Nginx高级数据结构源码分析(二)-----动态数组
ngx_array_t是一个顺序容器,它在Nginx中被大量使用。它以数组的形式存储元素,并支持在达到数组容量的上限动态时改变数组的大小。它类似于C++中的vector容器,而且内置了Nginx封装的内存池,因此,它分配的内存也是在内存池中申请得到。
ngx_array_t具备以下三个优点;
(1)访问速度快;
(2)允许元素个数具备不确定性;
(3)负责元素占用内存的分配,这些内存将有内存池统一管理。
动态数组的扩容方式有两种:
(1)如果当前内存池中剩余的空间大于或者等于本次需要新增的空间,那么本次扩容将只扩充新增的空间。
(2)如果当前内存池中剩余的空间小于本次需要新增的空间,那么对ngx_array_push方法来说,会将原先动态数组的容量扩容一倍,而对于ngx_array_push_n来说,扩容多少则根据参数与原先动态数组的容量来决定。
动态数组的结构体:
typedef struct {
void *elts;//首地址
ngx_uint_t nelts;//已使用的元素个数
size_t size;//每个数组元素占用的内存大小
ngx_uint_t nalloc;//可以容纳元素的个数的总大小
ngx_pool_t *pool;//内存池对象
} ngx_array_t;
static ngx_inline ngx_int_t
ngx_array_init(ngx_array_t *array, ngx_pool_t *pool, ngx_uint_t n, size_t size)//初始化数组
{
/*
* set "array->nelts" before "array->elts", otherwise MSVC thinks
* that "array->nelts" may be used without having been initialized
*/
array->nelts = 0; //首地址为0
array->size = size; //每个元素所占内存大小
array->nalloc = n; //分配的元素个数
array->pool = pool; //内存池对象
//申请n*size这么大的内存空间
array->elts = ngx_palloc(pool, n * size);
if (array->elts == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
return NGX_OK;
}
ngx_array_t *
ngx_array_create(ngx_pool_t *p, ngx_uint_t n, size_t size)//创建数组
{
ngx_array_t *a;
a = ngx_palloc(p, sizeof(ngx_array_t));//申请数组本身的内存
if (a == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (ngx_array_init(a, p, n, size) != NGX_OK) {//初始化,即申请可以存储元素的内存
return NULL;
}
return a;
}
void
ngx_array_destroy(ngx_array_t *a)//销毁数组
{
ngx_pool_t *p;
p = a->pool;
if ((u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nalloc == p->d.last) {//释放存放元素的内存。为什么要判断呢???
p->d.last -= a->size * a->nalloc;
}
if ((u_char *) a + sizeof(ngx_array_t) == p->d.last) {//释放节点内存/为什么要判断呢???
p->d.last = (u_char *) a;
}
}<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>
void *
ngx_array_push(ngx_array_t *a)
{
void *elt, *new;
size_t size;
ngx_pool_t *p;
if (a->nelts == a->nalloc) {//若数组满了则。。。
/* the array is full */
size = a->size * a->nalloc;
p = a->pool;
if ((u_char *) a->elts + size == p->d.last//为什么又加这个等号判断:??????
&& p->d.last + a->size d.end)//如果这个内存池节点还有空余内存
{
/*
* the array allocation is the last in the pool
* and there is space for new allocation
*/
p->d.last += a->size;
a->nalloc++;
} else { //没有则重新申请一块两倍大小的内存
/* allocate a new array */
new = ngx_palloc(p, 2 * size);
if (new == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ngx_memcpy(new, a->elts, size);//将原来数组元素复制到新的内存空间
a->elts = new;
a->nalloc *= 2;
}
}
elt = (u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nelts; //添加新元素
a->nelts++;
return elt;
}
void *
ngx_array_push_n(ngx_array_t *a, ngx_uint_t n)//加入n个元素
{
void *elt, *new;
size_t size;
ngx_uint_t nalloc;
ngx_pool_t *p;
size = n * a->size;
if (a->nelts + n > a->nalloc) {//如果加在一起的个数大于数组元素个数
/* the array is full */
p = a->pool;
if ((u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nalloc == p->d.last//等号仍然不知到为什么要判断????
&& p->d.last + size d.end) //若内存池节点剩余内存可以存放加入的元素
{
/*
* the array allocation is the last in the pool
* and there is space for new allocation
*/
p->d.last += size;
a->nalloc += n;
} else {
/* allocate a new array */
nalloc = 2 * ((n >= a->nalloc) ? n : a->nalloc);//在加入的元素个数和原来数组可存放的元素个数中选择比较大的那个乘以2
new = ngx_palloc(p, nalloc * a->size);//申请内存
if (new == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ngx_memcpy(new, a->elts, a->nelts * a->size);//复制原来的元素
a->elts = new; //更新两个变量
a->nalloc = nalloc;
}
}
elt = (u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nelts; //可存放元素的内存起始地址
a->nelts += n; //更新
return elt;
}版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
以上就介绍了Nginx高级数据结构源码分析(二)-----动态数组,包括了方面的内容,希望对PHP教程有兴趣的朋友有所帮助。

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

AI Hentai Generator
Générez AI Hentai gratuitement.

