
选择了脚本语言就要忍受其速度,这句话在某种程度上说明了 python 作为脚本的一个不足之处,那就是执行效率和性能不够理想,特别是在 performance 较差的机器上,因此有必要进行一定的代码优化来提高程序的执行效率。如何进行 Python 性能优化,是本文探讨的主要问题。本文会涉及常见的代码优化方法,性能优化工具的使用以及如何诊断代码的性能瓶颈等内容,希望可以给 Python 开发人员一定的参考。
Python 代码优化常见技巧
代码优化能够让程序运行更快,它是在不改变程序运行结果的情况下使得程序的运行效率更高,根据 80/20 原则,实现程序的重构、优化、扩展以及文档相关的事情通常需要消耗 80% 的工作量。优化通常包含两方面的内容:减小代码的体积,提高代码的运行效率。
改进算法,选择合适的数据结构
一个良好的算法能够对性能起到关键作用,因此性能改进的首要点是对算法的改进。在算法的时间复杂度排序上依次是:
O(1) -> O(lg n) -> O(n lg n) -> O(n^2) -> O(n^3) -> O(n^k) -> O(k^n) -> O(n!)
因此如果能够在时间复杂度上对算法进行一定的改进,对性能的提高不言而喻。但对具体算法的改进不属于本文讨论的范围,读者可以自行参考这方面资料。下面的内容将集中讨论数据结构的选择。
字典 (dictionary) 与列表 (list)
Python 字典中使用了 hash table,因此查找操作的复杂度为 O(1),而 list 实际是个数组,在 list 中,查找需要遍历整个 list,其复杂度为 O(n),因此对成员的查找访问等操作字典要比 list 更快。
清单 1. 代码 dict.py
from time import time
t = time()
list = ['a','b','is','python','jason','hello','hill','with','phone','test',
'dfdf','apple','pddf','ind','basic','none','baecr','var','bana','dd','wrd']
#list = dict.fromkeys(list,True)
print list
filter = []
for i in range (1000000):
for find in ['is','hat','new','list','old','.']:
if find not in list:
filter.append(find)
print "total run time:"
print time()-t上述代码运行大概需要 16.09seconds。如果去掉行 #list = dict.fromkeys(list,True) 的注释,将 list 转换为字典之后再运行,时间大约为 8.375 seconds,效率大概提高了一半。因此在需要多数据成员进行频繁的查找或者访问的时候,使用 dict 而不是 list 是一个较好的选择。
集合 (set) 与列表 (list)
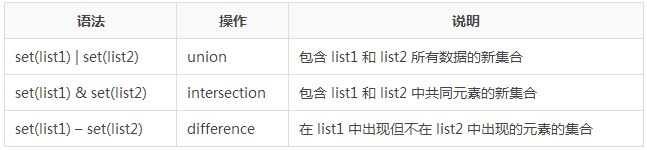
set 的 union, intersection,difference 操作要比 list 的迭代要快。因此如果涉及到求 list 交集,并集或者差的问题可以转换为 set 来操作。
清单 2. 求 list 的交集:
from time import time
t = time()
lista=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,13,34,53,42,44]
listb=[2,4,6,9,23]
intersection=[]
for i in range (1000000):
for a in lista:
for b in listb:
if a == b:
intersection.append(a)
print "total run time:"
print time()-t上述程序的运行时间大概为:
total run time: 38.4070000648
清单 3. 使用 set 求交集
from time import time
t = time()
lista=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,13,34,53,42,44]
listb=[2,4,6,9,23]
intersection=[]
for i in range (1000000):
list(set(lista)&set(listb))
print "total run time:"
print time()-t改为 set 后程序的运行时间缩减为 8.75,提高了 4 倍多,运行时间大大缩短。读者可以自行使用表 1 其他的操作进行测试。
表 1. set 常见用法
对循环的优化
对循环的优化所遵循的原则是尽量减少循环过程中的计算量,有多重循环的尽量将内层的计算提到上一层。 下面通过实例来对比循环优化后所带来的性能的提高。程序清单 4 中,如果不进行循环优化,其大概的运行时间约为 132.375。
清单 4. 为进行循环优化前
from time import time
t = time()
lista = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
listb =[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9,0.01]
