 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Stanford's 2 billion parameter end-test multi-modal AI Agent model has been greatly upgraded, and can be used by mobile phones, cars and robots
Stanford's 2 billion parameter end-test multi-modal AI Agent model has been greatly upgraded, and can be used by mobile phones, cars and robots
Stanford's 2 billion parameter end-test multi-modal AI Agent model has been greatly upgraded, and can be used by mobile phones, cars and robots
The world’s first ultra-small multi-modal AI Agent modelOctopus V3, from the NEXA AI team of Stanford University, making Agent smarter, faster, and reducing energy consumption and costs.

In early April this year, NEXA AI launched the much-anticipated Octopus V2, which surpassed GPT in function call performance -4, reduces the amount of text required for inference by 95%, bringing new possibilities to end-side AI applications. Its patented core technology "functional token" significantly reduces the length of text required for reasoning through innovative function calling methods.
This approach enables efficient training of models with only 2 billion parameters and surpasses in accuracy and latency GPT-4 adapts to the deployment needs of various end devices.
Since Octopus V2 was released in the LLM community, it has received widespread attention and attracted praise from a large number of experts and researchers in the field of artificial intelligence, such as Julien Chaumond, CTO of Hugging Face, and Rowan, founder of the well-known AI newsletter AI Cheung, as well as Figure AI founder Brett Adcock, OPPO edge artificial intelligence team leader Manoj Kumar, etc. They are hailed as "creating a new era of device-side AI technology."
On the well-known open source AI platform Hugging Face, Octopus V2 has been downloaded more than 12,000 times.
In less than a month, the NEXA AI team released the next-generation multi-modal AI Agent model Octopus V3, demonstrating further breakthroughs: with Image processing and multi-language text processing capabilities pave the way for end-side devices such as smartphones to truly enter the AI era.
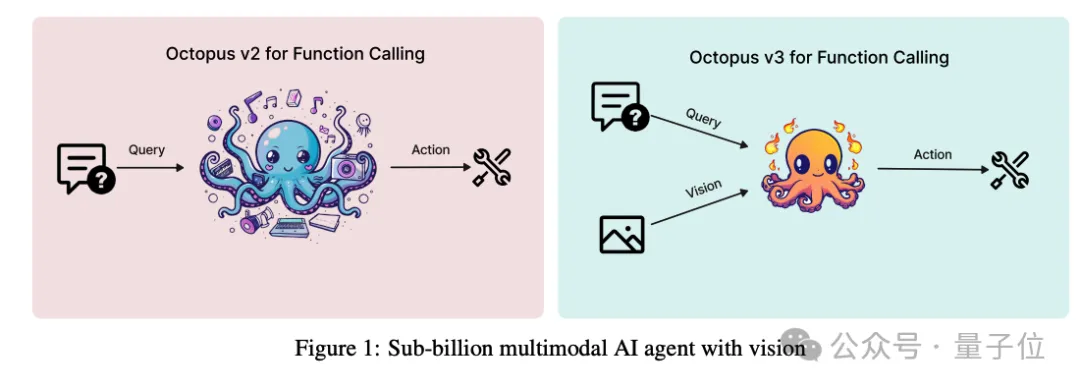
The first multi-modal AI Agent model with less than 1 billion parameters
Octopus V3 not only has multi-modal capabilities, The function calling performance far exceeds similar models and is comparable to GPT-4V GPT4; while the number of model parameters does not reach 1 billion, and it has multi-language capabilities.
In other words, compared with traditional large-scale language models, it is smaller in size and consumes less energy. It can more easily run on various small-end devices, such as Raspberry Pi, and achieve high speed. and accurate function calls.
This means that in the future, AI Agent can be widely used in smartphones, AR/VR, robots, smart cars and other end-side devices to provide users with a more interactive experience. Smooth and smart.
On the other hand, because V3 has multi-modal processing capabilities, it can handle text and image input at the same time, coupled with multi-language capabilities, it will also make the user experience richer.
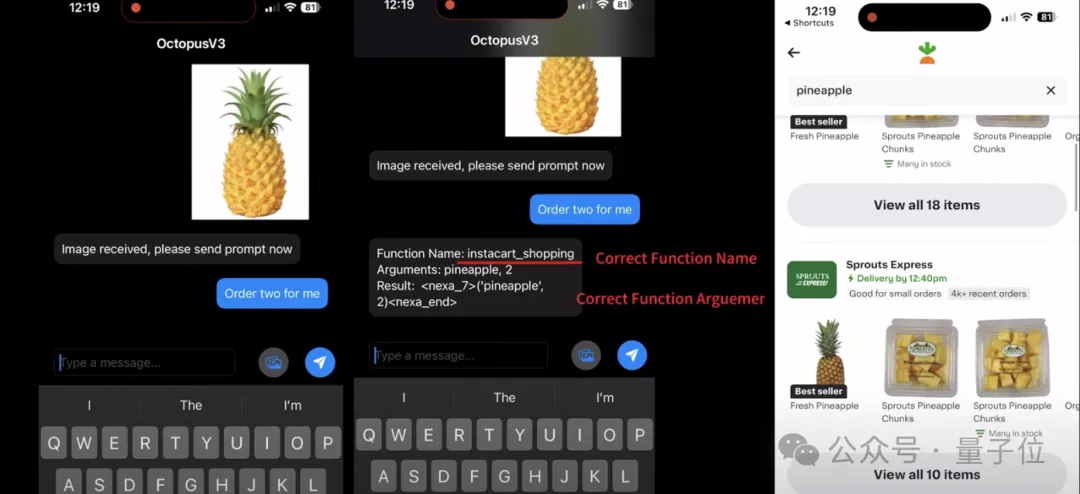
For example, in the Instacart shopping application, users can let the AI Agent automatically search for products for them through a picture of a pineapple and simple conversation instructions, improving efficiency and user experience.
