 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Some problems in the prototype of Javascript drag and drop (analyzing the code line by line, allowing you to easily understand the principles of drag and drop)_javascript skills
Some problems in the prototype of Javascript drag and drop (analyzing the code line by line, allowing you to easily understand the principles of drag and drop)_javascript skills
Some problems in the prototype of Javascript drag and drop (analyzing the code line by line, allowing you to easily understand the principles of drag and drop)_javascript skills
Today we will solve some problems in the last drag prototype. What are the problems below?
Attached is the Javascript code from the previous issue for everyone to check the problem.
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function() {
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
var disX = 0;
var disY = 0;
oDiv.onmousedown = function(ev) {
var oEvent = ev || event;
disX = oEvent.clientX - oDiv.offsetLeft;
disY = oEvent.clientY - oDiv.offsetTop;
oDiv.onmousemove = function(ev) {
var oEvent = ev || event;
oDiv.style.left = oEvent.clientX - disX+'px';
oDiv.style.top = oEvent.clientY - disY+'px';
};
oDiv.onmouseup = function() {
oDiv.onmousemove = null;
oDiv.onmouseup = null;
};
};
};
</script>1. If I move the mouse faster during the current drag,  you will find that the mouse comes out of the div, and the div will not follow the mouse at this time.
you will find that the mouse comes out of the div, and the div will not follow the mouse at this time.
Then why does this problem occur?
The reason is actually very simple. We add the mousemove event to the div, so once the mouse leaves the div, the mousemove will no longer be triggered at this time.
Solution: The event is loaded on the document. Because your mouse is still in the page no matter what, mousemove will be triggered no matter what. This way, it can be moved quickly without any problem.
Then we modify the code accordingly.
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function() {
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
var disX = 0;
var disY = 0;
oDiv.onmousedown = function(ev) {
var oEvent = ev || event;
disX = oEvent.clientX - oDiv.offsetLeft;
disY = oEvent.clientY - oDiv.offsetTop;
// 事件加载document 上
document.onmousemove = function(ev) {
var oEvent = ev || event;
oDiv.style.left = oEvent.clientX - disX+'px';
oDiv.style.top = oEvent.clientY - disY+'px';
};
oDiv.onmouseup = function() {
document.onmousemove = null;
oDiv.onmouseup = null;
};
};
};
</script>Then this problem can be solved.
2. Let’s see if there are any problems now. Although the problem of dragging quickly is solved, when I move the mouse to this position
Now you can clearly see that the mouse is not on the div. If you lift the mouse at this time, you can see that it will still move after coming back.  This is another bug!
This is another bug!
Actually, this problem is the same as the one above. So the solution is very simple. Let’s add mouseup to the document. Let’s try it out
document.onmouseup = function() {
document.onmousemove = null;
document.onmouseup = null;
};In this way, if you move to the position just now, the previous bug will not appear, and there will be no problem if you move fast. Everything is normal.
3. Let’s look at browser compatibility issues
In fact, there is such a problem in lower versions of Firefox
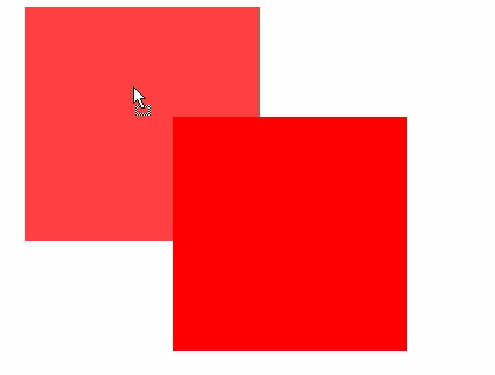 . How does it appear? When you drag it for the first time, it is correct. When you drag it once, hold down and move, and you will find that there will be this shadow behind it. What's going on?
. How does it appear? When you drag it for the first time, it is correct. When you drag it once, hold down and move, and you will find that there will be this shadow behind it. What's going on?
Actually, what we are dragging is an empty div. Firefox has a bug, so what if we add some content to the div

You will find that now there is no problem again.
So the Firefox bug only appears in empty divs.
Solution:
It’s actually very simple, we just need to prevent the browser default event return false; in onmousedown. Why add it to onmousedown?
You can think about which event dragging starts from, right? It starts from onmousedown. Dragging starts when the mouse is pressed. So it needs to be loaded in onmousedown.
In fact, I just added a return false; to block the Firefox bug.
No matter how much you drag it, there will be no problem.
Attached is the code:
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function() {
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
var disX = 0;
var disY = 0;
oDiv.onmousedown = function(ev) {
var oEvent = ev || event;
disX = oEvent.clientX - oDiv.offsetLeft;
disY = oEvent.clientY - oDiv.offsetTop;
// 事件加载document 上
document.onmousemove = function(ev) {
var oEvent = ev || event;
oDiv.style.left = oEvent.clientX - disX+'px';
oDiv.style.top = oEvent.clientY - disY+'px';
};
document.onmouseup = function() {
document.onmousemove = null;
document.onmouseup = null;
};
return false;
};
};
</script>Now the program is complete, but there are still some problems in user experience.
For example, the user may drag this div out of the browser, so how to solve it?
Then let’s add a judgment. This is very simple, if you go out from the left
, then it is directly equal to 0, and he will not be able to get out from the left. Then the same goes for the above.
So how to prevent being unable to exit from the right? ? Just draw a picture and it will become clear. In fact, we can calculate it by just subtracting the width of the div from the visible width of the page.
Then this is the so-called maximum value. Just judge if the moving distance exceeds this maximum value, it will be equal to this maximum value. Then it's the same below.
Attached is the complete code:
<script type="text/javascript">
// 拖拽空div 低版本的火狐有bug
window.onload = function() {
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");var disX = 0;
var disY = 0;
oDiv.onmousedown = function(ev) {
var oEvent = ev || event;
disX = oEvent.clientX - oDiv.offsetLeft;
disY = oEvent.clientY - oDiv.offsetTop;
document.onmousemove = function(ev) {
var oEvent = ev || event;
// 存储div当前的位置
var oDivLeft = oEvent.clientX - disX;
var oDivTop = oEvent.clientY - disY;
// 从左边拖出去了
if (oDivLeft < 0) {
oDivLeft = 0;
} else if (oDivLeft > document.documentElement.clientWidth - oDiv.offsetWidth) {
oDivLeft = document.documentElement.clientWidth - oDiv.offsetWidth;
}
if (oDivTop < 0) {
oDivTop = 0;
} else if (oDivTop > document.documentElement.clientHeight - oDiv.offsetHeight) {
oDivTop = document.documentElement.clientHeight - oDiv.offsetHeight;
}
oDiv.style.left = oDivLeft + 'px';
oDiv.style.top = oDivTop + 'px';
};
document.onmouseup = function() {
document.onmousemove = null;
document.onmouseup = null;
};
return false; // 阻止默认事件,解决火狐的bug
};
};
</script>Then the drag and drop is now relatively complete. O(∩_∩)O

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service