for i in range (1000000):
for a in range(len(lista)):
for b in range(len(listb)):
x=lista[a]+listb[b]
print "total run time:"
print time()-t现在进行如下优化,将长度计算提到循环外,range 用 xrange 代替,同时将第三层的计算 lista[a] 提到循环的第二层。
清单 5. 循环优化后
from time import time
t = time()
lista = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
listb =[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9,0.01]
len1=len(lista)
len2=len(listb)
for i in xrange (1000000):
for a in xrange(len1):
temp=lista[a]
for b in xrange(len2):
x=temp+listb[b]
print "total run time:"
print time()-t上述优化后的程序其运行时间缩短为 102.171999931。在清单 4 中 lista[a] 被计算的次数为 1000000*10*10,而在优化后的代码中被计算的次数为 1000000*10,计算次数大幅度缩短,因此性能有所提升。
充分利用 Lazy if-evaluation 的特性
python 中条件表达式是 lazy evaluation 的,也就是说如果存在条件表达式 if x and y,在 x 为 false 的情况下 y 表达式的值将不再计算。因此可以利用该特性在一定程度上提高程序效率。
清单 6. 利用 Lazy if-evaluation 的特性
from time import time
t = time()
abbreviations = ['cf.', 'e.g.', 'ex.', 'etc.', 'fig.', 'i.e.', 'Mr.', 'vs.']
for i in range (1000000):
for w in ('Mr.', 'Hat', 'is', 'chasing', 'the', 'black', 'cat', '.'):
if w in abbreviations:
#if w[-1] == '.' and w in abbreviations:
pass
print "total run time:"
print time()-t在未进行优化之前程序的运行时间大概为 8.84,如果使用注释行代替第一个 if,运行的时间大概为 6.17。
字符串的优化
python 中的字符串对象是不可改变的,因此对任何字符串的操作如拼接,修改等都将产生一个新的字符串对象,而不是基于原字符串,因此这种持续的 copy 会在一定程度上影响 python 的性能。对字符串的优化也是改善性能的一个重要的方面,特别是在处理文本较多的情况下。字符串的优化主要集中在以下几个方面:
在字符串连接的使用尽量使用 join() 而不是 +:在代码清单 7 中使用 + 进行字符串连接大概需要 0.125 s,而使用 join 缩短为 0.016s。因此在字符的操作上 join 比 + 要快,因此要尽量使用 join 而不是 +。
清单 7. 使用 join 而不是 + 连接字符串
from time import time
t = time()
s = ""
list = ['a','b','b','d','e','f','g','h','i','j','k','l','m','n']
for i in range (10000):
for substr in list:
s+= substr
print "total run time:"
print time()-t同时要避免:
s = ""
for x in list:
s += func(x)而是要使用:
slist = [func(elt) for elt in somelist] s = "".join(slist)
当对字符串可以使用正则表达式或者内置函数来处理的时候,选择内置函数。如 str.isalpha(),str.isdigit(),str.startswith((‘x’, ‘yz’)),str.endswith((‘x’, ‘yz’))
对字符进行格式化比直接串联读取要快,因此要使用
out = "<html>%s%s%s%s</html>" % (head, prologue, query, tail)
而避免
out = "<html>" + head + prologue + query + tail + "</html>"
使用列表解析(list comprehension)和生成器表达式(generator expression)
列表解析要比在循环中重新构建一个新的 list 更为高效,因此我们可以利用这一特性来提高运行的效率。
from time import time
t = time()
list = ['a','b','is','python','jason','hello','hill','with','phone','test',
'dfdf','apple','pddf','ind','basic','none','baecr','var','bana','dd','wrd']
