 développement back-end
développement back-end
 Golang
Golang
 Aller à la programmation | Bases des chaînes | Codage des caractères
Aller à la programmation | Bases des chaînes | Codage des caractères
Aller à la programmation | Bases des chaînes | Codage des caractères
Introduction
Dans la leçon précédente, nous avons appris que les caractères de Go sont codés en UTF-8 et stockés sous forme d'octet ou de rune. Parlons maintenant de la chaîne, qui est une collection de caractères. Apprenons-le ensemble.
Points de connaissances :
- Qu'est-ce qu'une chaîne
- Créer une chaîne
- Déclarer une chaîne
- Fonctions de chaîne communes
Qu'est-ce qu'une chaîne
Dans le premier programme que nous avons appris en Go, nous avons imprimé la chaîne bonjour tout le monde.
String est un type de données de base dans Go, également connu sous le nom de chaîne littérale. Il peut être compris comme une collection de caractères et occupe un bloc continu de mémoire. Ce bloc de mémoire peut stocker tout type de données, comme des lettres, du texte, des emoji, etc.
Cependant, contrairement à d'autres langages, les chaînes dans Go sont en lecture seule et ne peuvent pas être modifiées.
Créer une chaîne
Les chaînes peuvent être déclarées de plusieurs manières. Jetons un coup d'œil à la première méthode. Créez un nouveau fichier appelé string.go :
touch ~/project/string.go
Écrivez le code suivant :
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Use the var keyword to create a string variable a
var a string = "labex"
a = "labex" // Assign "labex" to variable a
// Declare variable a and assign its value
var b string = "shiyanlou"
// Type declaration can be omitted
var c = "Monday"
// Use := for quick declaration and assignment
d := "Hangzhou"
fmt.Println(a, b, c, d)
}
Le code ci-dessus montre comment créer des chaînes à l'aide du mot-clé var et de l'opérateur :=. Si vous attribuez une valeur lors de la création d'une variable avec var, vous pouvez omettre la déclaration de type, comme indiqué lors de la création de la variable b.
Le résultat attendu est le suivant :
labex shiyanlou Monday Hangzhou
Déclarer une chaîne
Dans la plupart des cas, nous utilisons des guillemets doubles "" pour déclarer des chaînes. L’avantage des guillemets doubles est qu’ils peuvent être utilisés comme séquence d’échappement. Par exemple, dans le programme ci-dessous, nous utilisons la séquence d'échappement n pour créer une nouvelle ligne :
package main
import "fmt"
func main(){
x := "shiyanlou\nlabex"
fmt.Println(x)
}
Le résultat attendu est le suivant :
shiyanlou labex
Voici quelques séquences d'échappement courantes :
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| n | New line |
| r | Carriage return |
| t | Tab |
| b | Backspace |
| \ | Backslash |
| ' | Single quote |
| " | Double quote |
If you want to preserve the original format of the text or need to use multiple lines, you can use backticks to represent them:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Output Pascal's Triangle
yangHuiTriangle := `
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 15 6 1
1 7 21 35 35 21 7 1
1 8 28 56 70 56 28 8 1`
fmt.Println(yangHuiTriangle)
// Output the ASCII art of "labex"
ascii := `
# ## # # ### # ## ####
# # # ## # # # # # # # #
# # # # # # # # # # # # #
# ##### # # # # # # # ##### # #
# # # # ## # # # # # # #
##### # # # # ## # # # # ### `
fmt.Println(ascii)
}
After running the program, you will see the following output:
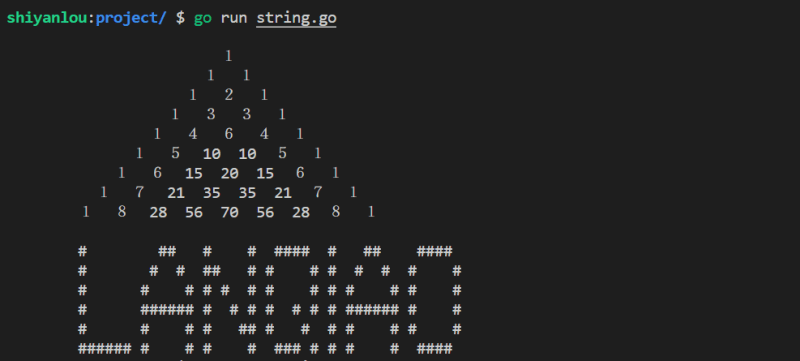
Backticks are commonly used in prompts, HTML templates, and other cases where you need to preserve the original format of the output.
