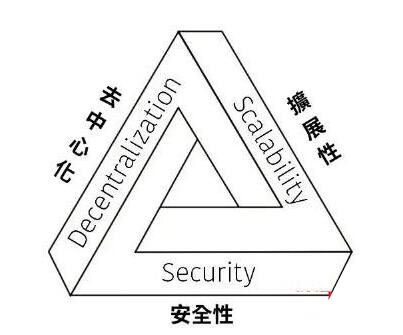
Blockchain Impossible Triangle
Element 1: Decentralization Decentralization
means that the nodes that maintain the network are scattered everywhere , and no node can individually control or manipulate the entire network. Decentralization is to prevent single points of failure and avoid monopoly control by central institutions.
Element 2: SecuritySecurity
Security means that the data in the blockchain cannot be changed once it is written, and the encryption algorithm is used to protect the information from unauthorized persons. Tampering or reading.
means that the blockchain system needs to have sufficient defense capabilities against various attacks, including preventing double-spending attacks and ensuring the irreversibility of transactions.
Element Three: Scalability Scalability
Scalability refers to the ability of the blockchain network to effectively handle a large number of transactions and users. However, in reality, when many existing blockchains develop to a certain scale, since each node needs to process all transactions, the transaction speed will decrease and cannot achieve efficient scalability.
So in the blockchain impossible triangle, some people call the scalability part "fast" or "speed".
Blockchain Impossible Triangle in Practical Application
Bitcoin
Bitcoin places its focus on security and decentralization, thus leading to Bitcoin The scalability of the coin is limited. Because Bitcoin’s block size and block time settings limit its transaction processing capabilities. When demand is high, this can lead to transaction delays and rising fees.
Ethereum
Ethereum also focuses on security and decentralization, and as a smart contract platform, it needs to ensure that user assets and protocols are safe. Therefore, the scalability of Ethereum is poor, especially when the application volume of DeFi and NFT increases significantly, the problems of transaction delays and rising fees are particularly prominent.
EOS and Solana
These two blockchain projects mainly focus on scalability and are therefore very efficient in terms of processing speed and throughput. In order to achieve such performance, they made some compromises in the degree of centralization of the network, such as limiting the number of validators.
Polygon
Polygon is a Layer 2 solution that improves scalability by providing an Ethereum-compatible chain. But this solution also requires sacrificing decentralization to a certain extent, such as shifting part of the transaction verification work to a few nodes.
The impact of the impossible triangle of blockchain
- Limitations of blockchain applications: Many blockchain applications (such as DeFi, DApp, etc.) require a certain degree of decentralization and security to ensure its operation. In order to achieve these goals, it is usually necessary to sacrifice some scalability, which makes these applications likely to encounter performance bottlenecks when facing large-scale users.
- Blockchain choices and trade-offs: Different blockchains will make different choices based on their goals and usage. For example, Bitcoin and Ethereum chose decentralization and security at the expense of certain scalability. On the other hand, some new blockchain platforms (such as EOS, Solana, etc.) choose to sacrifice a certain degree of decentralization to achieve higher scalability.
- The driving force of blockchain innovation: The Impossible Triangle of blockchain is also an important factor driving technological innovation. To solve this dilemma, many projects are working on new consensus algorithms, sharding technology, Layer 2 solutions, etc. to improve the performance of the blockchain. This effort promotes the continued development and progress of blockchain technology.
- Long-term development and trust of blockchain: The blockchain impossible triangle reminds us that the balance between blockchain’s scalability, security and decentralization not only affects its performance in the short term , and also affects its ability to build trust and achieve sustainable development in the long term. This has important implications for our understanding and assessment of the potential and limitations of blockchain technology.
A breakthrough to solve the impossible triangle of blockchain?
Solving the challenges of the impossible triangle of blockchain requires innovative technical solutions. The following are some possible solutions currently being explored:
Sharding
Sharding is a technology that can divide the network into multiple parts. Each shard can independently process transactions and smart contracts. This approach can greatly increase the scalability of the blockchain while maintaining a certain degree of decentralization and security. Ethereum 2.0 is an example of trying to use sharding to solve the impossible triangle problem.
Ethereum is the most well-known blockchain platform that uses sharding technology. Ethereum 2.0 plans to increase its processing power by introducing sharding technology. When sharding is completed, each shard will be able to process transactions independently, thereby greatly increasing the transaction speed of Ethereum.
Layer 2 solutions
These solutions build a secondary blockchain on top of the existing blockchain (also known as "Layer1") , to improve scalability. These Layer 2 solutions can speed up transaction processing and reduce transaction fees without compromising the security or decentralized nature of the underlying blockchain.
Lightning Network is an example of a major Layer 2 solution. The Lightning Network is a Layer 2 solution built on the Bitcoin blockchain that allows users to conduct instant, large-scale and small-amount transactions without recording every transaction on the main blockchain.
Cross-chain interoperability
This method refers to allowing different blockchains to communicate and operate with each other. In this way, the resources and advantages of different blockchains can be combined to solve the impossible triangle problem.
