Javascript图像处理—平滑处理实现原理_javascript技巧
前言
上一篇文章,我们讲解了图像的虚拟边缘,这篇文章开始进行平滑(也就是模糊)处理。
基本原理
这里直接引用OpenCV 2.4+ C++ 平滑处理和OpenCV 2.4+ C++ 边缘梯度计算的相关内容:
平滑也称模糊, 是一项简单且使用频率很高的图像处理方法。
平滑处理时需要用到一个滤波器
。 最常用的滤波器是线性 滤波器,线性滤波处理的输出像素值(例如:)是输入像素值(例如:
)的加权平均:
, 它仅仅是一个加权系数。
称为核
这里涉及一种叫做“卷积”的运算,那么卷积是什么呢?
卷积是在每一个图像块与某个算子(核)之间进行的运算。
核?!
nbsp;dsds
核就是一个固定大小的数值数组。该数组带有一个锚点
,一般位于数组中央。
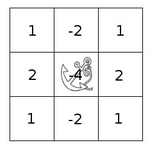
可是这怎么运算啊?
假如你想得到图像的某个特定位置的卷积值,可用下列方法计算:
将核的锚点放在该特定位置的像素上,同时,核内的其他值与该像素邻域的各像素重合;将核内各值与相应像素值相乘,并将乘积相加;将所得结果放到与锚点对应的像素上;对图像所有像素重复上述过程。
用公式表示上述过程如下:
在图像边缘的卷积怎么办呢?
计算卷积前,需要通过复制源图像的边界创建虚拟像素,这样边缘的地方也有足够像素计算卷积了。这就是为什么上一篇文章需要做虚拟边缘函数。
均值平滑
均值平滑实际上就是内核元素全是1的卷积运算,然后再除以内核的大小,用数学表达式来表示就是:

下面我们来实现均值平滑函数blur:
function blur(__src, __size1, __size2, __borderType, __dst){
if(__src.type && __src.type == "CV_RGBA"){
var height = __src.row,
width = __src.col,
dst = __dst || new Mat(height, width, CV_RGBA),
dstData = dst.data;
var size1 = __size1 || 3,
size2 = __size2 || size1,
size = size1 * size2;
if(size1 % 2 !== 1 || size2 % 2 !== 1){
console.error("size大小必须是奇数");
return __src;
}
var startX = Math.floor(size1 / 2),
startY = Math.floor(size2 / 2);
var withBorderMat = copyMakeBorder(__src, startY, startX, 0, 0, __borderType),
mData = withBorderMat.data,
mWidth = withBorderMat.col;
var newValue, nowX, offsetY, offsetI;
var i, j, c, y, x;
for(i = height; i--;){
offsetI = i * width;
for(j = width; j--;){
for(c = 3; c--;){
newValue = 0;
for(y = size2; y--;){
offsetY = (y + i) * mWidth * 4;
for(x = size1; x--;){
nowX = (x + j) * 4 + c;
newValue += mData[offsetY + nowX];
}
}
dstData[(j + offsetI) * 4 + c] = newValue / size;
}
dstData[(j + offsetI) * 4 + 3] = mData[offsetY + startY * mWidth * 4 + (j + startX) * 4 + 3];
}
}
}else{
console.error("不支持类型。");
}
return dst;
}
其中size1和size2分别是核的横向和纵向大小,并且必须是正奇数。
高斯平滑
最有用的滤波器 (尽管不是最快的)。 高斯滤波是将输入数组的每一个像素点与高斯内核
卷积将卷积和当作输出像素值。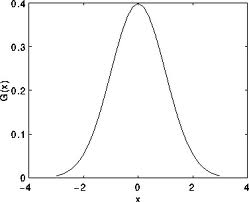
参考一维高斯函数,我们可以看见,他是个中间大两边小的函数。
所以高斯滤波器其加权数是中间大,四周小的。
其二维高斯函数为:
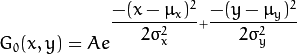
其中
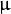 为均值 (峰值对应位置),
为均值 (峰值对应位置),
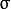 代表标准差 (变量
代表标准差 (变量
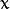 和 变量
和 变量
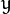 各有一个均值,也各有一个标准差)。
各有一个均值,也各有一个标准差)。
这里参考OpenCV的实现,不过应该还有优化空间,因为还没用到分离滤波器。
首先我们做一个getGaussianKernel来返回高斯滤波器的一维数组。
function getGaussianKernel(__n, __sigma){
var SMALL_GAUSSIAN_SIZE = 7,
smallGaussianTab = [[1],
[0.25, 0.5, 0.25],
[0.0625, 0.25, 0.375, 0.25, 0.0625],
[0.03125, 0.109375, 0.21875, 0.28125, 0.21875, 0.109375, 0.03125]
];
var fixedKernel = __n & 2 == 1 && __n > 1] : 0;
var sigmaX = __sigma > 0 ? __sigma : ((__n - 1) * 0.5 - 1) * 0.3 + 0.8,
scale2X = -0.5 / (sigmaX * sigmaX),
sum = 0;
var i, x, t, kernel = [];
for(i = 0; i x = i - (__n - 1) * 0.5;
t = fixedKernel ? fixedKernel[i] : Math.exp(scale2X * x * x);
kernel[i] = t;
sum += t;
}
sum = 1 / sum;
for(i = __n; i--;){
kernel[i] *= sum;
}
return kernel;
};
