
Dans les 2 derniers blogs, nous avons vu comment installer neo4j et y charger des données. Dans ce blog, nous allons voir comment créer un moteur de requête graphique simple qui répond à notre question mais en récupérant les données de neo4j.
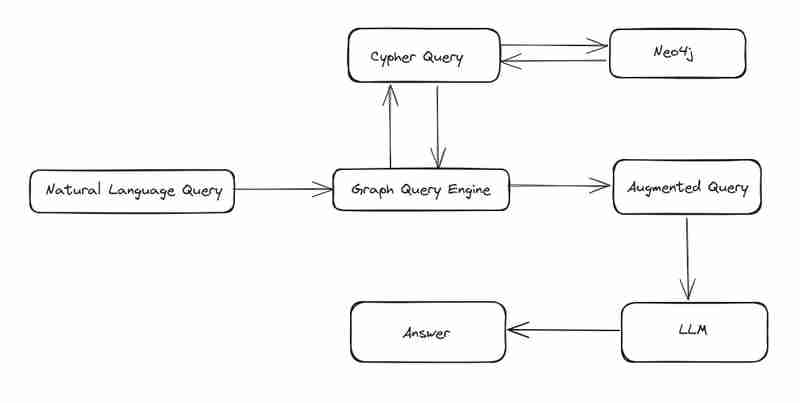
Pour créer une requête chiffrée, nous devons fournir des informations sur le schéma et les propriétés à GPT avec notre question. L'utilisation de ces métadonnées GPT nous donnera une requête.
J'ai structuré l'invite pour renvoyer 3 requêtes pour chaque entrée de l'utilisateur
class GraphQueryEngine:
def __init__(self):
self.client = OpenAI(api_key="")
self.url = "bolt://localhost:7687"
self.auth = ("neo4j", "neo4j@123")
def get_response(self, user_input):
"""Used to get cypher queries from user input"""
completion = self.client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
messages=[
{"role": "system",
"content": "You are an expert in generating Cypher queries for a Neo4j database. Your task is to understand the input and generate only Cypher read queries. Do not return anything other than the Cypher queries, as the returned result will be executed directly in the database."},
{"role": "user",
"content": f"""
Schema Information:
NODES: Product_type - Contains the distinct types of products such as headphones/mobiles/laptops/washing machines, Product_details - Contains products within a product_type for example apple, samsung within mobiles, DELL within laptops
NODE PROPERTIES: In node Product_type there are name(name of the product type - String), embedding(embedding of the name), and in node Product_details there are name(name of the product - string), price(price of the product - integer), description(description of the product), product_release_date(when product was release on - date), available_stock(stock left - integer), review_rating(product review - float)
DIRECTION OF RELATIONSHIPS: Node Product_type is connected to node Product_details using relationship CONTAINS
Based on the schema, generate three read-only Cypher queries related to Product_type (e.g., chairs, headphones, fridge) or Product_details (e.g., name, description) or combination of both. Ensure that product category uses Product_type and product name/ price
Query 1: Use regular expressions (avoid 'contains') - Exclude the 'embedding' property from the result.
Query 2: Use `apoc.text.levenshteinSimilarity > 0.5` - Exclude the 'embedding' property from the result.
Query 3: Use `gds.similarity.cosine()` to reorder nodes based on similarity scores. The query must include a `%s` placeholder for embedding input but exclude the 'embedding' property in the result.
Generate targeted queries using relationships only when necessary. The embedding property should only be used in the logic and must not appear in the query results.
Strictly return only the Cypher queries with no embeddings. The returned result will be executed directly in the database.
