Android单元测试与模拟测试详解
测试与基本规范
为什么需要测试?
为了稳定性,能够明确的了解是否正确的完成开发。
更加易于维护,能够在修改代码后保证功能不被破坏。
集成一些工具,规范开发规范,使得代码更加稳定( 如通过 phabricator differential 发diff时提交需要执行的单元测试,在开发流程上就可以保证远端代码的稳定性)。
2. 测什么?
一般单元测试:
列出想要测试覆盖的异常情况,进行验证。
性能测试。
模拟测试: 根据需求,测试用户真正在使用过程中,界面的反馈与显示以及一些依赖系统架构的组件的应用测试。
3. 需要注意
考虑可读性,对于方法名使用表达能力强的方法名,对于测试范式可以考虑使用一种规范, 如 RSpec-style。方法名可以采用一种格式,如: [测试的方法]_[测试的条件]_[符合预期的结果]。
不要使用逻辑流关键字(If/else、for、do/while、switch/case),在一个测试方法中,如果需要有这些,拆分到单独的每个测试方法里。
测试真正需要测试的内容,需要覆盖的情况,一般情况只考虑验证输出(如某操作后,显示什么,值是什么)。
考虑耗时,Android Studio默认会输出耗时。
不需要考虑测试private的方法,将private方法当做黑盒内部组件,测试对其引用的public方法即可;不考虑测试琐碎的代码,如getter或者setter。
每个单元测试方法,应没有先后顺序;尽可能的解耦对于不同的测试方法,不应该存在Test A与Test B存在时序性的情况。
4. 创建测试
选择对应的类
将光标停留在类名上
按下ALT + ENTER
在弹出的弹窗中选择Create Test
Android Studio中的单元测试与模拟测试
control + shift + R (Android Studio 默认执行单元测试快捷键)。
1. 本地单元测试
直接在开发机上面进行运行测试。
在没有依赖或者仅仅只需要简单的Android库依赖的情况下,有限考虑使用该类单元测试。
./gradlew check
(1)代码存储
如果是对应不同的flavor或者是build type,直接在test后面加上对应后缀(如对应名为myFlavor的单元测试代码,应该放在src/testMyFlavor/java下面)。
src/test/java
(2)Google官方推荐引用
dependencies {
// Required -- JUnit 4 framework,用于单元测试,google官方推荐
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
// Optional -- Mockito framework,用于模拟架构,google官方推荐
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1546.html
testCompile 'org.mockito:mockito-core:1.10.19'
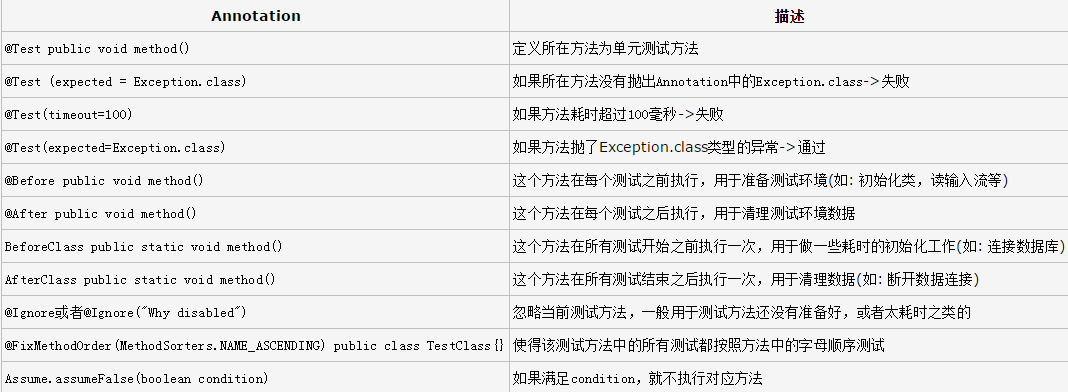
}(3)JUnit
Annotation
2. 模拟测试
需要运行在Android设备或者虚拟机上的测试。
主要用于测试: 单元(Android SDK层引用关系的相关的单元测试)、UI、应用组件集成测试(Service、Content Provider等)。
./gradlew connectedAndroidTest
(1)代码存储:
src/androidTest/java
(2)Google官方推荐引用
dependencies {
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support:support-annotations:23.0.1'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:runner:0.4.1'
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:rules:0.4.1'
// Optional -- Hamcrest library
androidTestCompile 'org.hamcrest:hamcrest-library:1.3'
// Optional -- UI testing with Espresso
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1546.html
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.1'
// Optional -- UI testing with UI Automator
androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.uiautomator:uiautomator-v18:2.1.1'
}(3)常见的UI测试
需要模拟Android系统环境。
主要三点:
UI加载好后展示的信息是否正确。
在用户某个操作后UI信息是否展示正确。
展示正确的页面供用户操作。