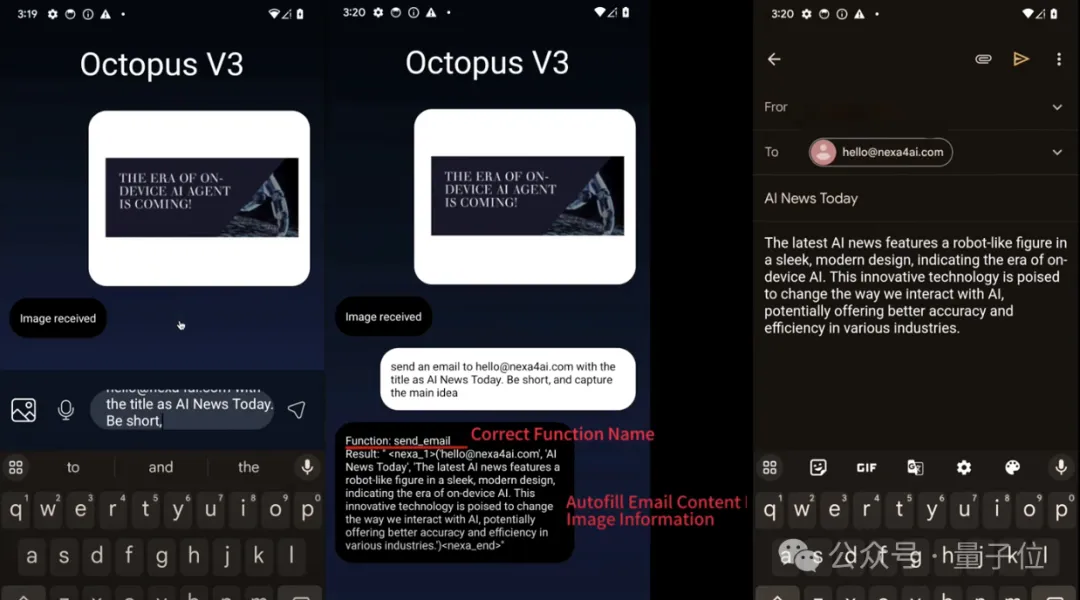
For another example, in scenarios such as sending emails, Octopus V3 can automatically extract information and fill in the email content based on an image with text, providing users with more intelligent, Convenient service.
From software interaction to smart cars, device-side AI has huge potential
Based on these characteristics, Octopus V2 and V3 have rich and diverse application scenarios and a wide range of applications. Application prospects.
In addition to the mobile phone scenarios mentioned above, when Octopus V2 is applied to smart cars, it can also bring new interactive experiences. Current voice assistants are often difficult to help car owners complete more complex tasks, such as temporarily changing destinations during driving, adding additional stops, etc. After applying Octopus V3, the AI assistant can quickly and accurately complete corresponding tasks based on relatively vague and simple instructions.
Combined with the capabilities of V2 and V3, from information retrieval to completion of design based on instructions, users can obtain a smooth AI experience in virtual scenes: In a community user’s VR scene demo, input simple voice commands Finally, AI Agent can help users quickly complete a living room design, replace sofas, change the color of lights, etc. with just a few clicks. After the user enters the travel instructions, the user quickly arrives in Japan, and the AI Agent can also help the user search for corresponding attractions and provide rich information in simple conversational communication.
Data shows that the global large-scale language model market is growing rapidly. Granview Research reports that the global large language model market size is estimated at US$4.35 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 35.9% from 2024 to 2030. Similarly, the edge artificial intelligence market is also showing a booming momentum - it is expected that the global edge artificial intelligence market will grow at a compound annual growth rate of 21.0% from 2023 to 2030, and will reach US$66.478 billion by 2030.
The NEXA AI team was founded by outstanding researchers at Stanford University.
Founder and Chief Scientist Alex Chen (Chen Wei) is studying for a PhD at Stanford University. He has extensive experience in artificial intelligence research and has served as a Chinese researcher at Stanford University. Chairman of the Stanford Chinese Entrepreneurs Organization.
Co-founder and Chief Technology Officer Zack Li (Li Zhiyuan) is also a graduate of Stanford University and has 4 years of end-side experience in Google and Amazon Lab126 laboratories With front-line research and development experience in AI, he also served as the chairman of the Stanford Chinese Entrepreneurship Association.