{user_input}
"""},
],
)
response = completion.choices[0].message.content
completion = self.client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
messages=[
{"role": "system",
"content": "You are an expert in parsing generating Cypher queries."},
{"role": "user",
"content": f"""Use this input - {response} and parse and return only the cypher queries from the input, ensure that in the cypher query if it returns embeddings then remove the embeddings alone from the query"""},
],
response_format=CypherQuery,
)
event = completion.choices[0].message.parsed
cypher_queries = event.cypher_queries
print("################################## CYPHER QUERIES ######################################")
for query in cypher_queries:
print(query)
return cypher_queries
def populate_embedding_in_query(self, user_input, cypher_queries):
"""Used to add embeddings of the user input in the 3rd query"""
model = "text-embedding-3-small"
user_input = user_input.replace("\n", " ")
embeddings = self.client.embeddings.create(input=[user_input], model=model).data[0].embedding
cypher_queries[2] = cypher_queries[2] % embeddings
return cypher_queries
def execute_read_query(self, query):
"""Execute the cypher query"""
results = []
with GraphDatabase.driver(self.url, auth=self.auth) as driver:
with driver.session() as session:
try:
result = session.run(query)
# Collect the result from the read query
records = [record.data() for record in result]
if records:
results.append(records)
except Exception as error:
print(f"Error in executing query")
return results
def fetch_data(self, cypher_queries):
"""Return the fetched data from DB post formatting"""
results = None
for idx in range(len(cypher_queries)):
try:
results = self.execute_read_query(cypher_queries[idx])
if results:
if idx == len(cypher_queries) - 1:
results = results[0][:10]
break
except Exception:
pass
return results
def get_final_response(self, user_input, fetched_data):
"""Augumented generation using data fetched from DB"""
completion = self.client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
messages=[
{"role": "system",
"content": "You are a chatbot for an ecommerce website, you help users to identify their desired products"},
{"role": "user", "content": f"""User query - {user_input}
Use the below metadata to answer my query
{fetched_data}
"""},
],
)
response = completion.choices[0].message.content
return response
from openai import OpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import List
from neo4j import GraphDatabase
class CypherQuery(BaseModel):
cypher_queries: List[str]
class GraphQueryEngine:
def __init__(self):
self.client = OpenAI(api_key="")
self.url = "bolt://localhost:7687"
self.auth = ("neo4j", "neo4j@123")
def populate_embedding_in_query(self, user_input, cypher_queries):
"""Used to add embeddings of the user input in the 3rd query"""
model = "text-embedding-3-small"
user_input = user_input.replace("\n", " ")
embeddings = self.client.embeddings.create(input=[user_input], model=model).data[0].embedding
cypher_queries[2] = cypher_queries[2] % embeddings
return cypher_queries
def execute_read_query(self, query):
"""Execute the cypher query"""
results = []
with GraphDatabase.driver(self.url, auth=self.auth) as driver:
with driver.session() as session:
try:
result = session.run(query)
# Collect the result from the read query
records = [record.data() for record in result]
if records:
results.append(records)
except Exception as error:
print(f"Error in executing query")
return results
def get_response(self, user_input):
"""Used to get cypher queries from user input"""
completion = self.client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
messages=[
{"role": "system",
"content": "You are an expert in generating Cypher queries for a Neo4j database. Your task is to understand the input and generate only Cypher read queries. Do not return anything other than the Cypher queries, as the returned result will be executed directly in the database."},
{"role": "user",
"content": f"""
Schema Information:
NODES: Product_type - Contains the distinct types of products such as headphones/mobiles/laptops/washing machines, Product_details - Contains products within a product_type for example apple, samsung within mobiles, DELL within laptops
NODE PROPERTIES: In node Product_type there are name(name of the product type - String), embedding(embedding of the name), and in node Product_details there are name(name of the product - string), price(price of the product - integer), description(description of the product), product_release_date(when product was release on - date), available_stock(stock left - integer), review_rating(product review - float)
DIRECTION OF RELATIONSHIPS: Node Product_type is connected to node Product_details using relationship CONTAINS
Based on the schema, generate three read-only Cypher queries related to Product_type (e.g., chairs, headphones, fridge) or Product_details (e.g., name, description) or combination of both. Ensure that product category uses Product_type and product name/ price
Query 1: Use regular expressions (avoid 'contains') - Exclude the 'embedding' property from the result.
Query 2: Use `apoc.text.levenshteinSimilarity > 0.5` - Exclude the 'embedding' property from the result.
Query 3: Use `gds.similarity.cosine()` to reorder nodes based on similarity scores. The query must include a `%s` placeholder for embedding input but exclude the 'embedding' property in the result.
