Why Nodejs chooses JavaScript as the carrier language_node.js
Let’s first take a look at the introduction on the NodeJS official website:
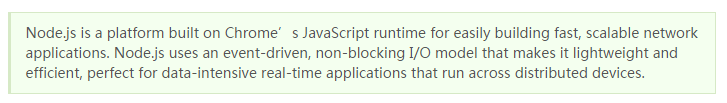
Its characteristics are:
1. It is a Javascript running environment
2. Rely on Chrome V8 engine for code interpretation
3. Event-driven
4. Non-blocking I/O
5. Lightweight, scalable, suitable for real-time data interaction applications
6. Single process, single thread
(1), why Nodejs chooses JavaScript as the carrier language
In fact, when implementing Node.js, the author Ryan Dahl did not choose JavaScript. He tried C and Lua, but they lacked the features of some high-level languages, such as closures and functional programming, making the program complicated. , difficult to maintain.
JavaScript is a language that supports the functional programming paradigm and fits well with the event-driven programming model of Node.js. Coupled with the V8 engine provided by Google, the execution speed of the JavaScript language is greatly improved.
What is finally presented to us is Node.js, not Node.c, Node.lua or other language implementations.
(2), Node.js is not a JS application, but a JS running platform
When seeing the name Node.js, beginners may mistakenly think that it is a Javascript application. In fact, Node.js is written in C language and is a Javascript running environment.
Node.js uses the V8 engine of the Google Chrome browser, which has very good performance and also provides many system-level APIs, such as file operations, network programming, etc.
The following are all modules involved in NodeJS:

The Javascript code on the browser side will be subject to various security restrictions when running, and has limited operations on the customer system.
In contrast, Node.js is a comprehensive background runtime that provides Javascript with many functions that other languages can achieve.
(3), Features of Node.js
Node.js is also relatively innovative in design. It runs in single-process, single-thread mode (this is consistent with the way Javascript runs),
The event-driven mechanism is implemented by Node.js through an internal single thread to efficiently maintain the event loop queue. There is no multi-threaded resource occupation and context switching. This means that in the face of large-scale http requests, Node.js relies on Event-driven takes care of everything,
Web service developers who are used to traditional languages may be very familiar with multi-threaded concurrency and collaboration, but when faced with Node.js, we need to accept and understand its characteristics.
2. Important concepts
1. What is Event Loop? (very important concept)
Event Loop is a very important concept, which refers to an operating mechanism of a computer system.
If you want to understand Event Loop, you must start with the running mode of the program. The program after running is called a process. Generally, a process can only perform one task at a time.
If there are many tasks to be performed, there are no more than three solutions.
(1), line up. Because a process can only execute one task at a time, it has to wait until the previous task is completed before executing the subsequent task.
(2), create a new process. Use the fork command to create a new process for each task.
(3), create a new thread. Because processes consume too many resources, today's programs often allow a process to contain multiple threads, and the threads complete tasks.
Take the JavaScript language as an example. It is a single-threaded language, and all tasks are completed on one thread, that is, the first method above is used. Once a large number of tasks are encountered or a time-consuming task is encountered, the web page will appear "suspended" because JavaScript cannot stop and cannot respond to the user's behavior.
You may ask, why is JavaScript single-threaded? Can’t it be implemented as multi-threaded?
This has something to do with history:
A major feature of the JavaScript language is that it is single-threaded, which means that it can only do one thing at a time. So why can't JavaScript have multiple threads? This can improve efficiency.
JavaScript’s single thread is related to its purpose. As a browser scripting language, JavaScript's main purpose is to interact with users and manipulate the DOM. This determines that it can only be single-threaded, otherwise it will cause very complex synchronization problems.
For example, suppose JavaScript has two threads at the same time. One thread adds content to a certain DOM node, and the other thread deletes the node. In this case, which thread should the browser use?
Therefore, in order to avoid complexity, JavaScript has been single-threaded since its birth. This has become the core feature of this language and will not change in the future.
In order to take advantage of the computing power of multi-core CPUs, HTML5 proposes the Web Worker standard, which allows JavaScript scripts to create multiple threads, but the child threads are completely controlled by the main thread and must not operate the DOM.
Therefore, this new standard does not change the single-threaded nature of JavaScript.
Return to EventLoop:
Single thread means that all tasks need to be queued, and the next task will not be executed until the previous task is completed. If the previous task takes a long time, the next task will have to wait.
If the queue is due to a large amount of calculation and the CPU is too busy, forget it, but many times the CPU is idle because the IO device (input and output device) is very slow (such as Ajax operations to read data from the network) , I have to wait for the results to come out before proceeding.
The designers of the JavaScript language realized that at this time, the main thread can completely ignore the IO device, suspend the waiting tasks, and run the later tasks first. Wait until the IO device returns the result, then go back and continue executing the suspended task.
Therefore, all tasks can be divided into two types, one is synchronous task (synchronous) and the other is asynchronous task (asynchronous). Synchronous tasks refer to tasks queued for execution on the main thread. Only the previous task has been executed.
Only the latter task can be executed; asynchronous tasks refer to tasks that do not enter the main thread but enter the "task queue". Only the "task queue" notifies the main thread that an asynchronous task can be executed. The task will then enter the main thread for execution.
