
DOM(Document Object Model)即文档对象模型,针对HTML和XML文档的API(应用程序接口);
DOM描绘了一个层次化的节点树,运行开发人员可以添加/移除和修改页面的某一部分;
一 DOM介绍
D(文档):可以理解为整个Web加载的网页文档;
O(对象):可以理解为类似window对象之类的东西,可以调用属性和方法,这里说的是document对象;
M(模型):可以理解为网页文档的树形结构;
1.节点
加载HTML页面时,Web浏览器生成一个树形结构,用来表示页面内部结构;
DOM将这种节点结构理解为由节点组成;
html元素为根节点;head元素是html的子节点;meta元素和title元素之间是兄弟关系;
2.节点种类:元素节点/文本节点/属性节点
DOM depicts a hierarchical node tree, and developers can add/remove and modify certain parts of the page;
Element node search method
Method
getElementById() Get the node of a specific ID element;
getElementsByTagName() Get the node list of the same element;
getElementsByName() Get a list of nodes with the same name;
getAttribute() Get the value of the node attribute of a specific element;
setAttribute() Set the value of the node attribute of a specific element;
removeAttribute() removes the node attribute of a specific element;
1.getElementById()
//The method receives a parameter: get the ID of the element;
// If the corresponding element is found, return the HTMLDivElement object of the element; if it does not exist, return null;
Document.getElementById('box'); // [object HTMLDivElement];
// When we obtain a specific element node through getElementById(), this node object is obtained by us;
// Through this node object, we can access a series of its properties;
(1). Access the attributes of element nodes
Attributes Description
tagName Get the tag name of the element node;
innerHTML Get the content in the element node, non-W3C DOM specification;
Document.getElementById('box').tagName; // =>DIV;
Document.getElementById('box').innerHTML; // =>Test Div;
Attributes Description
id name of the element node;
title The title attribute value of the element node;
style style CSS inline style attribute value;
className Class of CSS element;
Document.getElementById('box').title; // Get title;
Document.getElementById('box').style.color; // Get the color value in the style object; that is, the style value set within the element row;
Document.getElementById('box').style.color='red'; // Set the color value in the style object;
Document.getElementById('box').className='pox'; // Set class;
document.getElementById('box').bbb; // Get the value of a custom attribute, not supported by non-IE;
2.getElementsByTagName()
//The method returns an object array HTMLCollection (NodeList) array, which stores a list of nodes with the same element name;
Document.getElementsByTagName('*'); // Use wildcards to get all elements;
// PS: When IE uses wildcards, it will treat the specification statement of the HTML at the beginning of the document as the first element node;
document.getElementsByTagName('li'); // =>[object HTMLCollection];Get all li elements;
Document.getElementsByTagName('li').[0]; // Get the first li element;
3.getElementsByName()
Get elements with the same name (name) setting and return an object array HTMLCollection (NodeList);
Document.getElementsByName('add'); // Get the input element collection with name='add';
// PS: For attributes that are not legal in HTML, there will be differences in compatibility obtained by JS;
// IE supports legal name attributes, but there will be incompatibility issues with custom attributes;
4.getAttribute()
The method will get the value of an attribute in the element;
But it is somewhat different from the method of directly using ".attr" to obtain attribute values;
Document.getElementById('box').getAttribute('mydiv'); // Get custom attribute value;
Document.getElementById('box').mydiv; // Get custom attribute values, only supported by IE;
5.setAttribute()
The method will set an attribute and value in the element; it receives two parameters: attribute name and value;
If the attribute itself already exists, it will be overwritten;
