
A shell built-in command is a command or a function that is called from the shell and is executed directly in the shell. The bash shell executes the command directly without calling other programs. You can use the help command to view information about Bash built-in commands. Below are several different types of built-in commands.
The types are as follows:
Bourne Shell built-in commands: Built-in commands are inherited from Bourne Shell.
Bash built-in commands: A list of Bash-specific built-in commands.
Modify Shell Behavior: Built-in commands that modify shell properties and optional behavior.
Special built-in commands: Built-in commands that are specially classified by POSIX.
There are the following commands:
$ help $ help | less $ help | grep read
Sample output:
GNU bash, version 4.1.5(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
These shell commands are defined internally. Type `help' to see this list.
Type `help name' to find out more about the function `name'.
Use `info bash' to find out more about the shell in general.
Use `man -k' or `info' to find out more about commands not in this list.
A star (*) next to a name means that the command is disabled.
job_spec [&] history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or hist>
(( expression )) if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif C>
. filename [arguments] jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] or jobs >
: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigs>
[ arg... ] let arg [arg ...]
[[ expression ]] local [option] name[=value] ...
alias [-p] [name[=value] ... ] logout [n]
bg [job_spec ...] mapfile [-n count] [-O origin] [-s c>
bind [-lpvsPVS] [-m keymap] [-f filen> popd [-n] [+N | -N]
break [n] printf [-v var] format [arguments]
builtin [shell-builtin [arg ...]] pushd [-n] [+N | -N | dir]
caller [expr] pwd [-LP]
case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]...)> read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [->
cd [-L|-P] [dir] readarray [-n count] [-O origin] [-s>
command [-pVv] command [arg ...] readonly [-af] [name[=value] ...] or>
compgen [-abcdefgjksuv] [-o option] > return [n]
complete [-abcdefgjksuv] [-pr] [-DE] > select NAME [in WORDS ... ;] do COMM>
compopt [-o|+o option] [-DE] [name ..> set [--abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option>
continue [n] shift [n]
coproc [NAME] command [redirections] shopt [-pqsu] [-o] [optname ...]
declare [-aAfFilrtux] [-p] [name[=val> source filename [arguments]
dirs [-clpv] [+N] [-N] suspend [-f]
disown [-h] [-ar] [jobspec ...] test [expr]
echo [-neE] [arg ...] time [-p] pipeline
enable [-a] [-dnps] [-f filename] [na> times
eval [arg ...] trap [-lp] [[arg] signal_spec ...]
exec [-cl] [-a name] [command [argume> true
exit [n] type [-afptP] name [name ...]
export [-fn] [name[=value] ...] or ex> typeset [-aAfFilrtux] [-p] name[=val>
false ulimit [-SHacdefilmnpqrstuvx] [limit>
fc [-e ename] [-lnr] [first] [last] o> umask [-p] [-S] [mode]
fg [job_spec] unalias [-a] name [name ...]
for NAME [in WORDS ... ] ; do COMMAND> unset [-f] [-v] [name ...]
for (( exp1; exp2; exp3 )); do COMMAN> until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
function name { COMMANDS ; } or name > variables - Names and meanings of so>
getopts optstring name [arg] wait [id]
hash [-lr] [-p pathname] [-dt] [name > while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
help [-dms] [pattern ...] { COMMANDS ; }
Another option is to use the following command:
compgen -b compgen -b | more
Run the following to get detailed information:
help command help read
To get only a list of all built-in commands with short descriptions, execute the following:
$ help -d
Use the following syntax to find out more related built-in commands:
help name help cd help fg help for help read help :
Sample output:
:: : Null command. No effect; the command does nothing. Exit Status: Always succeeds
Use type command or command command:
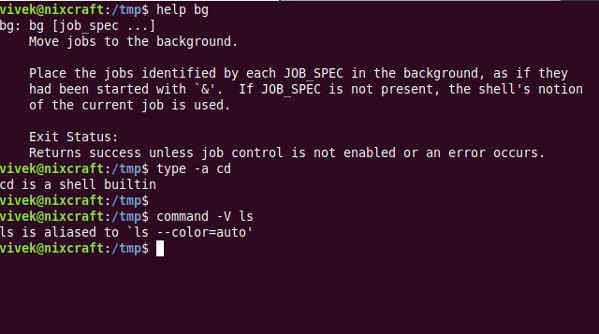
type -a command-name-here type -a cd type -a uname type -a : type -a ls
or:
type -a cd uname : ls uname
Sample output:
cd is a shell builtin
uname is /bin/uname
: is a shell builtin
ls is aliased to `ls --color=auto'
ls is /bin/ls
l is a function
l ()
{
ls --color=auto
}or:
command -V ls command -V cd command -V foo
Author: Vivek Gite
The above is the detailed content of List all Bash Shell built-in commands. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




