如何创建MySQL5的视图
基本语法: CREATE [OR REPLACE] [ALGORITHM = {UNDEFINED | MERGE | TEMPTABLE}] VIEW view_name [( column_list )] AS select_statement [WITH [CASCADED | LOCAL] CHECK OPTION] This statement creates a new view, or replaces an existing one if the
<STRONG>基本语法:</STRONG>
CREATE [OR REPLACE] [ALGORITHM = {UNDEFINED | MERGE | TEMPTABLE}]
VIEW <EM class=replaceable><CODE>view_name</CODE></EM> [(<EM class=replaceable><CODE>column_list</CODE></EM>)]
AS <EM class=replaceable><CODE>select_statement</CODE></EM>
[WITH [CASCADED | LOCAL] CHECK OPTION]
This statement creates a new view, or replaces an existing one if the <FONT face=新宋体>OR REPLACE</FONT> clause is given. The <FONT face=新宋体>select_statement</FONT> is a <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> statement that provides the definition of the view. The statement can select from base tables or other views.
This statement requires the <FONT face=新宋体>CREATE VIEW</FONT> privilege for the view, and some privilege for each column selected by the <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> statement. For columns used elsewhere in the <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> statement you must have the <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> privilege. If the <FONT face=新宋体>OR REPLACE</FONT> clause is present, you must also have the <FONT face=新宋体>DELETE</FONT> privilege for the view.
A view belongs to a database. By default, a new view is created in the current database. To create the view explicitly in a given database, specify the name as <FONT face=新宋体>db_name.view_name</FONT> when you create it.
mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>CREATE VIEW test.v AS SELECT * FROM t;</CODE></STRONG>
Tables and views share the same namespace within a database, so a database cannot contain a table and a view that have the same name.
Views must have unique column names with no duplicates, just like base tables. By default, the names of the columns retrieved by the <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> statement are used for the view column names. To define explicit names for the view columns, the optional <FONT face=新宋体>column_list</FONT> clause can be given as a list of comma-separated identifiers. The number of names in <FONT face=新宋体>column_list</FONT> must be the same as the number of columns retrieved by the <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> statement.
Columns retrieved by the <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> statement can be simple references to table columns. They can also be expressions that use functions, constant values, operators, and so forth.
Unqualified table or view names in the <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> statement are interpreted with respect to the default database. A view can refer to tables or views in other databases by qualifying the table or view name with the proper database name.
A view can be created from many kinds of <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> statements. It can refer to base tables or other views. It can use joins, <FONT face=新宋体>UNION</FONT>, and subqueries. The <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> need not even refer to any tables. The following example defines a view that selects two columns from another table, as well as an expression calculated from those columns:
mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>CREATE TABLE t (qty INT, price INT);</CODE></STRONG> mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>INSERT INTO t VALUES(3, 50);</CODE></STRONG> mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>CREATE VIEW v AS SELECT qty, price, qty*price AS value FROM t;</CODE></STRONG> mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>SELECT * FROM v;</CODE></STRONG> +------+-------+-------+ | qty | price | value | +------+-------+-------+ | 3 | 50 | 150 | +------+-------+-------+
A view definition is subject to the following restrictions:
-
The
<FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT>statement cannot contain a subquery in the<FONT face=新宋体>FROM</FONT>clause. -
The
<FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT>statement cannot refer to system or user variables. -
The
<FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT>statement cannot refer to prepared statement parameters. -
Within a stored routine, the definition cannot refer to routine parameters or local variables.
-
Any table or view referred to in the definition must exist. However, after a view has been created, it is possible to drop a table or view that the definition refers to. To check a view definition for problems of this kind, use the
<FONT face=新宋体>CHECK TABLE</FONT>statement. -
The definition cannot refer to a
<FONT face=新宋体>TEMPORARY</FONT>table, and you cannot create a<FONT face=新宋体>TEMPORARY</FONT>view. -
The tables named in the view definition must already exist.
-
You cannot associate a trigger with a view.
<FONT face=新宋体>ORDER BY</FONT> is allowed in a view definition, but it is ignored if you select from a view using a statement that has its own <FONT face=新宋体>ORDER BY</FONT>.