然后通过两个这个一维数组,便可以计算出一个完整的高斯内核,再利用blur里面用到的循环方法,就可以算出高斯平滑后的矩阵了。
function GaussianBlur(__src, __size1, __size2, __sigma1, __sigma2, __borderType, __dst){
if(__src.type && __src.type == "CV_RGBA"){
var height = __src.row,
width = __src.col,
dst = __dst || new Mat(height, width, CV_RGBA),
dstData = dst.data;
var sigma1 = __sigma1 || 0,
sigma2 = __sigma2 || __sigma1;
var size1 = __size1 || Math.round(sigma1 * 6 + 1) | 1,
size2 = __size2 || Math.round(sigma2 * 6 + 1) | 1,
size = size1 * size2;
if(size1 % 2 !== 1 || size2 % 2 !== 1){
console.error("size必须是奇数。");
return __src;
}
var startX = Math.floor(size1 / 2),
startY = Math.floor(size2 / 2);
var withBorderMat = copyMakeBorder(__src, startY, startX, 0, 0, __borderType),
mData = withBorderMat.data,
mWidth = withBorderMat.col;
var kernel1 = getGaussianKernel(size1, sigma1),
kernel2,
kernel = new Array(size1 * size2);
if(size1 === size2 && sigma1 === sigma2)
kernel2 = kernel1;
else
kernel2 = getGaussianKernel(size2, sigma2);
var i, j, c, y, x;
for(i = kernel2.length; i--;){
for(j = kernel1.length; j--;){
kernel[i * size1 + j] = kernel2[i] * kernel1[j];
}
}
var newValue, nowX, offsetY, offsetI;
for(i = height; i--;){
offsetI = i * width;
for(j = width; j--;){
for(c = 3; c--;){
newValue = 0;
for(y = size2; y--;){
offsetY = (y + i) * mWidth * 4;
for(x = size1; x--;){
nowX = (x + j) * 4 + c;
newValue += (mData[offsetY + nowX] * kernel[y * size1 + x]);
}
}
dstData[(j + offsetI) * 4 + c] = newValue;
}
dstData[(j + offsetI) * 4 + 3] = mData[offsetY + startY * mWidth * 4 + (j + startX) * 4 + 3];
}
}
}else{
console.error("不支持的类型");
}
return dst;
}
中值平滑
中值滤波将图像的每个像素用邻域 (以当前像素为中心的正方形区域)像素的
中值代替 。依然使用blur里面用到的循环,只要得到核中的所有值,再通过sort排序便可以得到中值,然后锚点由该值替代。
function medianBlur(__src, __size1, __size2, __borderType, __dst){
if(__src.type && __src.type == "CV_RGBA"){
var height = __src.row,
width = __src.col,
dst = __dst || new Mat(height, width, CV_RGBA),
dstData = dst.data;
var size1 = __size1 || 3,
size2 = __size2 || size1,
size = size1 * size2;
if(size1 % 2 !== 1 || size2 % 2 !== 1){
console.error("size必须是奇数");
return __src;
}
var startX = Math.floor(size1 / 2),
startY = Math.floor(size2 / 2);
var withBorderMat = copyMakeBorder(__src, startY, startX, 0, 0, __borderType),
mData = withBorderMat.data,
mWidth = withBorderMat.col;
var newValue = [], nowX, offsetY, offsetI;
var i, j, c, y, x;
for(i = height; i--;){
offsetI = i * width;
for(j = width; j--;){
for(c = 3; c--;){
for(y = size2; y--;){
offsetY = (y + i) * mWidth * 4;
for(x = size1; x--;){
nowX = (x + j) * 4 + c;
newValue[y * size1 + x] = mData[offsetY + nowX];
}
}
newValue.sort();
dstData[(j + offsetI) * 4 + c] = newValue[Math.round(size / 2)];
}
dstData[(j + offsetI) * 4 + 3] = mData[offsetY + startY * mWidth * 4 + (j + startX) * 4 + 3];
}
}
}else{
console.error("类型不支持");
}
return dst;
};

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

Video Face Swap
Échangez les visages dans n'importe quelle vidéo sans effort grâce à notre outil d'échange de visage AI entièrement gratuit !

