 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of the differences between document and window and load and ready in jQuery_jquery
Detailed explanation of the differences between document and window and load and ready in jQuery_jquery
Detailed explanation of the differences between document and window and load and ready in jQuery_jquery
Children who have used JavaScript should know the window object and document object, and should also have heard of the load event and ready event. Of course Xiaocai also knows it, and thinks he understands it very well. It was not until something went wrong recently that he realized that it was not the case. So simple.
First of all, let’s talk about window and document. Intuitively speaking, window represents the browser window, and document represents the dom element loaded in the browser window. Furthermore, document is an attribute of window, and window It is the top-level object.
What’s the difference between the two? It's easy to understand. Suppose there is a browser now, and the page loaded in it is very long and exceeds one screen. Of course, scroll bars will definitely appear. At this time, $(window).height() and $(document). height() is not equal, the height of the document must be larger than that of the window, because the window is always that big. See the picture below:
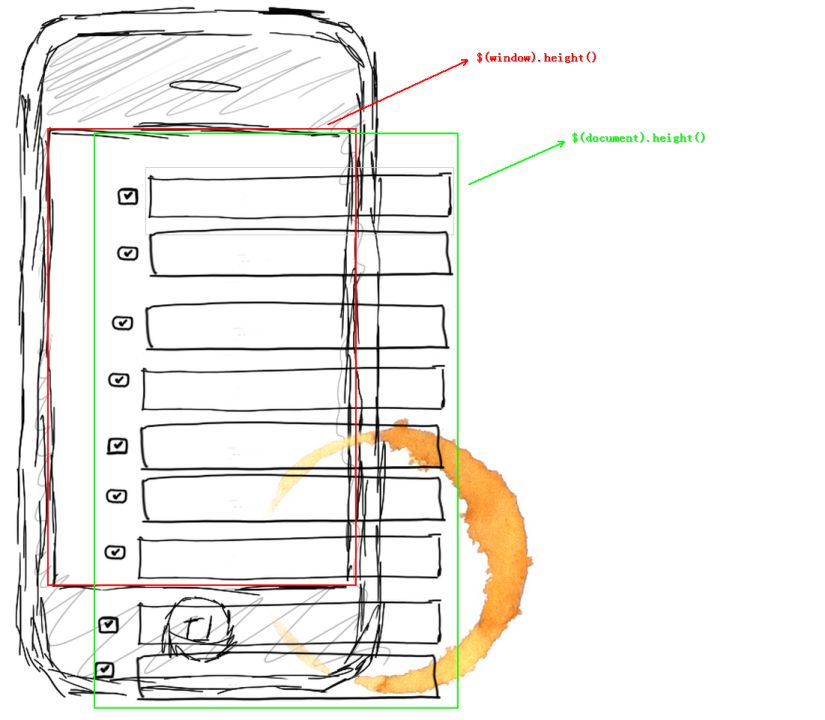
Let’s talk about the load event and ready event (load and ready here refer to jQuery events, the same below).
Let’s talk about load first. The load event is mainly used to replace the native window.onload. It can only be used in two scenarios:
·On the window object. For example $(window).load(fn);.
· Elements with URLs (images, scripts, frames, iframes). For example $("img").load(fn);.
In addition, there is no load event for any element, such as: $(document).load(fn); this is wrong writing and will not be executed at all.
The load event needs to be completely loaded before the page can be triggered. The so-called complete loading means not only that the DOM structure is loaded, but also that all link references are loaded. For example, if there are a large number of pictures on the page, you must wait until each picture is loaded before it is fully loaded.
The most important thing is that the jQuery official document clearly states that the cross-browser compatibility of the load event is very poor (It doesn't work consistently nor reliably cross-browser). After Xiaocai testing, Google Chrome only supports $(window).load(fn);, while Firefox supports $(window).load(fn); and $("img").load(fn);.
Therefore, it is strongly not recommended to use the load event unless necessary.