Document.getElementById('box').setAttribute('align','center'); // Set attributes and values;
// PS: In IE7 and below, using the setAttribute() method to set class and style attributes has no effect;
6.removeAttribute()
method can remove HTML attributes;
Document.getElementById('box').removeAttribute('style'); // Remove style attribute;
Three DOM nodes
1.node node attributes
//Nodes can be divided into: element nodes/attribute nodes and text nodes;
// These nodes have three attributes: nodeName/nodeType and nodeValue;
Information node attributes
Node type nodeName nodeType nodeValue
Element Name of element 1 null
Attribute Attribute name Attribute value 2 Attribute value
Text Contents
Document.getElementById('box').nodeType; // =>1; Element node;
2. Hierarchical node attributes
// Hierarchical nodes can be divided into: parent nodes and child nodes/sibling nodes;
// When we get one of the element nodes, we can use the hierarchical node attribute to get its related level nodes;
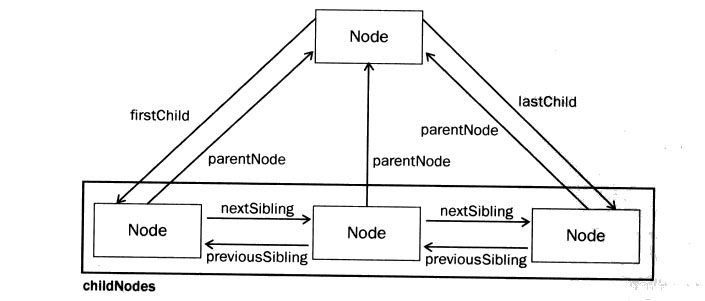
Node relationship diagram
Hierarchical node attributes
Attributes Description
childNodes Read all child nodes of the current element node;
firstChild Read the first child node of the current element node;
lastChild Get the last child node of the current element node;
ownerDocument Gets the document root node of the node, which is equivalent to document;
parentNode Get the parent node of the current node;
previousSibling Get the previous sibling node of the current node;
nextSibling Get the next sibling node of the current node;
attributes Get the set of all attribute nodes of the current element node;
(1).childNodes attribute
The attribute gets all the child nodes of a certain element node. These child nodes include element nodes and text nodes;
PS: When using childNodes[n] to return child node objects, it is possible to return element child nodes, such as: HTMLElement;
It may also return text sub-nodes, such as: Text;
Element sub-nodes can use nodeName or tagName to obtain the tag name; text sub-nodes can be obtained using nodeValue;
var box = document.getElementById('box');
for(var i=0; i
If(box.childNodes[i].nodeType === 1){
console.log('Element node:' box.childNodes[i].nodeName);
Determine it is a text node and output the text content;
}else if(box.childNodes[i].nodeType ===3){
console.log('Text node:' box.childNodes[i].nodeValue);
}
}
PS1: When obtaining a text node (the key point is that it is no longer an element node), you cannot use the innerHTML attribute to output text content;
This non-standard attribute must be used to obtain the element node before the text contained in it can be output;
alert(box.innerHTML); The first difference between innerHTML and nodeValue;
PS2: When innerHTML and nodeValue are assigned values, nodeValue will escape the HTML contained in the text into special characters, thereby achieving the effect of forming plain text;
And innerHTML will parse special characters in the text;
box.childNodes[0].nodeValue = 'abc'; =>abc;
box.innerHTML = 'abc';
firstChild = childNodes[0]; Get the first child node of the current element;
lastChild = childNodes[box.childNodes.length-1]; Get the last child node of the current element;
Returns the document object root node of the node. The returned object is equivalent to document;
alert(box.ownerDocument === document); // =>true;Root node;
parentNode: Returns the parent node of this node;
previousSibling: Returns the previous sibling node of this node;
nextSibling: Returns the next sibling node of this node;
alert(box.parentNode.nodeName); // Get the label name of the parent node;
alert(box.firstChild.nextSibling); // Get the second node;