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)
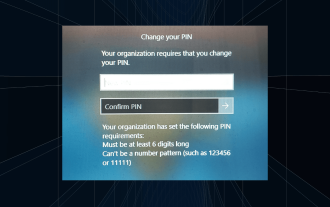 Solution : Votre organisation vous demande de modifier votre code PIN
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
Solution : Votre organisation vous demande de modifier votre code PIN
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
Le message « Votre organisation vous a demandé de modifier votre code PIN » apparaîtra sur l'écran de connexion. Cela se produit lorsque la limite d'expiration du code PIN est atteinte sur un ordinateur utilisant les paramètres de compte basés sur l'organisation, sur lesquels ils contrôlent les appareils personnels. Cependant, si vous configurez Windows à l'aide d'un compte personnel, le message d'erreur ne devrait idéalement pas apparaître. Même si ce n'est pas toujours le cas. La plupart des utilisateurs qui rencontrent des erreurs déclarent utiliser leur compte personnel. Pourquoi mon organisation me demande-t-elle de modifier mon code PIN sous Windows 11 ? Il est possible que votre compte soit associé à une organisation et votre approche principale devrait être de le vérifier. Contacter votre administrateur de domaine peut vous aider ! De plus, des paramètres de stratégie locale mal configurés ou des clés de registre incorrectes peuvent provoquer des erreurs. Tout de suite
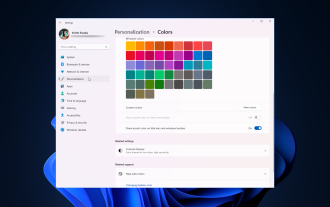 Comment ajuster les paramètres de bordure de fenêtre sous Windows 11 : modifier la couleur et la taille
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Comment ajuster les paramètres de bordure de fenêtre sous Windows 11 : modifier la couleur et la taille
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Windows 11 met au premier plan un design frais et élégant ; l'interface moderne vous permet de personnaliser et de modifier les moindres détails, tels que les bordures des fenêtres. Dans ce guide, nous discuterons des instructions étape par étape pour vous aider à créer un environnement qui reflète votre style dans le système d'exploitation Windows. Comment modifier les paramètres de bordure de fenêtre ? Appuyez sur + pour ouvrir l'application Paramètres. WindowsJe vais dans Personnalisation et clique sur Paramètres de couleur. Changement de couleur Paramètres des bordures de fenêtre Fenêtre 11" Largeur = "643" Hauteur = "500" > Recherchez l'option Afficher la couleur d'accent sur la barre de titre et les bordures de fenêtre et activez le commutateur à côté. Pour afficher les couleurs d'accent dans le menu Démarrer et la barre des tâches Pour afficher la couleur du thème dans le menu Démarrer et la barre des tâches, activez Afficher le thème dans le menu Démarrer et la barre des tâches.
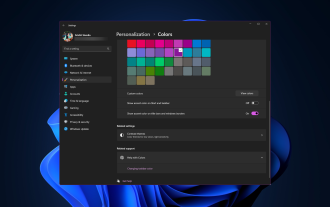 Comment changer la couleur de la barre de titre sous Windows 11 ?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Comment changer la couleur de la barre de titre sous Windows 11 ?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Par défaut, la couleur de la barre de titre sous Windows 11 dépend du thème sombre/clair que vous choisissez. Cependant, vous pouvez le changer pour la couleur de votre choix. Dans ce guide, nous discuterons des instructions étape par étape sur trois façons de le modifier et de personnaliser votre expérience de bureau pour la rendre visuellement attrayante. Est-il possible de changer la couleur de la barre de titre des fenêtres actives et inactives ? Oui, vous pouvez modifier la couleur de la barre de titre des fenêtres actives à l'aide de l'application Paramètres, ou vous pouvez modifier la couleur de la barre de titre des fenêtres inactives à l'aide de l'Éditeur du Registre. Pour connaître ces étapes, passez à la section suivante. Comment changer la couleur de la barre de titre sous Windows 11 ? 1. Appuyez sur + pour ouvrir la fenêtre des paramètres à l'aide de l'application Paramètres. WindowsJe vais dans "Personnalisation" puis
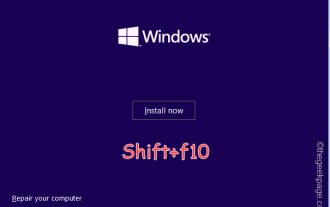 Problèmes d'erreur OOBELANGUAGE dans la réparation de Windows 11/10
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
Problèmes d'erreur OOBELANGUAGE dans la réparation de Windows 11/10
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
Voyez-vous « Un problème est survenu » avec l'instruction « OOBELANGUAGE » sur la page Windows Installer ? L'installation de Windows s'arrête parfois à cause de telles erreurs. OOBE signifie expérience hors des sentiers battus. Comme l'indique le message d'erreur, il s'agit d'un problème lié à la sélection de la langue OOBE. Il n'y a rien à craindre, vous pouvez résoudre ce problème avec une astucieuse modification du registre à partir de l'écran OOBE lui-même. Solution rapide – 1. Cliquez sur le bouton « Réessayer » en bas de l'application OOBE. Cela permettra de poursuivre le processus sans autre problème. 2. Utilisez le bouton d'alimentation pour forcer l'arrêt du système. Après le redémarrage du système, OOBE devrait continuer. 3. Déconnectez le système d'Internet. Terminez tous les aspects d'OOBE en mode hors ligne