(4)Espresso
谷歌官方提供用于UI交互测试
import static android.support.test.espresso.Espresso.onView;
import static android.support.test.espresso.action.ViewActions.click;
import static android.support.test.espresso.assertion.ViewAssertions.matches;
import static android.support.test.espresso.matcher.ViewMatchers.isDisplayed;
import static android.support.test.espresso.matcher.ViewMatchers.withId;
// 对于Id为R.id.my_view的View: 触发点击,检测是否显示
onView(withId(R.id.my_view)).perform(click())
.check(matches(isDisplayed()));
// 对于文本打头是"ABC"的View: 检测是否没有Enable
onView(withText(startsWith("ABC"))).check(matches(not(isEnabled()));
// 按返回键
pressBack();
// 对于Id为R.id.button的View: 检测内容是否是"Start new activity"
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1537.html
onView(withId(R.id.button)).check(matches(withText(("Start new activity"))));
// 对于Id为R.id.viewId的View: 检测内容是否不包含"YYZZ"
onView(withId(R.id.viewId)).check(matches(withText(not(containsString("YYZZ")))));
// 对于Id为R.id.inputField的View: 输入"NewText",然后关闭软键盘
onView(withId(R.id.inputField)).perform(typeText("NewText"), closeSoftKeyboard());
// 对于Id为R.id.inputField的View: 清除内容
onView(withId(R.id.inputField)).perform(clearText());启动一个打开Activity的Intent
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
public class SecondActivityTest {
@Rule
public ActivityTestRule<SecondActivity> rule =
new ActivityTestRule(SecondActivity.class, true,
// 这个参数为false,不让SecondActivity自动启动
// 如果为true,将会在所有@Before之前启动,在最后一个@After之后关闭
false);
@Test
public void demonstrateIntentPrep() {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.putExtra("EXTRA", "Test");
// 启动SecondActivity并传入intent
rule.launchActivity(intent);
// 对于Id为R.id.display的View: 检测内容是否是"Text"
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1532.html
onView(withId(R.id.display)).check(matches(withText("Test")));
}
}(5)异步交互
建议关闭设备中”设置->开发者选项中”的动画,因为这些动画可能会是的Espresso在检测异步任务的时候产生混淆: 窗口动画缩放(Window animation scale)、过渡动画缩放(Transition animation scale)、动画程序时长缩放(Animator duration scale)。
针对AsyncTask,在测试的时候,如触发点击事件以后抛了一个AsyncTask任务,在测试的时候直接onView(withId(R.id.update)).perform(click()),然后直接进行检测,此时的检测就是在AsyncTask#onPostExecute之后。
// 通过实现IdlingResource,block住当非空闲的时候,当空闲时进行检测,非空闲的这段时间处理异步事情
public class IntentServiceIdlingResource implements IdlingResource {