alert(box.lastChild.previousSibling); // Get the penultimate node;
(5).attributes attribute
Attribute returns the attribute node collection of the node;
alert(document.getElementById('box').attributes); // =>NamedNodeMap;
(6). Ignore blank text nodes
var body = document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0];// 获取body元素节点;
alert(body.childNodes.length); // 非IE=7; IE=3;
// PS:在非IE中,标准的DOM具有识别空白文本节点的功能,而IE自动忽略了;
function filterSpaceNode1(nodes){
// 新数组;
var ret = [];
for(var i=0; i<nodes.length; i++){
// 如果识别到空白文本节点,就不添加到数组;
if(nodes[i].nodeType ===3 && /^\s+$/.test(nodes[i].nodeValue)) continue;
// 把每次的元素节点,添加到数组里;
ret.push(nodes[i]);
}
return ret;
}
// PS:上面的方法,采用忽略空白文件节点的方法,把得到的元素节点累加到数组里返回;
function filterSpaceNode2(nodes){
for(var i=0; i<nodes.length; i++){
if(nodes[i].nodeType ===3 && /^\s+$/.test(nodes[i].nodeValue)){
// 得到空白节点之后,一道父节点上,删除子节点;
nodes[i].parentNode.removeChild(nodes[i]);
}
}
return nodes;
}
// PS:firstChild等方法在获取节点时遇到空白节点,处理方法;
function removeWhileNode(nodes){
for(var i=0; i<nodes.childNodes.length; i++){
if(nodes.childNodes[i].nodeType ===3 && /^\s+$/.test(nodes.childNodes[i].nodeValue)){
nodes.childNodes[i].parentNode.removeChild(nodes.childNodes[i]);
}
}
return nodes;
}Four node operations
// DOM can not only search for nodes, but also create nodes/copy nodes/insert nodes/delete nodes and replace nodes
Node operation methods
Methods Explanation
write() This method can insert any string into the document;
createElement() Create an element node;
appendChild() Appends the new node to the end of the child node list;
createTextNode() Create a file node;
insertBefore() Insert the new node in front;
replaceChild() Replace the old node with the new node;
cloneNode() Copy node;
removeChild() Remove node;
(1).write() method
//The write() method can insert any string into the document;
document.write('
This is a paragraph!
'); // Parsed text;(3).appendChild() method
The appendChild() method adds a new node to the end of a node’s child node list;
var box = document.getElementById('box');
var p = document.createElement('p'); // Create a new element node
;
box.appendChild(p); //Add the new element node
to the end of the child node;
(4).createTextNode() method
This method creates a text node;
var text = document.createTextNode('paragraph');
p.appendChild(text); //Add the text node to the end of the child node;
(5).insertBefore() method
// 该方法可以把节点添加到指定节点的前面;
box.parentNode.insertBefore(p,box); // 在<div>之前添加一个<p>;
box.insertBefore(newNode,null); // 将newNode添加到box自列表的最后节点;
//PS:insertBefore()方法可以给当前元素的前面创建一个节点,但没有提供给当前元素的后面创建一个节点;
function insertAfter(newElement,targetElement){
// 得到父节点;
var parent = targetElement.parentNode;
// 如果最后一个子节点是当前元素,那么直接添加即可;
if(parent.lastChild === targetElement){
parent.appendChild(newElement);
}else{
// 否则,在当前节点的下一个节点之前添加;达成在当前节点后面添加节点的需求;
parentNode.insertBefore(newElement,targetElement.nextSibling);
}
} (6).replaceChild() method
This method can replace the node with the specified node;
box.parentNode.replaceChild(p,box); // Replace
;
(7).cloneNode() method
// This method can copy the child node; the node copy returned after copying belongs to the document, but no parent node is specified for it;
// The parameter is true: perform deep copy, which is to copy the node and its entire child node tree;
// The parameter is false: perform shallow copy, only copy the node itself;
var box = document.getElementById('box');
var clone = box.firstChild.cloneNode(true); // Get the first child node, true means copy the content;
box.appendChild(clone); // Add to the end of the child node list;
(8).removeChild() method
This method deletes the specified node;
box.parentNode.removeChild(box);
Summary: In the next chapter~