As shown below:
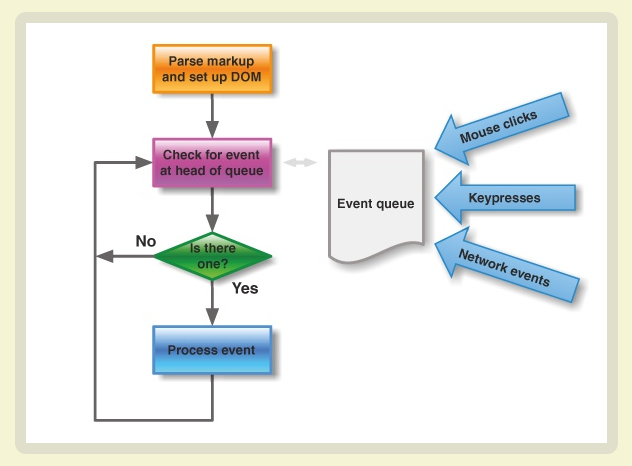
As long as the main thread is empty, it will read the "task queue". This is the running mechanism of JavaScript. This process keeps repeating.
3. Example explanation
Okay, no more "nonsense", let's start our first NodeJS application: "Hello Big Bear".
Open your favorite editor and create a HelloWorld.js file.
The code is as follows:
Let’s run and test this code. First, execute your script with Node.js:
Open the command line tool CMD, switch to your working directory, and run the command "node HelloWorld.js"
Next, open the browser and visit http://localhost:8888/, you will see a webpage that says "Hello, Big Bear!"
A little expanded knowledge:
As shown in the figure below, this is part of the source code of http.js in NodeJS. createServer is a very user-friendly interface. The internal implementation adopts the singleton mode. The advantage of this is that the creation and initialization tasks of the instance are Effective separation, dedicated responsibilities, and reduced coupling are ideas that everyone can learn from when programming.
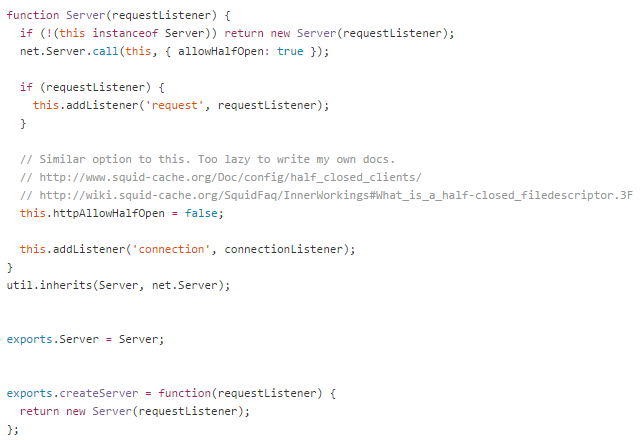
Hahaha, isn’t it very interesting? This is just a short experience. Many knowledge points will be explained later. Everyone will slowly understand O(∩_∩)O haha~
4. General Overview
1. It is a Javascript running environment
2. Rely on Chrome V8 engine for code interpretation
3. Event-driven
4. Non-blocking I/O
5. Lightweight, scalable, suitable for real-time data interaction applications
6. Single process, single thread
The last thing I want to say is: There are not many examples in this article, but these concepts are very important. You must have a clear understanding. This will lay a solid foundation for future NodeJS learning. Friends, come on and work hard together.
Hahaha, this article is over and will be continued. I hope to communicate with you more and make progress together. . . . . . Huhuhu...(*^__^*)

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js can be used as a backend framework as it offers features such as high performance, scalability, cross-platform support, rich ecosystem, and ease of development.
 How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
To connect to a MySQL database, you need to follow these steps: Install the mysql2 driver. Use mysql2.createConnection() to create a connection object that contains the host address, port, username, password, and database name. Use connection.query() to perform queries. Finally use connection.end() to end the connection.
 What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
There are two npm-related files in the Node.js installation directory: npm and npm.cmd. The differences are as follows: different extensions: npm is an executable file, and npm.cmd is a command window shortcut. Windows users: npm.cmd can be used from the command prompt, npm can only be run from the command line. Compatibility: npm.cmd is specific to Windows systems, npm is available cross-platform. Usage recommendations: Windows users use npm.cmd, other operating systems use npm.
 What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
The following global variables exist in Node.js: Global object: global Core module: process, console, require Runtime environment variables: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column Constants: undefined, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Java are design and features: Event-driven vs. thread-driven: Node.js is event-driven and Java is thread-driven. Single-threaded vs. multi-threaded: Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop, and Java uses a multi-threaded architecture. Runtime environment: Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, while Java runs on the JVM. Syntax: Node.js uses JavaScript syntax, while Java uses Java syntax. Purpose: Node.js is suitable for I/O-intensive tasks, while Java is suitable for large enterprise applications.
 Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Yes, Node.js is a backend development language. It is used for back-end development, including handling server-side business logic, managing database connections, and providing APIs.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application
 Which one to choose between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Which one to choose between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Node.js and Java each have their pros and cons in web development, and the choice depends on project requirements. Node.js excels in real-time applications, rapid development, and microservices architecture, while Java excels in enterprise-grade support, performance, and security.