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
 Comment la distance de Wasserstein est-elle utilisée dans les tâches de traitement d'images ?
Jan 23, 2024 am 10:39 AM
Comment la distance de Wasserstein est-elle utilisée dans les tâches de traitement d'images ?
Jan 23, 2024 am 10:39 AM
La distance de Wasserstein, également connue sous le nom de distance de EarthMover (EMD), est une mesure utilisée pour mesurer la différence entre deux distributions de probabilité. Par rapport à la divergence KL ou à la divergence JS traditionnelle, la distance de Wasserstein prend en compte les informations structurelles entre les distributions et présente donc de meilleures performances dans de nombreuses tâches de traitement d'image. En calculant le coût minimum de transport entre deux distributions, la distance de Wasserstein permet de mesurer la quantité minimale de travail nécessaire pour transformer une distribution en une autre. Cette métrique est capable de capturer les différences géométriques entre les distributions, jouant ainsi un rôle important dans des tâches telles que la génération d'images et le transfert de style. Par conséquent, la distance de Wasserstein devient le concept
 Analyse approfondie des principes de fonctionnement et des caractéristiques du modèle Vision Transformer (VIT)
Jan 23, 2024 am 08:30 AM
Analyse approfondie des principes de fonctionnement et des caractéristiques du modèle Vision Transformer (VIT)
Jan 23, 2024 am 08:30 AM
VisionTransformer (VIT) est un modèle de classification d'images basé sur Transformer proposé par Google. Contrairement aux modèles CNN traditionnels, VIT représente les images sous forme de séquences et apprend la structure de l'image en prédisant l'étiquette de classe de l'image. Pour y parvenir, VIT divise l'image d'entrée en plusieurs patchs et concatène les pixels de chaque patch via des canaux, puis effectue une projection linéaire pour obtenir les dimensions d'entrée souhaitées. Enfin, chaque patch est aplati en un seul vecteur, formant la séquence d'entrée. Grâce au mécanisme d'auto-attention de Transformer, VIT est capable de capturer la relation entre les différents correctifs et d'effectuer une extraction efficace des fonctionnalités et une prédiction de classification. Cette représentation d'image sérialisée est
 Application de la technologie de l'IA à la reconstruction d'images en super-résolution
Jan 23, 2024 am 08:06 AM
Application de la technologie de l'IA à la reconstruction d'images en super-résolution
Jan 23, 2024 am 08:06 AM
La reconstruction d'images en super-résolution est le processus de génération d'images haute résolution à partir d'images basse résolution à l'aide de techniques d'apprentissage en profondeur, telles que les réseaux neuronaux convolutifs (CNN) et les réseaux contradictoires génératifs (GAN). Le but de cette méthode est d'améliorer la qualité et les détails des images en convertissant des images basse résolution en images haute résolution. Cette technologie trouve de nombreuses applications dans de nombreux domaines, comme l’imagerie médicale, les caméras de surveillance, les images satellites, etc. Grâce à la reconstruction d’images en super-résolution, nous pouvons obtenir des images plus claires et plus détaillées, ce qui permet d’analyser et d’identifier plus précisément les cibles et les caractéristiques des images. Méthodes de reconstruction Les méthodes de reconstruction d'images en super-résolution peuvent généralement être divisées en deux catégories : les méthodes basées sur l'interpolation et les méthodes basées sur l'apprentissage profond. 1) Méthode basée sur l'interpolation Reconstruction d'images en super-résolution basée sur l'interpolation
 Comment gérer les problèmes de traitement d'image et de conception d'interface graphique dans le développement C#
Oct 08, 2023 pm 07:06 PM
Comment gérer les problèmes de traitement d'image et de conception d'interface graphique dans le développement C#
Oct 08, 2023 pm 07:06 PM
Comment gérer les problèmes de traitement d'image et de conception d'interface graphique dans le développement C# nécessite des exemples de code spécifiques Introduction : Dans le développement de logiciels modernes, le traitement d'image et la conception d'interface graphique sont des exigences courantes. En tant que langage de programmation généraliste de haut niveau, C# possède de puissantes capacités de traitement d’images et de conception d’interface graphique. Cet article sera basé sur C#, expliquera comment gérer les problèmes de traitement d'image et de conception d'interface graphique, et donnera des exemples de code détaillés. 1. Problèmes de traitement d'image : Lecture et affichage d'images : En C#, la lecture et l'affichage d'images sont des opérations de base. Peut être utilisé.N
 Développement Java : comment implémenter la reconnaissance et le traitement d'images
Sep 21, 2023 am 08:39 AM
Développement Java : comment implémenter la reconnaissance et le traitement d'images