ResourceCallback resourceCallback;
private Context context;
public IntentServiceIdlingResource(Context context) { this.context = context; }
@Override public String getName() { return IntentServiceIdlingResource.class.getName(); }
@Override public void registerIdleTransitionCallback( ResourceCallback resourceCallback) { this.resourceCallback = resourceCallback; }
@Override public boolean isIdleNow() {
// 是否是空闲
// 如果IntentService 没有在运行,就说明异步任务结束,IntentService特质就是启动以后处理完Intent中的事务,理解关闭自己
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1531.html
boolean idle = !isIntentServiceRunning();
if (idle && resourceCallback != null) {
// 回调告知异步任务结束
resourceCallback.onTransitionToIdle();
}
return idle;
}
private boolean isIntentServiceRunning() {
ActivityManager manager = (ActivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
// Get all running services
List<ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo> runningServices = manager.getRunningServices(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// check if our is running
for (ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo info : runningServices) {
if (MyIntentService.class.getName().equals(info.service.getClassName())) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
// 使用IntentServiceIdlingResource来测试,MyIntentService服务启动结束这个异步事务,之后的结果。
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
public class IntegrationTest {
@Rule
public ActivityTestRule rule = new ActivityTestRule(MainActivity.class);
IntentServiceIdlingResource idlingResource;
@Before
public void before() {
Instrumentation instrumentation = InstrumentationRegistry.getInstrumentation();
Context ctx = instrumentation.getTargetContext();
idlingResource = new IntentServiceIdlingResource(ctx);
// 注册这个异步监听
Espresso.registerIdlingResources(idlingResource);
}
@After
public void after() {
// 取消注册这个异步监听
Espresso.unregisterIdlingResources(idlingResource);
}
@Test
public void runSequence() {
// MainActivity中点击R.id.action_settings这个View的时候,会启动MyIntentService
onView(withId(R.id.action_settings)).perform(click());
// 这时候IntentServiceIdlingResource#isIdleNow会返回false,因为MyIntentService服务启动了
// 这个情况下,这里会block住.............
// 直到IntentServiceIdlingResource#isIdleNow返回true,并且回调了IntentServiceIdlingResource#onTransitionToIdle