Finally, let’s talk about ready. The ready event can be added to any element, such as $(window).ready(fn);, $(document).ready(fn);, $(“div”).ready(fn );etc.
The ready event does not require the page to be completely loaded, it only needs to be loaded to trigger the DOM structure.
Multiple ready events can be registered at the same time. When executed, they will be executed in the order of registration. Note that even if you register the ready events of different elements, they will be executed in order. For example, the following code:
$(window).ready(function(){
alert("window");
});
$(document).ready(function(){
alert("document");
});
$("div").ready(function(){
alert("div");
});
According to common sense, the div should be loaded first, so alert("div"); is executed first, and then alert("document"); or alert("window");, but unfortunately, alert( "div"); is the last one executed. Therefore, no matter whether the ready event is registered on the same element or not, it will be executed in the order of registration.
The last item, the ready event conflicts with window.onload (or
). If window.onload (or ) is used, it will cause ready event is not executed.After so much discussion, it was finally proven that: $(document).ready(fn); has the best compatibility and security. If there is such a need, try to use this method.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Detailed explanation of jQuery reference methods: Quick start guide
Feb 27, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Detailed explanation of jQuery reference methods: Quick start guide
Feb 27, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Detailed explanation of jQuery reference method: Quick start guide jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used in website development. It simplifies JavaScript programming and provides developers with rich functions and features. This article will introduce jQuery's reference method in detail and provide specific code examples to help readers get started quickly. Introducing jQuery First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the HTML file. It can be introduced through a CDN link or downloaded
 How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery? In front-end development, we often encounter the need to manipulate the height attributes of elements. Sometimes, we may need to dynamically change the height of an element, and sometimes we need to remove the height attribute of an element. This article will introduce how to use jQuery to remove the height attribute of an element and provide specific code examples. Before using jQuery to operate the height attribute, we first need to understand the height attribute in CSS. The height attribute is used to set the height of an element
 How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery? In jQuery, the method of sending a PUT request is similar to sending other types of requests, but you need to pay attention to some details and parameter settings. PUT requests are typically used to update resources, such as updating data in a database or updating files on the server. The following is a specific code example using the PUT request method in jQuery. First, make sure you include the jQuery library file, then you can send a PUT request via: $.ajax({u
 jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Title: jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page In web development, we often need to modify and operate elements on the page. When using jQuery, sometimes you need to modify the text content of all a tags in the page at once, which can save time and energy. The following will introduce how to use jQuery to quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page, and give specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library file and ensure that the following code is introduced into the page: <
 Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Title: Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags. jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM operations. In web development, we often encounter the need to modify the text content of the link tag (a tag) on the page. This article will explain how to use jQuery to achieve this goal, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the page. Add the following code in the HTML file:
 GTA 6 document gives a detailed overview of all leaks
Sep 08, 2024 am 06:37 AM
GTA 6 document gives a detailed overview of all leaks
Sep 08, 2024 am 06:37 AM
On September 3, version 1.5 of the Grand Theft Auto VI document which provides a detailed overview of everything that is known about the game to date. The updated version of the document was announced in a trailer published on X (formerly Twitter).??
 How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute? When using jQuery to operate DOM elements, you often encounter situations where you need to determine whether an element has a specific attribute. In this case, we can easily implement this function with the help of the methods provided by jQuery. The following will introduce two commonly used methods to determine whether a jQuery element has specific attributes, and attach specific code examples. Method 1: Use the attr() method and typeof operator // to determine whether the element has a specific attribute
 Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM manipulation and event handling in web pages. In jQuery, the eq() method is used to select elements at a specified index position. The specific usage and application scenarios are as follows. In jQuery, the eq() method selects the element at a specified index position. Index positions start counting from 0, i.e. the index of the first element is 0, the index of the second element is 1, and so on. The syntax of the eq() method is as follows: $("s