Associate Professor at Stanford University and Deputy Director of the Stanford Technology Entrepreneurship ProgramCharles (Chuck) Eesley serves as an advisor, providing guidance and support to the team.
 △Left: Li Zhiyuan; Right: Chen Wei
△Left: Li Zhiyuan; Right: Chen Wei
Currently, NEXA AI’s original technology has applied for patent protection.
The founding team of NEXA AI stated that they will continue to be committed to promoting the development of end-side AI technology, increasing the influence of its innovative technologies through open source models, and creating a smarter and more efficient future life for users.
Paper address: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.11459
The above is the detailed content of Stanford's 2 billion parameter end-test multi-modal AI Agent model has been greatly upgraded, and can be used by mobile phones, cars and robots. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Top 10 latest releases of virtual currency trading platforms for bulk transactions
Apr 22, 2025 am 08:18 AM
Top 10 latest releases of virtual currency trading platforms for bulk transactions
Apr 22, 2025 am 08:18 AM
The following factors should be considered when choosing a bulk trading platform: 1. Liquidity: Priority is given to platforms with an average daily trading volume of more than US$5 billion. 2. Compliance: Check whether the platform holds licenses such as FinCEN in the United States, MiCA in the European Union. 3. Security: Cold wallet storage ratio and insurance mechanism are key indicators. 4. Service capability: Whether to provide exclusive account managers and customized transaction tools.
 Summary of the top ten Apple version download portals for digital currency exchange apps
Apr 22, 2025 am 09:27 AM
Summary of the top ten Apple version download portals for digital currency exchange apps
Apr 22, 2025 am 09:27 AM
Provides a variety of complex trading tools and market analysis. It covers more than 100 countries, has an average daily derivative trading volume of over US$30 billion, supports more than 300 trading pairs and 200 times leverage, has strong technical strength, a huge global user base, provides professional trading platforms, secure storage solutions and rich trading pairs.
 What are the top ten virtual currency trading apps? Recommended on the top ten digital currency exchange platforms
Apr 22, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
What are the top ten virtual currency trading apps? Recommended on the top ten digital currency exchange platforms
Apr 22, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
The top ten secure digital currency exchanges in 2025 are: 1. Binance, 2. OKX, 3. gate.io, 4. Coinbase, 5. Kraken, 6. Huobi, 7. Bitfinex, 8. KuCoin, 9. Bybit, 10. Bitstamp. These platforms adopt multi-level security measures, including separation of hot and cold wallets, multi-signature technology, and a 24/7 monitoring system to ensure the safety of user funds.
 What are the stablecoins? How to trade stablecoins?
Apr 22, 2025 am 10:12 AM
What are the stablecoins? How to trade stablecoins?
Apr 22, 2025 am 10:12 AM
Common stablecoins are: 1. Tether, issued by Tether, pegged to the US dollar, widely used but transparency has been questioned; 2. US dollar, issued by Circle and Coinbase, with high transparency and favored by institutions; 3. DAI, issued by MakerDAO, decentralized, and popular in the DeFi field; 4. Binance Dollar (BUSD), cooperated by Binance and Paxos, and performed excellent in transactions and payments; 5. TrustTo
 How many stablecoin exchanges are there now? How many types of stablecoins are there?
Apr 22, 2025 am 10:09 AM
How many stablecoin exchanges are there now? How many types of stablecoins are there?
Apr 22, 2025 am 10:09 AM
As of 2025, the number of stablecoin exchanges is about 1,000. 1. Stable coins supported by fiat currencies include USDT, USDC, etc. 2. Cryptocurrency-backed stablecoins such as DAI and sUSD. 3. Algorithm stablecoins such as TerraUSD. 4. There are also hybrid stablecoins.
 Which of the top ten transactions in the currency circle? The latest currency circle app recommendations
Apr 24, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Which of the top ten transactions in the currency circle? The latest currency circle app recommendations
Apr 24, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Choosing a reliable exchange is crucial. The top ten exchanges such as Binance, OKX, and Gate.io have their own characteristics. New apps such as CoinGecko and Crypto.com are also worth paying attention to.
 What are the next thousand-fold coins in 2025?
Apr 24, 2025 pm 01:45 PM
What are the next thousand-fold coins in 2025?
Apr 24, 2025 pm 01:45 PM
As of April 2025, seven cryptocurrency projects are considered to have significant growth potential: 1. Filecoin (FIL) achieves rapid development through distributed storage networks; 2. Aptos (APT) attracts DApp developers with high-performance Layer 1 public chains; 3. Polygon (MATIC) improves Ethereum network performance; 4. Chainlink (LINK) serves as a decentralized oracle network to meet smart contract needs; 5. Avalanche (AVAX) trades quickly and
 What is DLC currency? What is the prospect of DLC currency
Apr 24, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
What is DLC currency? What is the prospect of DLC currency
Apr 24, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
DLC coins are blockchain-based cryptocurrencies that aim to provide an efficient and secure trading platform, support smart contracts and cross-chain technologies, and are suitable for the financial and payment fields.