For other options or clauses in the definition, they are added to the options or clauses of the statement that references the view, but the effect is undefined. For example, if a view definition includes a <FONT face=新宋体>LIMIT</FONT> clause, and you select from the view using a statement that has its own <FONT face=新宋体>LIMIT</FONT> clause, it is undefined which limit applies. This same principle applies to options such as <FONT face=新宋体>ALL</FONT>, <FONT face=新宋体>DISTINCT</FONT>, or <FONT face=新宋体>SQL_SMALL_RESULT</FONT> that follow the <FONT face=新宋体>SELECT</FONT> keyword, and to clauses such as <FONT face=新宋体>INTO</FONT>, <FONT face=新宋体>FOR UPDATE</FONT>, <FONT face=新宋体>LOCK IN SHARE MODE</FONT>, and <FONT face=新宋体>PROCEDURE</FONT>.
If you create a view and then change the query processing environment by changing system variables, that may affect the results you get from the view:
mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>CREATE VIEW v AS SELECT CHARSET(CHAR(65)), COLLATION(CHAR(65));</CODE></STRONG> Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>SET NAMES 'latin1';</CODE></STRONG> Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>SELECT * FROM v;</CODE></STRONG> +-------------------+---------------------+ | CHARSET(CHAR(65)) | COLLATION(CHAR(65)) | +-------------------+---------------------+ | latin1 | latin1_swedish_ci | +-------------------+---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>SET NAMES 'utf8';</CODE></STRONG> Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>SELECT * FROM v;</CODE></STRONG> +-------------------+---------------------+ | CHARSET(CHAR(65)) | COLLATION(CHAR(65)) | +-------------------+---------------------+ | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | +-------------------+---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
The optional <FONT face=新宋体>ALGORITHM</FONT> clause is a MySQL extension to standard SQL. <FONT face=新宋体>ALGORITHM</FONT> takes three values: <FONT face=新宋体>MERGE</FONT>, <FONT face=新宋体>TEMPTABLE</FONT>, or <FONT face=新宋体>UNDEFINED</FONT>. The default algorithm is <FONT face=新宋体>UNDEFINED</FONT> if no <FONT face=新宋体>ALGORITHM</FONT> clause is present. The algorithm affects how MySQL processes the view.
For <FONT face=新宋体>MERGE</FONT>, the text of a statement that refers to the view and the view definition are merged such that parts of the view definition replace corresponding parts of the statement.
For <FONT face=新宋体>TEMPTABLE</FONT>, the results from the view are retrieved into a temporary table, which then is used to execute the statement.
For <FONT face=新宋体>UNDEFINED</FONT>, MySQL chooses which algorithm to use. It prefers <FONT face=新宋体>MERGE</FONT> over <FONT face=新宋体>TEMPTABLE</FONT> if possible, because <FONT face=新宋体>MERGE</FONT> is usually more efficient and because a view cannot be updatable if a temporary table is used.
A reason to choose <FONT face=新宋体>TEMPTABLE</FONT> explicitly is that locks can be released on underlying tables after the temporary table has been created and before it is used to finish processing the statement. This might result in quicker lock release than the <FONT face=新宋体>MERGE</FONT> algorithm so that other clients that use the view are not blocked as long.
A view algorithm can be <FONT face=新宋体>UNDEFINED</FONT> three ways:
-
No
<FONT face=新宋体>ALGORITHM</FONT>clause is present in the<FONT face=新宋体>CREATE VIEW</FONT>statement. -
The
<FONT face=新宋体>CREATE VIEW</FONT>statement has an explicit<FONT face=新宋体>ALGORITHM = UNDEFINED</FONT>clause. -
<FONT face=新宋体>ALGORITHM = MERGE</FONT>is specified for a view that can be processed only with a temporary table. In this case, MySQL generates a warning and sets the algorithm to<FONT face=新宋体>UNDEFINED</FONT>.