Some cross-chain bridge protocols, such as Stargate, Cosmos and Polkadot, are exploring this approach.
Summary
No matter how much we appreciate the revolutionary potential of blockchain, we must recognize that this technology also faces some important challenges. The Impossible Triangle does not mean that the development path of blockchain technology has been completely closed. On the contrary, it provides a thinking framework that allows us to understand the limitations of blockchain more clearly and inspires us to find new ways to overcome these limitations. methods to promote the development of technology.
Whether we are observers, developers or users, we all look forward to witnessing how blockchain technology unlocks new possibilities and realizes its true potential. I believe that in the near future, we will be able to use blockchain technology that is decentralized, secure, and fast.
The above is the detailed content of One article to clarify what is the Impossible Triangle of Blockchain?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What is Ouyi for? What is Ouyi
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
What is Ouyi for? What is Ouyi
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
OKX is a global digital asset trading platform. Its main functions include: 1. Buying and selling digital assets (spot trading), 2. Trading between digital assets, 3. Providing market conditions and data, 4. Providing diversified trading products (such as derivatives), 5. Providing asset value-added services, 6. Convenient asset management.
 How to roll positions in digital currency? What are the digital currency rolling platforms?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
How to roll positions in digital currency? What are the digital currency rolling platforms?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Digital currency rolling positions is an investment strategy that uses lending to amplify trading leverage to increase returns. This article explains the digital currency rolling process in detail, including key steps such as selecting trading platforms that support rolling (such as Binance, OKEx, gate.io, Huobi, Bybit, etc.), opening a leverage account, setting a leverage multiple, borrowing funds for trading, and real-time monitoring of the market and adjusting positions or adding margin to avoid liquidation. However, rolling position trading is extremely risky, and investors need to operate with caution and formulate complete risk management strategies. To learn more about digital currency rolling tips, please continue reading.
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 Binance binance computer version entrance Binance binance computer version PC official website login entrance
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
Binance binance computer version entrance Binance binance computer version PC official website login entrance
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
This article provides a complete guide to login and registration on Binance PC version. First, we explained in detail the steps for logging in Binance PC version: search for "Binance Official Website" in the browser, click the login button, enter the email and password (enable 2FA to enter the verification code) to log in. Secondly, the article explains the registration process: click the "Register" button, fill in the email address, set a strong password, and verify the email address to complete the registration. Finally, the article also emphasizes account security, reminding users to pay attention to the official domain name, network environment, and regularly updating passwords to ensure account security and better use of various functions provided by Binance PC version, such as viewing market conditions, conducting transactions and managing assets.
 How to calculate the transaction fee of gate.io trading platform?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
How to calculate the transaction fee of gate.io trading platform?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
The handling fees of the Gate.io trading platform vary according to factors such as transaction type, transaction pair, and user VIP level. The default fee rate for spot trading is 0.15% (VIP0 level, Maker and Taker), but the VIP level will be adjusted based on the user's 30-day trading volume and GT position. The higher the level, the lower the fee rate will be. It supports GT platform coin deduction, and you can enjoy a minimum discount of 55% off. The default rate for contract transactions is Maker 0.02%, Taker 0.05% (VIP0 level), which is also affected by VIP level, and different contract types and leverages
 Tutorial on how to register, use and cancel Ouyi okex account
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
Tutorial on how to register, use and cancel Ouyi okex account
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
This article introduces in detail the registration, use and cancellation procedures of Ouyi OKEx account. To register, you need to download the APP, enter your mobile phone number or email address to register, and complete real-name authentication. The usage covers the operation steps such as login, recharge and withdrawal, transaction and security settings. To cancel an account, you need to contact Ouyi OKEx customer service, provide necessary information and wait for processing, and finally obtain the account cancellation confirmation. Through this article, users can easily master the complete life cycle management of Ouyi OKEx account and conduct digital asset transactions safely and conveniently.
 What are the recommended websites for virtual currency app software?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
What are the recommended websites for virtual currency app software?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
This article recommends ten well-known virtual currency-related APP recommendation websites, including Binance Academy, OKX Learn, CoinGecko, CryptoSlate, CoinDesk, Investopedia, CoinMarketCap, Huobi University, Coinbase Learn and CryptoCompare. These websites not only provide information such as virtual currency market data, price trend analysis, etc., but also provide rich learning resources, including basic blockchain knowledge, trading strategies, and tutorials and reviews of various trading platform APPs, helping users better understand and make use of them
 On which platform is web3 transaction?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
On which platform is web3 transaction?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
This article lists the top ten well-known Web3 trading platforms, including Binance, OKX, Gate.io, Kraken, Bybit, Coinbase, KuCoin, Bitget, Gemini and Bitstamp. The article compares the characteristics of each platform in detail, such as the number of currencies, trading types (spot, futures, options, NFT, etc.), handling fees, security, compliance, user groups, etc., aiming to help investors choose the most suitable trading platform. Whether it is high-frequency traders, contract trading enthusiasts, or investors who focus on compliance and security, they can find reference information from it.