total=[]
for i in range (1000000):
for w in list:
total.append(w)
print "total run time:"
print time()-t使用列表解析:
for i in range (1000000):
a = [w for w in list]上述代码直接运行大概需要 17s,而改为使用列表解析后 ,运行时间缩短为 9.29s。将近提高了一半。生成器表达式则是在 2.4 中引入的新内容,语法和列表解析类似,但是在大数据量处理时,生成器表达式的优势较为明显,它并不创建一个列表,只是返回一个生成器,因此效率较高。在上述例子上中代码 a = [w for w in list] 修改为 a = (w for w in list),运行时间进一步减少,缩短约为 2.98s。
其他优化技巧
如果需要交换两个变量的值使用 a,b=b,a 而不是借助中间变量 t=a;a=b;b=t;
>>> from timeit import Timer
>>> Timer("t=a;a=b;b=t","a=1;b=2").timeit()
0.25154118749729365
>>> Timer("a,b=b,a","a=1;b=2").timeit()
0.17156677734181258
>>>在循环的时候使用 xrange 而不是 range;使用 xrange 可以节省大量的系统内存,因为 xrange() 在序列中每次调用只产生一个整数元素。而 range() 將直接返回完整的元素列表,用于循环时会有不必要的开销。在 python3 中 xrange 不再存在,里面 range 提供一个可以遍历任意长度的范围的 iterator。
使用局部变量,避免”global” 关键字。python 访问局部变量会比全局变量要快得多,因 此可以利用这一特性提升性能。
if done is not None 比语句 if done != None 更快,读者可以自行验证;
在耗时较多的循环中,可以把函数的调用改为内联的方式;
使用级联比较 “x < y < z” 而不是 “x < y and y < z”;
while 1 要比 while True 更快(当然后者的可读性更好);
build in 函数通常较快,add(a,b) 要优于 a+b。
定位程序性能瓶颈
对代码优化的前提是需要了解性能瓶颈在什么地方,程序运行的主要时间是消耗在哪里,对于比较复杂的代码可以借助一些工具来定位,python 内置了丰富的性能分析工具,如 profile,cProfile 与 hotshot 等。其中 Profiler 是 python 自带的一组程序,能够描述程序运行时候的性能,并提供各种统计帮助用户定位程序的性能瓶颈。Python 标准模块提供三种 profilers:cProfile,profile 以及 hotshot。
profile 的使用非常简单,只需要在使用之前进行 import 即可。具体实例如下:
清单 8. 使用 profile 进行性能分析
import profile
def profileTest():
Total =1;
for i in range(10):
Total=Total*(i+1)
print Total
return Total
if __name__ == "__main__":
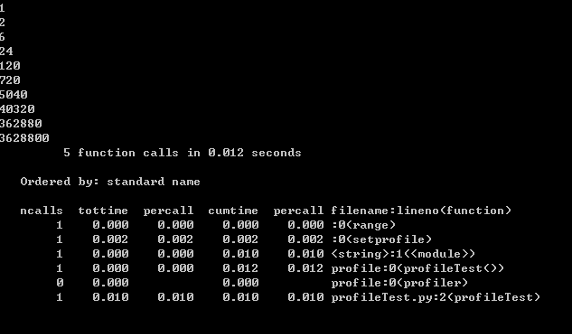
profile.run("profileTest()")程序的运行结果如下:
图 1. 性能分析结果
其中输出每列的具体解释如下:
ncalls:表示函数调用的次数;
tottime:表示指定函数的总的运行时间,除掉函数中调用子函数的运行时间;
percall:(第一个 percall)等于 tottime/ncalls;
cumtime:表示该函数及其所有子函数的调用运行的时间,即函数开始调用到返回的时间;
percall:(第二个 percall)即函数运行一次的平均时间,等于 cumtime/ncalls;
filename:lineno(function):每个函数调用的具体信息;
如果需要将输出以日志的形式保存,只需要在调用的时候加入另外一个参数。如 profile.run(“profileTest()”,”testprof”)。
对于 profile 的剖析数据,如果以二进制文件的时候保存结果的时候,可以通过 pstats 模块进行文本报表分析,它支持多种形式的报表输出,是文本界面下一个较为实用的工具。使用非常简单:
import pstats
p = pstats.Stats('testprof')
p.sort_stats("name").print_stats()其中 sort_stats() 方法能够对剖分数据进行排序, 可以接受多个排序字段,如 sort_stats(‘name’, ‘file’) 将首先按照函数名称进行排序,然后再按照文件名进行排序。常见的排序字段有 calls( 被调用的次数 ),time(函数内部运行时间),cumulative(运行的总时间)等。此外 pstats 也提供了命令行交互工具,执行 python – m pstats 后可以通过 help 了解更多使用方式。
对于大型应用程序,如果能够将性能分析的结果以图形的方式呈现,将会非常实用和直观,常见的可视化工具有 Gprof2Dot,visualpytune,KCacheGrind 等,读者可以自行查阅相关官网,本文不做详细讨论。