As mentioned earlier, <FONT face=新宋体>MERGE</FONT> is handled by merging corresponding parts of a view definition into the statement that refers to the view. The following examples briefly illustrate how the <FONT face=新宋体>MERGE</FONT> algorithm works. The examples assume that there is a view <FONT face=新宋体>v_merge</FONT> that has this definition:
CREATE ALGORITHM = MERGE VIEW v_merge (vc1, vc2) AS SELECT c1, c2 FROM t WHERE c3 > 100;
Example 1: Suppose that we issue this statement:
SELECT * FROM v_merge;
MySQL handles the statement as follows:
-
<FONT face=新宋体>v_merge</FONT>becomes<FONT face=新宋体>t</FONT> -
<FONT face=新宋体>*</FONT>becomes<FONT face=新宋体>vc1, vc2</FONT>, which corresponds to<FONT face=新宋体>c1, c2</FONT> -
The view
<FONT face=新宋体>WHERE</FONT>clause is added
The resulting statement to be executed becomes:
SELECT c1, c2 FROM t WHERE c3 > 100;
Example 2: Suppose that we issue this statement:
SELECT * FROM v_merge WHERE vc1 < 100;
This statement is handled similarly to the previous one, except that <FONT face=新宋体>vc1 < 100</FONT> becomes <FONT face=新宋体>c1 < 100</FONT> and the view <FONT face=新宋体>WHERE</FONT> clause is added to the statement <FONT face=新宋体>WHERE</FONT> clause using an <FONT face=新宋体>AND</FONT> connective (and parentheses are added to make sure the parts of the clause are executed with correct precedence). The resulting statement to be executed becomes:
SELECT c1, c2 FROM t WHERE (c3 > 100) AND (c1 < 100);
Effectively, the statement to be executed has a <FONT face=新宋体>WHERE</FONT> clause of this form:
WHERE (select WHERE) AND (view WHERE)
The <FONT face=新宋体>MERGE</FONT> algorithm requires a one-to relationship between the rows in the view and the rows in the underlying table. If this relationship does not hold, a temporary table must be used instead. Lack of a one-to-one relationship occurs if the view contains any of a number of constructs:
-
Aggregate functions (
<FONT face=新宋体>SUM()</FONT>,<FONT face=新宋体>MIN()</FONT>,<FONT face=新宋体>MAX()</FONT>,<FONT face=新宋体>COUNT()</FONT>, and so forth) -
<FONT face=新宋体>DISTINCT</FONT> -
<FONT face=新宋体>GROUP BY</FONT> -
<FONT face=新宋体>HAVING</FONT> -
<FONT face=新宋体>UNION</FONT>or<FONT face=新宋体>UNION ALL</FONT> -
Refers only to literal values (in this case, there is no underlying table)
Some views are updatable. That is, you can use them in statements such as <FONT face=新宋体>UPDATE</FONT>, <FONT face=新宋体>DELETE</FONT>, or <FONT face=新宋体>INSERT</FONT> to update the contents of the underlying table. For a view to be updatable, there must be a one-to relationship between the rows in the view and the rows in the underlying table. There are also certain other constructs that make a view non-updatable. To be more specific, a view is not updatable if it contains any of the following:
-
Aggregate functions (
<FONT face=新宋体>SUM()</FONT>,<FONT face=新宋体>MIN()</FONT>,<FONT face=新宋体>MAX()</FONT>,<FONT face=新宋体>COUNT()</FONT>, and so forth) -
<FONT face=新宋体>DISTINCT</FONT> -
<FONT face=新宋体>GROUP BY</FONT> -
<FONT face=新宋体>HAVING</FONT> -
<FONT face=新宋体>UNION</FONT>or<FONT face=新宋体>UNION ALL</FONT> -
Subquery in the select list
-
Join
-
Non-updatable view in the
<FONT face=新宋体>FROM</FONT>clause -
A subquery in the
<FONT face=新宋体>WHERE</FONT>clause that refers to a table in the<FONT face=新宋体>FROM</FONT>clause -
Refers only to literal values (in this case, there is no underlying table to update)
-
<FONT face=新宋体>ALGORITHM = TEMPTABLE</FONT>(use of a temporary table always makes a view non-updatable)
With respect to insertability (being updatable with <FONT face=新宋体>INSERT</FONT> statements), an updatable view is insertable if it also satisfies these additional requirements for the view columns:
-
There must be no duplicate view column names.
-
The view must contain all columns in the base table that do not have a default value.