 Comment activer ou désactiver les aperçus miniatures de la barre des tâches sur Windows 11
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Comment activer ou désactiver les aperçus miniatures de la barre des tâches sur Windows 11
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Les miniatures de la barre des tâches peuvent être amusantes, mais elles peuvent aussi être distrayantes ou ennuyeuses. Compte tenu de la fréquence à laquelle vous survolez cette zone, vous avez peut-être fermé plusieurs fois des fenêtres importantes par inadvertance. Un autre inconvénient est qu'il utilise plus de ressources système, donc si vous cherchez un moyen d'être plus efficace en termes de ressources, nous allons vous montrer comment le désactiver. Cependant, si vos spécifications matérielles peuvent le gérer et que vous aimez l'aperçu, vous pouvez l'activer. Comment activer l’aperçu miniature de la barre des tâches dans Windows 11 ? 1. Utilisez l'application Paramètres pour appuyer sur la touche et cliquez sur Paramètres. Windows, cliquez sur Système et sélectionnez À propos. Cliquez sur Paramètres système avancés. Accédez à l'onglet Avancé et sélectionnez Paramètres sous Performances. Sélectionnez "Effets visuels"
 Afficher le guide de mise à l'échelle sur Windows 11
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Afficher le guide de mise à l'échelle sur Windows 11
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Nous avons tous des préférences différentes en matière de mise à l'échelle de l'affichage sur Windows 11. Certaines personnes aiment les grandes icônes, d’autres les petites. Cependant, nous sommes tous d’accord sur le fait qu’il est important d’avoir la bonne échelle. Une mauvaise mise à l'échelle des polices ou une mise à l'échelle excessive des images peuvent nuire à la productivité lorsque vous travaillez. Vous devez donc savoir comment la personnaliser pour tirer le meilleur parti des capacités de votre système. Avantages du zoom personnalisé : Il s'agit d'une fonctionnalité utile pour les personnes qui ont des difficultés à lire du texte à l'écran. Cela vous aide à voir plus sur l’écran à la fois. Vous pouvez créer des profils d'extension personnalisés qui s'appliquent uniquement à certains moniteurs et applications. Peut aider à améliorer les performances du matériel bas de gamme. Cela vous donne plus de contrôle sur ce qui est sur votre écran. Comment utiliser Windows 11
 Quelles sont les différences entre Huawei GT3 Pro et GT4 ?
Dec 29, 2023 pm 02:27 PM
Quelles sont les différences entre Huawei GT3 Pro et GT4 ?
Dec 29, 2023 pm 02:27 PM
De nombreux utilisateurs choisiront la marque Huawei lors du choix des montres intelligentes. Parmi eux, les Huawei GT3pro et GT4 sont des choix très populaires. De nombreux utilisateurs sont curieux de connaître la différence entre Huawei GT3pro et GT4. Quelles sont les différences entre Huawei GT3pro et GT4 ? 1. Apparence GT4 : 46 mm et 41 mm, le matériau est un miroir en verre + un corps en acier inoxydable + une coque arrière en fibre haute résolution. GT3pro : 46,6 mm et 42,9 mm, le matériau est du verre saphir + corps en titane/corps en céramique + coque arrière en céramique 2. GT4 sain : en utilisant le dernier algorithme Huawei Truseen5.5+, les résultats seront plus précis. GT3pro : ajout d'un électrocardiogramme ECG, d'un vaisseau sanguin et de la sécurité
 10 façons de régler la luminosité sous Windows 11
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
10 façons de régler la luminosité sous Windows 11
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
La luminosité de l’écran fait partie intégrante de l’utilisation des appareils informatiques modernes, en particulier lorsque vous regardez l’écran pendant de longues périodes. Il vous aide à réduire la fatigue oculaire, à améliorer la lisibilité et à visualiser le contenu facilement et efficacement. Cependant, en fonction de vos paramètres, il peut parfois être difficile de gérer la luminosité, notamment sous Windows 11 avec les nouvelles modifications de l'interface utilisateur. Si vous rencontrez des difficultés pour régler la luminosité, voici toutes les manières de gérer la luminosité sous Windows 11. Comment modifier la luminosité sous Windows 11 [10 méthodes expliquées] Les utilisateurs d'un seul moniteur peuvent utiliser les méthodes suivantes pour régler la luminosité sous Windows 11. Cela inclut les systèmes de bureau utilisant un seul moniteur ainsi que les ordinateurs portables. Commençons. Méthode 1 : Utiliser le Centre d'action Le Centre d'action est accessible