// 这个情况下,继续执行,这时我们就可以测试异步结束以后的情况了。
onView(withText("Broadcast")).check(matches(notNullValue()));
}
}(6)自定义匹配器
// 定义
public static Matcher<View> withItemHint(String itemHintText) {
checkArgument(!(itemHintText.equals(null)));
return withItemHint(is(itemHintText));
}
public static Matcher<View> withItemHint(final Matcher<String> matcherText) {
checkNotNull(matcherText);
return new BoundedMatcher<View, EditText>(EditText.class) {
@Override
public void describeTo(Description description) {
description.appendText("with item hint: " + matcherText);
}
@Override
protected boolean matchesSafely(EditText editTextField) {
// 取出hint,然后比对下是否相同
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1524.html
return matcherText.matches(editTextField.getHint().toString());
}
};
}
// 使用
onView(withItemHint("test")).check(matches(isDisplayed()));拓展工具
1. AssertJ Android
square/assertj-android
极大的提高可读性。
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
// 断言: view是GONE的
assertThat(view).isGone();
MyClass test = new MyClass("Frodo");
MyClass test1 = new MyClass("Sauron");
MyClass test2 = new MyClass("Jacks");
List<MyClass> testList = new ArrayList<>();
testList.add(test);
testList.add(test1);
// 断言: test.getName()等于"Frodo"
assertThat(test.getName()).isEqualTo("Frodo");
// 断言: test不等于test1并且在testList中
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1519.html
assertThat(test).isNotEqualTo(test1)
.isIn(testList);
// 断言: test.getName()的字符串,是由"Fro"打头,以"do"结尾,忽略大小写会等于"frodo"
assertThat(test.getName()).startsWith("Fro")
.endsWith("do")
.isEqualToIgnoringCase("frodo");
// 断言: testList有2个数据,包含test,test1,不包含test2
assertThat(list).hasSize(2)
.contains(test, test1)
.doesNotContain(test2);
// 断言: 提取testList队列中所有数据中的成员变量名为name的变量,并且包含name为"Frodo"与"Sauron"
// 并且不包含name为"Jacks"
assertThat(testList).extracting("name")
.contains("Frodo", "Sauron")
.doesNotContain("Jacks");2. Hamcrest
JavaHamcrest
通过已有的通配方法,快速的对代码条件进行测试
org.hamcrest:hamcrest-junit:(version)
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
// 断言: a等于b
assertThat(a, equalTo(b));
assertThat(a, is(equalTo(b)));
assertThat(a, is(b));
// 断言: a不等于b
assertThat(actual, is(not(equalTo(b))));
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(5, 2, 4);
// 断言: list有3个数据
assertThat(list, hasSize(3));