-
The view columns must be simple column references and not derived columns. A derived column is one that is not a simple column reference but is derived from an expression. These are examples of derived columns:
3.14159 col1 + 3 UPPER(col2) col3 / col4 (<EM class=replaceable><CODE>subquery</CODE></EM>)
Copier après la connexion
A view that has a mix of simple column references and derived columns is not insertable, but it can be updatable if you update only those columns that are not derived. Consider this view:
CREATE VIEW v AS SELECT col1, 1 AS col2 FROM t;
This view is not insertable because <FONT face=新宋体>col2</FONT> is derived from an expression. But it is updatable if the update does not try to update <FONT face=新宋体>col2</FONT>. This update is allowable:
UPDATE v SET col1 = 0;
This update is not allowable because it attempts to update a derived column:
UPDATE v SET col2 = 0;
It is sometimes possible for a multiple-table view to be updatable, assuming that it can be processed with the <FONT face=新宋体>MERGE</FONT> algorithm. For this to work, the view must use an inner join (not an outer join or a <FONT face=新宋体>UNION</FONT>). Also, only a single table in the view definition can be updated, so the <FONT face=新宋体>SET</FONT> clause must name only columns from one of the tables in the view. Views that use <FONT face=新宋体>UNION ALL</FONT> are disallowed even though they might be theoretically updatable, because the implementation uses temporary tables to process them.
For a multiple-table updatable view, <FONT face=新宋体>INSERT</FONT> can work if it inserts into a single table. <FONT face=新宋体>DELETE</FONT> is not supported.
The <FONT face=新宋体>WITH CHECK OPTION</FONT> clause can be given for an updatable view to prevent inserts or updates to rows except those for which the <FONT face=新宋体>WHERE</FONT> clause in the <FONT face=新宋体>select_statement</FONT> is true.
In a <FONT face=新宋体>WITH CHECK OPTION</FONT> clause for an updatable view, the <FONT face=新宋体>LOCAL</FONT> and <FONT face=新宋体>CASCADED</FONT> keywords determine the scope of check testing when the view is defined in terms of another view. <FONT face=新宋体>LOCAL</FONT> keyword restricts the <FONT face=新宋体>CHECK OPTION</FONT> only to the view being defined. <FONT face=新宋体>CASCADED</FONT> causes the checks for underlying views to be evaluated as well. When neither keyword is given, the default is <FONT face=新宋体>CASCADED</FONT>. Consider the definitions for the following table and set of views:
mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>CREATE TABLE t1 (a INT);</CODE></STRONG>
mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>CREATE VIEW v1 AS SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE a < 2</CODE></STRONG>
-> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>WITH CHECK OPTION;</CODE></STRONG>
mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>CREATE VIEW v2 AS SELECT * FROM v1 WHERE a > 0</CODE></STRONG>
-> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>WITH LOCAL CHECK OPTION;</CODE></STRONG>
mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>CREATE VIEW v3 AS SELECT * FROM v1 WHERE a > 0</CODE></STRONG>
-> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>WITH CASCADED CHECK OPTION;</CODE></STRONG>
Here the <FONT face=新宋体>v2</FONT> and <FONT face=新宋体>v3</FONT> views are defined in terms of another view, <FONT face=新宋体>v1</FONT>. <FONT face=新宋体>v2</FONT> has a <FONT face=新宋体>LOCAL</FONT> check option, so inserts are tested only against the <FONT face=新宋体>v2</FONT> check. <FONT face=新宋体>v3</FONT> has a <FONT face=新宋体>CASCADED</FONT> check option, so inserts are tested not only against its own check, but against those of underlying views. The following statements illustrate these differences:
ql> INSERT INTO v2 VALUES (2); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> <STRONG class=userinput><CODE>INSERT INTO v3 VALUES (2);</CODE></STRONG> ERROR 1369 (HY000): CHECK OPTION failed 'test.v3'
The updatability of views may be affected by the value of the <font face="新宋体">updatable_views_with_limit</font> system variable. (完)

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
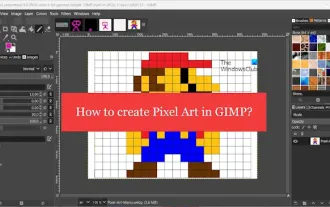 Comment créer du pixel art dans GIMP
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:24 PM
Comment créer du pixel art dans GIMP
Feb 19, 2024 pm 03:24 PM
Cet article vous intéressera si vous souhaitez utiliser GIMP pour la création de pixel art sous Windows. GIMP est un logiciel d'édition graphique bien connu qui est non seulement gratuit et open source, mais qui aide également les utilisateurs à créer facilement de belles images et de superbes designs. En plus de convenir aussi bien aux concepteurs débutants qu'aux professionnels, GIMP peut également être utilisé pour créer du pixel art, une forme d'art numérique qui utilise les pixels comme seuls éléments de base pour dessiner et créer. Comment créer du pixel art dans GIMP Voici les principales étapes pour créer des images pixel à l'aide de GIMP sur un PC Windows : Téléchargez et installez GIMP, puis lancez l'application. Créez une nouvelle image. Redimensionnez la largeur et la hauteur. Sélectionnez l'outil Crayon. Définissez le type de pinceau sur pixels. installation
 Comment créer un dossier sur Realme Phone ?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 02:30 PM
Comment créer un dossier sur Realme Phone ?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 02:30 PM
Titre : Guide du débutant Realme Phone : Comment créer des dossiers sur Realme Phone ? Dans la société actuelle, les téléphones portables sont devenus un outil indispensable dans la vie des gens. En tant que marque de smartphones populaire, RealMobile est appréciée des utilisateurs pour son système d'exploitation simple et pratique. Lors de l'utilisation des téléphones Realme, de nombreuses personnes peuvent être confrontées au besoin d'organiser des fichiers et des applications sur le téléphone, et la création de dossiers est un moyen efficace. Cet article explique comment créer des dossiers sur les téléphones Realme pour aider les utilisateurs à mieux gérer le contenu de leur téléphone. Non.
 Comment créer une famille avec Gree+
Mar 01, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
Comment créer une famille avec Gree+
Mar 01, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
De nombreux amis ont exprimé leur souhait de savoir comment créer une famille dans le logiciel Gree+. Voici la méthode de fonctionnement pour vous. Amis qui veulent en savoir plus, venez jeter un œil avec moi. Tout d’abord, ouvrez le logiciel Gree+ sur votre téléphone mobile et connectez-vous. Ensuite, dans la barre d'options en bas de la page, cliquez sur l'option « Mon » à l'extrême droite pour accéder à la page du compte personnel. 2. Après être arrivé sur ma page, il y a une option « Créer une famille » sous « Famille ». Après l'avoir trouvée, cliquez dessus pour entrer. 3. Accédez ensuite à la page pour créer une famille, entrez le nom de famille à définir dans la zone de saisie en fonction des invites, puis cliquez sur le bouton « Enregistrer » dans le coin supérieur droit après l'avoir saisi. 4. Enfin, une invite « enregistrement réussi » apparaîtra au bas de la page, indiquant que la famille a été créée avec succès.