Getting the Length of a String
In the previous lesson, we learned that English characters and general punctuation marks occupy one byte, while Chinese characters occupy three to four bytes.
Therefore, in Go, we can use the len() function to get the byte length of a string. If there are no characters that occupy multiple bytes, the len() function can be used to approximately measure the length of the string.
If a string contains characters that occupy multiple bytes, you can use the utf8.RuneCountInString function to get the actual number of characters in the string.
Let's see an example. Write the following code to the string.go file:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"unicode/utf8"
)
func main() {
// Declare two empty strings using var and :=
var a string
b := ""
c := "labex"
// Output byte length
fmt.Printf("The value of a is %s, the byte length of a is: %d\n", a, len(a))
fmt.Printf("The value of b is %s, the byte length of b is: %d\n", b, len(b))
fmt.Printf("The value of c is %s, the byte length of c is: %d\n", c, len(c))
// Output string length
fmt.Printf("The length of d is: %d\n", utf8.RuneCountInString(d))
}
The expected output is as follows:
The value of a is , the byte length of a is: 0 The value of b is , the byte length of b is: 0 The value of c is labex, the byte length of c is: 5 The length of d is: 9
In the program, we first declared two empty strings and the string labex. You can see that their byte lengths and actual lengths are the same.
Converting Strings and Integers
We can use functions from the strconv package to convert between strings and integers:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
func main() {
// Declare a string a and an integer b
a, b := "233", 223
// Use Atoi to convert an integer to a string
c, _ := strconv.Atoi(a)
// Use Sprintf and Itoa functions respectively
// to convert a string to an integer
d1 := fmt.Sprintf("%d", b)
d2 := strconv.Itoa(b)
fmt.Printf("The type of a: %T\n", a) // string
fmt.Printf("The type of b: %T\n", b) // int
fmt.Printf("The type of c: %T\n", c) // int
fmt.Printf("The type of d1: %T\n", d1) // string
fmt.Printf("The type of d2: %T\n", d2) // string
}
The expected output is as follows:
The type of a: string The type of b: int The type of c: int The type of d1: string The type of d2: string
In the program, we use the Sprintf() function from the fmt package, which has the following format:
func Sprintf(format string, a ...interface{}) string
format is a string with escape sequences, a is a constant or variable that provides values for the escape sequences, and ... means that there can be multiple variables of the same type as a. The string after the function represents that Sprintf returns a string. Here's an example of using this function:
a = Sprintf("%d+%d=%d", 1, 2, 3)
fmt.Println(a) // 1+2=3
In this code snippet, the format is passed with three integer variables 1, 2, and 3. The %d integer escape character in format is replaced by the integer values, and the Sprintf function returns the result after replacement, 1+2=3.
Also, note that when using strconv.Atoi() to convert an integer to a string, the function returns two values, the converted integer val and the error code err. Because in Go, if you declare a variable, you must use it, we can use an underscore _ to comment out the err variable.
When strconv.Atoi() converts correctly, err returns nil. When an error occurs during conversion, err returns the error message, and the value of val will be 0. You can change the value of string a and replace the underscore with a normal variable to try it yourself.
Concatenating Strings
The simplest way to concatenate two or more strings is to use the + symbol. We can also use the fmt.Sprintf() function to concatenate strings. Let's take a look at an example:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
a, b := "lan", "qiao"
// Concatenate using the simplest method, +
c1 := a + b
// Concatenate using the Sprintf function
c2 := fmt.Sprintf("%s%s", a, b)
fmt.Println(a, b, c1, c2) // lan qiao labex labex
}
The expected output is as follows:
lan qiao labex labex
In the program, we also used the Sprintf() function from the fmt package to concatenate strings and print the results.
Removing Leading and Trailing Spaces from a String
We can use the strings.TrimSpace function to remove leading and trailing spaces from a string. The function takes a string as input and returns the string with leading and trailing spaces removed. The format is as follows:
func TrimSpace(s string) string
Here is an example:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
a := " \t \n labex \n \t hangzhou"
fmt.Println(strings.TrimSpace(a))
}
The expected output is as follows:
labex
hangzhou
Summary
To summarize what we've learned in this lesson:
- The relationship between strings and characters
- Two ways to declare strings
- Concatenating strings
- Removing leading and trailing spaces from a string
In this lesson, we explained the strings we use in daily life. We've learned about the relationship between strings and characters, mastered string creation and declaration, and gained some knowledge of common string functions.