Sep 21, 2023 am 08:39 AM
Développement Java : Un guide pratique sur la reconnaissance et le traitement d'images Résumé : Avec le développement rapide de la vision par ordinateur et de l'intelligence artificielle, la reconnaissance et le traitement d'images jouent un rôle important dans divers domaines. Cet article expliquera comment utiliser le langage Java pour implémenter la reconnaissance et le traitement d'images, et fournira des exemples de code spécifiques. 1. Principes de base de la reconnaissance d'images La reconnaissance d'images fait référence à l'utilisation de la technologie informatique pour analyser et comprendre des images afin d'identifier des objets, des caractéristiques ou du contenu dans l'image. Avant d'effectuer la reconnaissance d'image, nous devons comprendre certaines techniques de base de traitement d'image, comme le montre la figure
 Comment utiliser la technologie IA pour restaurer d'anciennes photos (avec exemples et analyse de code)
Jan 24, 2024 pm 09:57 PM
Comment utiliser la technologie IA pour restaurer d'anciennes photos (avec exemples et analyse de code)
Jan 24, 2024 pm 09:57 PM
La restauration de photos anciennes est une méthode d'utilisation de la technologie de l'intelligence artificielle pour réparer, améliorer et améliorer de vieilles photos. Grâce à des algorithmes de vision par ordinateur et d’apprentissage automatique, la technologie peut identifier et réparer automatiquement les dommages et les imperfections des anciennes photos, les rendant ainsi plus claires, plus naturelles et plus réalistes. Les principes techniques de la restauration de photos anciennes incluent principalement les aspects suivants : 1. Débruitage et amélioration de l'image Lors de la restauration de photos anciennes, elles doivent d'abord être débruitées et améliorées. Des algorithmes et des filtres de traitement d'image, tels que le filtrage moyen, le filtrage gaussien, le filtrage bilatéral, etc., peuvent être utilisés pour résoudre les problèmes de bruit et de taches de couleur, améliorant ainsi la qualité des photos. 2. Restauration et réparation d'images Les anciennes photos peuvent présenter certains défauts et dommages, tels que des rayures, des fissures, une décoloration, etc. Ces problèmes peuvent être résolus par des algorithmes de restauration et de réparation d’images
 Notes d'étude PHP : reconnaissance faciale et traitement d'images
Oct 08, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Notes d'étude PHP : reconnaissance faciale et traitement d'images
Oct 08, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Notes d'étude PHP : Reconnaissance faciale et traitement d'images Préface : Avec le développement de la technologie de l'intelligence artificielle, la reconnaissance faciale et le traitement d'images sont devenus des sujets brûlants. Dans les applications pratiques, la reconnaissance faciale et le traitement d'images sont principalement utilisés dans la surveillance de la sécurité, le déverrouillage facial, la comparaison de cartes, etc. En tant que langage de script côté serveur couramment utilisé, PHP peut également être utilisé pour implémenter des fonctions liées à la reconnaissance faciale et au traitement d'images. Cet article vous présentera la reconnaissance faciale et le traitement d'images en PHP, avec des exemples de code spécifiques. 1. Reconnaissance faciale en PHP La reconnaissance faciale est un
 Algorithme SIFT (Scale Invariant Features)
Jan 22, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
Algorithme SIFT (Scale Invariant Features)
Jan 22, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
L'algorithme SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) est un algorithme d'extraction de caractéristiques utilisé dans les domaines du traitement d'images et de la vision par ordinateur. Cet algorithme a été proposé en 1999 pour améliorer les performances de reconnaissance et de correspondance d'objets dans les systèmes de vision par ordinateur. L'algorithme SIFT est robuste et précis et est largement utilisé dans la reconnaissance d'images, la reconstruction tridimensionnelle, la détection de cibles, le suivi vidéo et d'autres domaines. Il obtient l'invariance d'échelle en détectant les points clés dans plusieurs espaces d'échelle et en extrayant des descripteurs de caractéristiques locales autour des points clés. Les principales étapes de l'algorithme SIFT comprennent la construction d'un espace d'échelle, la détection des points clés, le positionnement des points clés, l'attribution de directions et la génération de descripteurs de caractéristiques. Grâce à ces étapes, l’algorithme SIFT peut extraire des fonctionnalités robustes et uniques, permettant ainsi un traitement d’image efficace.




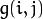 )是输入像素值(例如:
)是输入像素值(例如: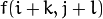 )的加权平均:
)的加权平均:
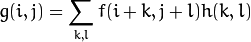
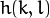 称为核
称为核