Generate targeted queries using relationships only when necessary. The embedding property should only be used in the logic and must not appear in the query results.
Strictly return only the Cypher queries with no embeddings. The returned result will be executed directly in the database.
{user_input}
"""},
],
)
response = completion.choices[0].message.content
completion = self.client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
messages=[
{"role": "system",
"content": "You are an expert in parsing generating Cypher queries."},
{"role": "user",
"content": f"""Use this input - {response} and parse and return only the cypher queries from the input, ensure that in the cypher query if it returns embeddings then remove the embeddings alone from the query"""},
],
response_format=CypherQuery,
)
event = completion.choices[0].message.parsed
cypher_queries = event.cypher_queries
print("################################## CYPHER QUERIES ######################################")
for query in cypher_queries:
print(query)
return cypher_queries
def get_final_response(self, user_input, fetched_data):
"""Augumented generation using data fetched from DB"""
completion = self.client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
messages=[
{"role": "system",
"content": "You are a chatbot for an ecommerce website, you help users to identify their desired products"},
{"role": "user", "content": f"""User query - {user_input}
Use the below metadata to answer my query
{fetched_data}
"""},
],
)
response = completion.choices[0].message.content
return response
def fetch_data(self, cypher_queries):
"""Return the fetched data from DB post formatting"""
results = None
for idx in range(len(cypher_queries)):
try:
results = self.execute_read_query(cypher_queries[idx])
if results:
if idx == len(cypher_queries) - 1:
results = results[0][:10]
break
except Exception:
pass
return results
user_input = input("Enter your question : ")
query_engine = GraphQueryEngine()
cypher_queries = query_engine.get_response(user_input)
cypher_queries = query_engine.populate_embedding_in_query(user_input, cypher_queries)
fetched_data = query_engine.fetch_data(cypher_queries)
response = query_engine.get_final_response(user_input, fetched_data)
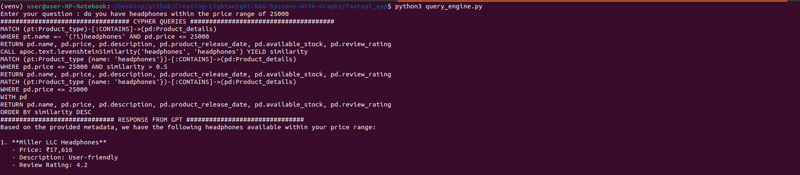
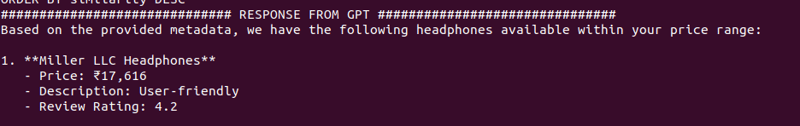
Dans le prochain blog, nous créerons une application FastAPI simple pour exposer cette configuration en tant qu'API.
J'espère que cela aide... !!!
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/in/praveenr2998/
Github - https://github.com/praveenr2998/Creating-Lightweight-RAG-Systems-With-Graphs/blob/main/fastapi_app/query_engine.py
Ce qui précède est le contenu détaillé de. pour plus d'informations, suivez d'autres articles connexes sur le site Web de PHP en chinois!
 niveau d'isolement des transactions par défaut de MySQL
niveau d'isolement des transactions par défaut de MySQL
 Qu'est-ce que la monnaie numérique
Qu'est-ce que la monnaie numérique
 La différence entre les fonctions fléchées et les fonctions ordinaires
La différence entre les fonctions fléchées et les fonctions ordinaires
 Nettoyer les fichiers indésirables dans Win10
Nettoyer les fichiers indésirables dans Win10
 point de symbole spécial
point de symbole spécial
 À quelles touches les flèches font-elles référence dans les ordinateurs ?
À quelles touches les flèches font-elles référence dans les ordinateurs ?
 Comment utiliser la fonction Print() en Python
Comment utiliser la fonction Print() en Python
 Il y a une page vierge supplémentaire dans Word et je ne parviens pas à la supprimer.
Il y a une page vierge supplémentaire dans Word et je ne parviens pas à la supprimer.