In the next lesson, we will learn about constants.
? Practice Now: Go String Fundamentals
Want to Learn More?
- ? Learn the latest Go Skill Trees
- ? Read More Go Tutorials
- ? Join our Discord or tweet us @WeAreLabEx
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

Video Face Swap
Échangez les visages dans n'importe quelle vidéo sans effort grâce à notre outil d'échange de visage AI entièrement gratuit !

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)

Sujets chauds
 1675
1675
 14
14
 1429
1429
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1278
1278
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 Golang vs Python: performance et évolutivité
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs Python: performance et évolutivité
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang est meilleur que Python en termes de performances et d'évolutivité. 1) Les caractéristiques de type compilation de Golang et le modèle de concurrence efficace le font bien fonctionner dans des scénarios de concurrence élevés. 2) Python, en tant que langue interprétée, s'exécute lentement, mais peut optimiser les performances via des outils tels que Cython.
 Golang et C: concurrence vs vitesse brute
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Golang et C: concurrence vs vitesse brute
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Golang est meilleur que C en concurrence, tandis que C est meilleur que Golang en vitesse brute. 1) Golang obtient une concurrence efficace par le goroutine et le canal, ce qui convient à la gestion d'un grand nombre de tâches simultanées. 2) C Grâce à l'optimisation du compilateur et à la bibliothèque standard, il offre des performances élevées près du matériel, adaptées aux applications qui nécessitent une optimisation extrême.
 Partage avec Go: un guide du débutant
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:21 AM
Partage avec Go: un guide du débutant
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:21 AM
GOISIDEALFORBEGINNERNERS et combinant pour pourcloudandNetWorkServicesDuetOtssimplicity, Efficiency, andCurrencyFeatures.1) InstallgofromTheofficialwebsiteandverifywith'goversion'..2)
 Golang vs C: Performance et comparaison de la vitesse
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:13 AM
Golang vs C: Performance et comparaison de la vitesse
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:13 AM
Golang convient au développement rapide et aux scénarios simultanés, et C convient aux scénarios où des performances extrêmes et un contrôle de bas niveau sont nécessaires. 1) Golang améliore les performances grâce à des mécanismes de collecte et de concurrence des ordures, et convient au développement de services Web à haute concurrence. 2) C réalise les performances ultimes grâce à la gestion manuelle de la mémoire et à l'optimisation du compilateur, et convient au développement du système intégré.
 Golang vs Python: différences et similitudes clés
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang vs Python: différences et similitudes clés
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang et Python ont chacun leurs propres avantages: Golang convient aux performances élevées et à la programmation simultanée, tandis que Python convient à la science des données et au développement Web. Golang est connu pour son modèle de concurrence et ses performances efficaces, tandis que Python est connu pour sa syntaxe concise et son écosystème de bibliothèque riche.
 Golang et C: les compromis en performance
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang et C: les compromis en performance
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Les différences de performance entre Golang et C se reflètent principalement dans la gestion de la mémoire, l'optimisation de la compilation et l'efficacité du temps d'exécution. 1) Le mécanisme de collecte des ordures de Golang est pratique mais peut affecter les performances, 2) la gestion manuelle de C et l'optimisation du compilateur sont plus efficaces dans l'informatique récursive.
 La course de performance: Golang vs C
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:07 AM
La course de performance: Golang vs C
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Golang et C ont chacun leurs propres avantages dans les compétitions de performance: 1) Golang convient à une concurrence élevée et à un développement rapide, et 2) C fournit des performances plus élevées et un contrôle fin. La sélection doit être basée sur les exigences du projet et la pile de technologie d'équipe.
 Golang contre Python: les avantages et les inconvénients
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Golang contre Python: les avantages et les inconvénients
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
GolangisidealforBuildingsCalableSystemsDuetoitSefficiency and Concurrency, tandis que les Implicites de l'Indrecosystem et le Golang'sDesignenCourageSlecElNCORES