// 断言: list中有5,2,4,并且顺序也一致
assertThat(list, contains(5, 2, 4));
// 断言: list中包含5,2,4
assertThat(list, containsInAnyOrder(2, 4, 5));
// 断言: list中的每一个数据都大于1
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1507.html
assertThat(list, everyItem(greaterThan(1)));
// 断言: fellowship中包含有成员变量"race",并且其值不是ORC
assertThat(fellowship, everyItem(hasProperty("race", is(not((ORC))))));
// 断言: object1中与object2相同的成员变量都是相同的值
assertThat(object1, samePropertyValuesAs(object2));
Integer[] ints = new Integer[] { 7, 5, 12, 16 };
// 断言: 数组中包含7,5,12,16
assertThat(ints, arrayContaining(7, 5, 12, 16));(1)几个主要的匹配器:
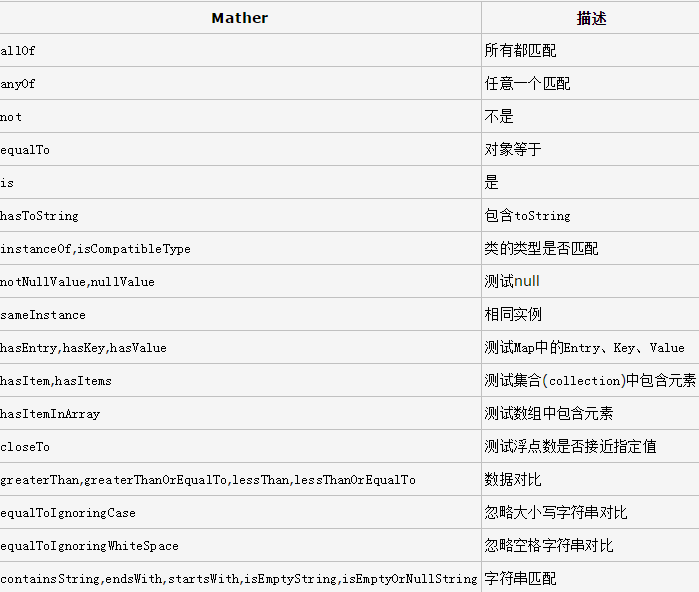
(2)自定义匹配器
// 自定义
import org.hamcrest.Description;
import org.hamcrest.TypeSafeMatcher;
public class RegexMatcher extends TypeSafeMatcher<String> {
private final String regex;
public RegexMatcher(final String regex) { this.regex = regex; }
@Override
public void describeTo(final Description description) { description.appendText("matches regular expression=`" + regex + "`"); }
@Override
public boolean matchesSafely(final String string) { return string.matches(regex); }
// 上层调用的入口
public static RegexMatcher matchesRegex(final String regex) {
return new RegexMatcher(regex);
}
}
// 使用
String s = "aaabbbaaa";
assertThat(s, RegexMatcher.matchesRegex("a*b*a"));3. Mockito
Mockito
Mock对象,控制其返回值,监控其方法的调用。
org.mockito:mockito-all:(version)
// import如相关类
import static org.mockito.Mockito.mock;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.verify;
// 创建一个Mock的对象
MyClass test = mock(MyClass.class);
// 当调用test.getUniqueId()的时候返回43
when(test.getUniqueId()).thenReturn(43);
// 当调用test.compareTo()传入任意的Int值都返回43
when(test.compareTo(anyInt())).thenReturn(43);
// 当调用test.compareTo()传入的是Target.class类型对象时返回43
when(test.compareTo(isA(Target.class))).thenReturn(43);
// 当调用test.close()的时候,抛IOException异常
doThrow(new IOException()).when(test).close();
// 当调用test.execute()的时候,什么都不做
doNothing().when(test).execute();
// 验证是否调用了两次test.getUniqueId()
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1503.html
verify(test, times(2)).getUniqueId();
// 验证是否没有调用过test.getUniqueId()
verify(test, never()).getUniqueId();
// 验证是否至少调用过两次test.getUniqueId()
verify(test, atLeast(2)).getUniqueId();
// 验证是否最多调用过三次test.getUniqueId()