 Comprendre les différences et les comparaisons entre SpringBoot et SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 09:20 AM
Comprendre les différences et les comparaisons entre SpringBoot et SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 09:20 AM
Comparez SpringBoot et SpringMVC et comprenez leurs différences Avec le développement continu du développement Java, le framework Spring est devenu le premier choix pour de nombreux développeurs et entreprises. Dans l'écosystème Spring, SpringBoot et SpringMVC sont deux composants très importants. Bien qu'ils soient tous deux basés sur le framework Spring, il existe certaines différences dans les fonctions et l'utilisation. Cet article se concentrera sur la comparaison de SpringBoot et Spring
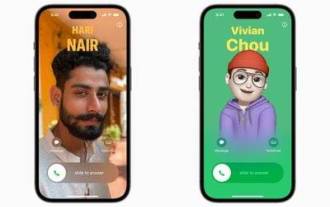 Comment créer une affiche de contact pour votre iPhone
Mar 02, 2024 am 11:30 AM
Comment créer une affiche de contact pour votre iPhone
Mar 02, 2024 am 11:30 AM
Dans iOS17, Apple a ajouté une fonctionnalité d'affichage de contacts à ses applications Téléphone et Contacts couramment utilisées. Cette fonctionnalité permet aux utilisateurs de définir des affiches personnalisées pour chaque contact, rendant le carnet d'adresses plus visuel et personnel. Les affiches de contact peuvent aider les utilisateurs à identifier et à localiser des contacts spécifiques plus rapidement, améliorant ainsi l'expérience utilisateur. Grâce à cette fonctionnalité, les utilisateurs peuvent ajouter des images ou des logos spécifiques à chaque contact en fonction de leurs préférences et de leurs besoins, ce qui rend l'interface du carnet d'adresses plus vivante. Apple dans iOS17 offre aux utilisateurs d'iPhone une nouvelle façon de s'exprimer et ajoute une affiche de contact personnalisable. La fonction Contact Poster vous permet d'afficher un contenu unique et personnalisé lorsque vous appelez d'autres utilisateurs d'iPhone. toi
 Un premier aperçu de Django : créez votre premier projet Django en utilisant la ligne de commande
Feb 19, 2024 am 09:56 AM
Un premier aperçu de Django : créez votre premier projet Django en utilisant la ligne de commande
Feb 19, 2024 am 09:56 AM
Commencez le parcours du projet Django : démarrez à partir de la ligne de commande et créez votre premier projet Django. Django est un framework d'application Web puissant et flexible. Il est basé sur Python et fournit de nombreux outils et fonctions nécessaires au développement d'applications Web. Cet article vous amènera à créer votre premier projet Django à partir de la ligne de commande. Avant de commencer, assurez-vous que Python et Django sont installés. Étape 1 : Créer le répertoire du projet Tout d'abord, ouvrez la fenêtre de ligne de commande et créez un nouveau répertoire
 Quelles sont les opinions de Word ?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 06:10 PM
Quelles sont les opinions de Word ?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 06:10 PM
Je suppose que de nombreux étudiants souhaitent acquérir les compétences de composition de Word, mais l'éditeur vous dit secrètement qu'avant d'acquérir les compétences de composition, vous devez comprendre clairement les vues de mots. Dans Word2007, 5 vues sont proposées aux utilisateurs. les vues incluent la vue pages, la vue mise en page de lecture, la vue mise en page Web, la vue plan et la vue normale. Découvrons ces 5 vues de mots avec l'éditeur aujourd'hui. 1. Vue de page La vue de page peut afficher l'apparence du résultat d'impression du document Word2007, qui comprend principalement les en-têtes, les pieds de page, les objets graphiques, les paramètres de colonne, les marges de page et d'autres éléments. Il s'agit de la vue de page la plus proche du résultat d'impression. 2. Mode de lecture Le mode de lecture affiche les documents Word2007 et Office dans le style de colonne d'un livre.
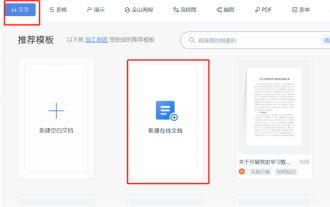 Comment créer un mot en ligne
Mar 21, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Comment créer un mot en ligne
Mar 21, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Savez-vous comment créer un document Word en ligne ? Les documents Word en ligne peuvent permettre à plusieurs personnes de collaborer et de modifier des documents en ligne. Ils disposent d'un espace de stockage cloud de grande capacité. Les documents peuvent être stockés de manière centralisée et peuvent être connectés à partir de plusieurs appareils. vous pouvez le visualiser et le modifier. Le plus important est qu'il prend en charge le partage en un clic, ce qui est particulièrement pratique pour partager vos documents avec des collègues. Aujourd'hui, nous allons vous présenter comment créer un document Word en ligne. En fait, la méthode est très simple. Les amis dans le besoin peuvent s'y référer. 1. Ouvrez d'abord le logiciel wpsoffice sur votre ordinateur, puis sur la page du nouveau fichier, ouvrez la barre d'éléments de texte, puis sélectionnez l'option du nouveau document en ligne. 2. Ensuite, la nouvelle page du document s'ouvrira, où nous pourrons choisir un modèle de document en ligne ou un document vierge.