verify(test, atMost(3)).getUniqueId();
// 验证是否这样调用过:test.query("test string")
verify(test).query("test string");
// 通过Mockito.spy() 封装List对象并返回将其mock的spy对象
List list = new LinkedList();
List spy = spy(list);
// 指定spy.get(0)返回"foo"
doReturn("foo").when(spy).get(0);
assertEquals("foo", spy.get(0));对访问方法时,传入参数进行快照
import org.mockito.ArgumentCaptor;
import org.mockito.Captor;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
@Captor
private ArgumentCaptor<Integer> captor;
@Test
public void testCapture(){
MyClass test = mock(MyClass.class);
test.compareTo(3, 4);
verify(test).compareTo(captor.capture(), eq(4));
assertEquals(3, (int)captor.getValue());
// 需要特别注意,如果是可变数组(vargars)参数,如方法 test.doSomething(String... params)
// 此时是使用ArgumentCaptor<String>,而非ArgumentCaptor<String[]>
ArgumentCaptor<String> varArgs = ArgumentCaptor.forClass(String.class);
test.doSomething("param-1", "param-2");
verify(test).doSomething(varArgs.capture());
// 这里直接使用getAllValues()而非getValue(),来获取可变数组参数的所有传入参数
assertThat(varArgs.getAllValues()).contains("param-1", "param-2");
}(1)对于静态的方法的Mock:
可以使用 PowerMock:
org.powermock:powermock-api-mockito:(version) & org.powermock:powermock-module-junit4:(version)(For PowerMockRunner.class)
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest({StaticClass1.class, StaticClass2.class})
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void testSomething() {
// mock完静态类以后,默认所有的方法都不做任何事情
mockStatic(StaticClass1.class);
when(StaticClass1.getStaticMethod()).andReturn("anything");
// 验证是否StaticClass1.getStaticMethod()这个方法被调用了一次
verifyStatic(time(1));
StaticClass1.getStaticMethod();
when(StaticClass1.getStaticMethod()).andReturn("what ever");
// 验证是否StaticClass2.getStaticMethod()这个方法被至少调用了一次
verifyStatic(atLeastOnce());
StaticClass2.getStaticMethod();
// 通过任何参数创建File的实力,都直接返回fileInstance对象
whenNew(File.class).withAnyArguments().thenReturn(fileInstance);
}
}或者是封装为非静态,然后用Mockito:
class FooWraper{ void someMethod() {
Foo.someStaticMethod();
}
}4. Robolectric
Robolectric
让模拟测试直接在开发机上完成,而不需要在Android系统上。所有需要使用到系统架构库的,如(Handler、HandlerThread)都需要使用Robolectric,或者进行模拟测试。
主要是解决模拟测试中耗时的缺陷,模拟测试需要安装以及跑在Android系统上,也就是需要在Android虚拟机或者设备上面,所以十分的耗时。基本上每次来来回回都需要几分钟时间。针对这类问题,业界其实已经有了一个现成的解决方案: Pivotal实验室推出的Robolectric。通过使用Robolectrict模拟Android系统核心库的Shadow Classes的方式,我们可以像写本地测试一样写这类测试,并且直接运行在工作环境的JVM上,十分方便。
5. Robotium
RobotiumTech/robotium
(Integration Tests)模拟用户操作,事件流测试。
@RunWith(RobolectricTestRunner.class)
@Config(constants = BuildConfig.class)
public class MyActivityTest{
@Test
public void doSomethingTests(){
// 获取Application对象
Application application = RuntimeEnvironment.application;
// 启动WelcomeActivity
WelcomeActivity activity = Robolectric.setupActivity(WelcomeActivity.class);
// 触发activity中Id为R.id.login的View的click事件
// http://www.manongjc.com/article/1502.html
activity.findViewById(R.id.login).performClick();
Intent expectedIntent = new Intent(activity, LoginActivity.class);
// 在activity之后,启动的Activity是否是LoginActivity
assertThat(shadowOf(activity).getNextStartedActivity()).isEqualTo(expectedIntent);
}
}通过模拟用户的操作的行为事件流进行测试,这类测试无法避免需要在虚拟机或者设备上面运行的。是一些用户操作流程与视觉显示强相关的很好的选择。
6. Test Butler
linkedin/test-butler
避免设备/模拟器系统或者环境的错误,导致测试的失败。
通常我们在进行UI测试的时候,会遇到由于模拟器或者设备的错误,如系统的crash、ANR、或是未预期的Wifi、CPU罢工,或者是锁屏,这些外再环境因素导致测试不过。Test-Butler引入就是避免这些环境因素导致UI测试不过。
该库被谷歌官方推荐过,并且收到谷歌工程师的Review。
拓展思路
1. Android Robots
Instrumentation Testing Robots – Jake Wharton
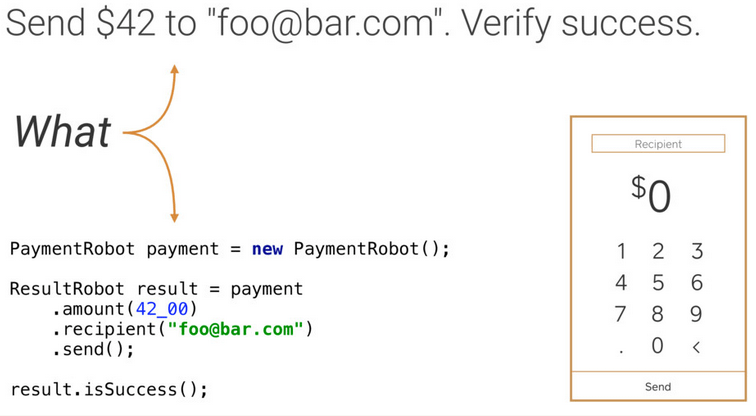
假如我们需要测试: 发送 $42 到 “foo@bar.com”,然后验证是否成功。
(1)通常的做法
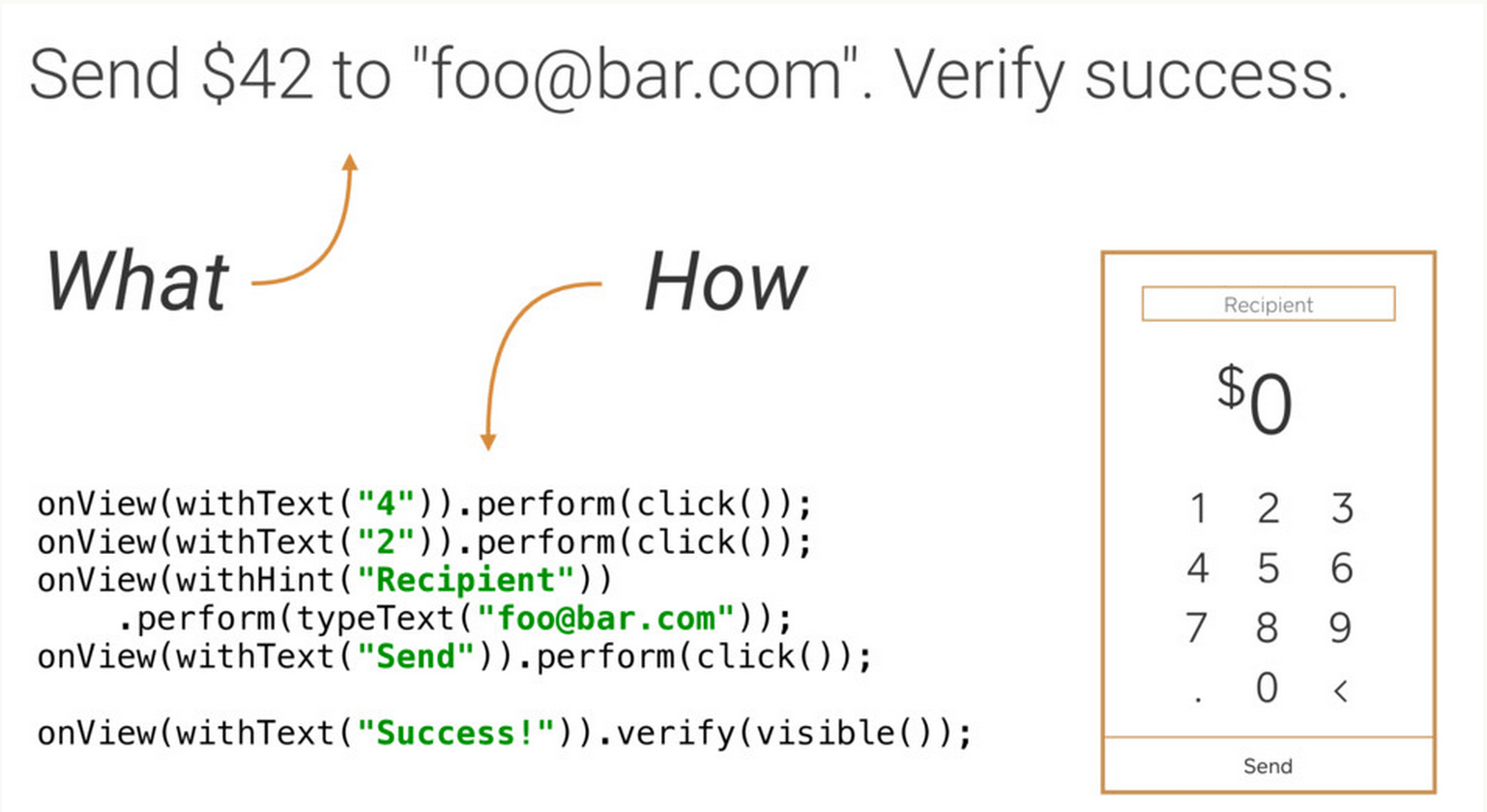
(2)Robot思想
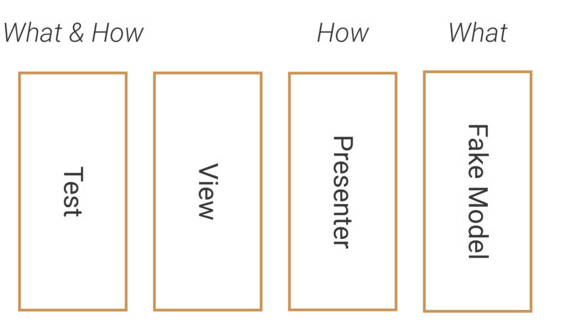
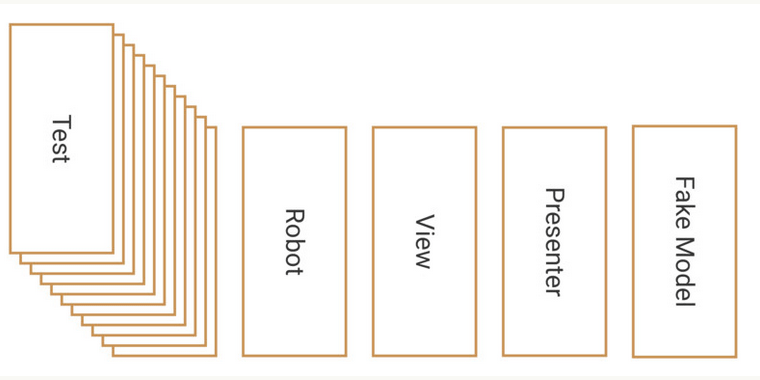
在写真正的UI测试的时候,只需要关注要测试什么,而不需要关注需要怎么测试,换句话说就是让测试逻辑与View或Presenter解耦,而与数据产生关系。
首先通过封装一个Robot去处理How的部分:

然后在写测试的时候,只关注需要测试什么:
终的思想原理

Outils d'IA chauds

Undresser.AI Undress
Application basée sur l'IA pour créer des photos de nu réalistes

AI Clothes Remover
Outil d'IA en ligne pour supprimer les vêtements des photos.

Undress AI Tool
Images de déshabillage gratuites

Clothoff.io
Dissolvant de vêtements AI

Video Face Swap
Échangez les visages dans n'importe quelle vidéo sans effort grâce à notre outil d'échange de visage AI entièrement gratuit !

Article chaud

Outils chauds

Bloc-notes++7.3.1
Éditeur de code facile à utiliser et gratuit

SublimeText3 version chinoise
Version chinoise, très simple à utiliser

Envoyer Studio 13.0.1
Puissant environnement de développement intégré PHP

Dreamweaver CS6
Outils de développement Web visuel

SublimeText3 version Mac
Logiciel d'édition de code au niveau de Dieu (SublimeText3)




